U.S.-Iran Nuclear Talks: Stalemate On Key Issues

Table of Contents
Sanctions Relief and Verification
A core disagreement centers around sanctions relief and verification mechanisms to ensure Iran's compliance. The success of any renewed agreement hinges on finding a mutually acceptable solution to these intertwined challenges. The U.S. and Iran hold vastly different perspectives on the scope and implementation of sanctions relief, and the methods used to verify Iranian compliance.
The Scope of Sanctions Relief
Iran demands comprehensive sanctions relief, encompassing all restrictions imposed by the U.S. and its allies. They argue that the re-imposition of sanctions following the U.S. withdrawal from the JCPOA in 2018 constitutes a breach of good faith and undermines any future agreements. The U.S., however, is hesitant to grant blanket sanctions relief, citing concerns about Iran's past non-compliance and its continued support for regional proxies.
- Specific sanctions being debated: These include sanctions targeting Iran's oil exports, its central bank, and its access to the international financial system.
- Economic impact of sanctions on Iran: The sanctions have severely crippled Iran's economy, leading to hyperinflation, unemployment, and widespread hardship. This economic pressure is a key factor in Iran's negotiating position.
- U.S. concerns about Iran's past non-compliance: The U.S. points to Iran's past violations of the JCPOA, including its enrichment of uranium beyond agreed-upon limits, as justification for its cautious approach to sanctions relief.
Verification Mechanisms and International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Concerns
The role of the IAEA in verifying Iran's nuclear program is another major sticking point. The IAEA has raised concerns about Iran's undeclared nuclear activities, demanding full transparency and unfettered access to Iranian nuclear facilities. Iran, however, resists what it perceives as intrusive inspections, arguing that some aspects of its nuclear program are sensitive and require protection.
- Outstanding IAEA concerns about Iran's undeclared nuclear activities: These include unanswered questions about the origin and purpose of uranium particles found at undeclared sites.
- Iran's demands regarding IAEA inspections: Iran seeks assurances that inspections will not be used for purposes beyond verification, and that its sensitive nuclear data will be protected.
- The role of international monitoring: Maintaining a robust international monitoring mechanism is crucial for building confidence and ensuring compliance by all parties.
Iran's Nuclear Enrichment Program
Limitations on Iran's uranium enrichment program remain a critical obstacle. The level of enrichment and the capacity of Iran's enrichment facilities are central to the negotiations. A key concern for the U.S. and its allies is Iran's potential to rapidly produce weapons-grade uranium, which could significantly destabilize the region.
Enrichment Levels and Capacity
The JCPOA limited Iran's uranium enrichment to 3.67%, far below the 90% required for a nuclear weapon. Iran currently exceeds these limits, raising serious concerns. Iran argues that higher enrichment levels are necessary for peaceful purposes, such as medical isotopes.
- The difference between current enrichment levels and those allowed under the JCPOA: This discrepancy highlights the significant gap between Iran's current activities and the agreed-upon limitations.
- Concerns about Iran's potential to rapidly produce weapons-grade uranium: This potential poses a grave threat to regional and international security.
- Iran's arguments for higher enrichment levels: Iran insists that its enrichment program is for peaceful purposes and that higher enrichment levels are necessary for its civilian nuclear program.
Research and Development
Restrictions on Iran's nuclear research and development (R&D) activities are also a point of contention. The U.S. is concerned about the dual-use nature of certain research, which could be used to mask weapons development.
- Iran's argument that research is necessary for peaceful purposes: Iran maintains that its R&D activities are solely for civilian applications.
- U.S. concerns about the dual-use nature of certain research: The U.S. worries that some research could easily be adapted for weapons development.
- The potential for research to mask weapons development: This concern underscores the importance of stringent verification and monitoring mechanisms.
Regional Security Concerns and Proxies
The broader regional implications of the talks, particularly the role of Iranian-backed proxies, significantly impact the negotiations. Concerns about these groups in countries like Iraq, Lebanon, and Yemen are inextricably linked to the nuclear issue.
Iranian-backed Militias in the Region
The U.S. demands assurances that Iran will curtail its support for these groups, viewing their actions as destabilizing. Iran denies direct involvement in such activities but refuses to completely cut ties.
- U.S. demands regarding Iranian support for these groups: The U.S. seeks concrete steps to reduce Iranian influence on these groups.
- Iran's denial of direct involvement in destabilizing actions: Iran maintains that these groups operate independently.
- The linkage between the nuclear program and regional security: The U.S. argues that a peaceful nuclear program is inseparable from a commitment to regional stability.
The Role of Other Regional Actors
Other regional actors, like Saudi Arabia and Israel, play significant roles, influencing the negotiations with their own security concerns and perspectives.
- Saudi Arabia's concerns about Iran's regional ambitions: Saudi Arabia sees Iran as a major threat to its regional dominance.
- Israel's opposition to the revival of the JCPOA: Israel is strongly opposed to any agreement that doesn't sufficiently curb Iran's nuclear ambitions.
- The potential for broader regional conflict: The failure of the U.S.-Iran nuclear talks could increase the risk of a broader regional conflict.
Conclusion
The U.S.-Iran nuclear talks remain deadlocked due to significant disagreements on sanctions relief, Iran's nuclear program, and regional security concerns. The lack of progress jeopardizes the prospects of a peaceful resolution and increases the risk of further escalation. Resolving these complex issues requires a renewed commitment from all parties to compromise and a willingness to address the underlying concerns of all stakeholders. Further engagement and a concerted diplomatic effort are crucial to finding a path forward and reviving the possibility of a comprehensive agreement on U.S.-Iran nuclear talks. Continued monitoring of these U.S.-Iran nuclear talks is vital for understanding the evolving geopolitical landscape in the Middle East. The future of regional stability depends on finding a solution to these critical challenges.

Featured Posts
-
 Invest Smart A Guide To The Countrys Newest Business Hotspots
Apr 28, 2025
Invest Smart A Guide To The Countrys Newest Business Hotspots
Apr 28, 2025 -
 The Luigi Mangione Supporters Their Perspectives And Priorities
Apr 28, 2025
The Luigi Mangione Supporters Their Perspectives And Priorities
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Canadian Travel Boycott A Fed Snapshot Reveals Economic Repercussions
Apr 28, 2025
Canadian Travel Boycott A Fed Snapshot Reveals Economic Repercussions
Apr 28, 2025 -
 V Mware Costs To Skyrocket 1050 At And T On Broadcoms Proposed Price Increase
Apr 28, 2025
V Mware Costs To Skyrocket 1050 At And T On Broadcoms Proposed Price Increase
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Times Trump Interview 9 Key Takeaways On Annexing Canada Xi Jinping And Third Term Loopholes
Apr 28, 2025
Times Trump Interview 9 Key Takeaways On Annexing Canada Xi Jinping And Third Term Loopholes
Apr 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Examining The Financials The Impact Of Musks X Debt Sale
Apr 28, 2025
Examining The Financials The Impact Of Musks X Debt Sale
Apr 28, 2025 -
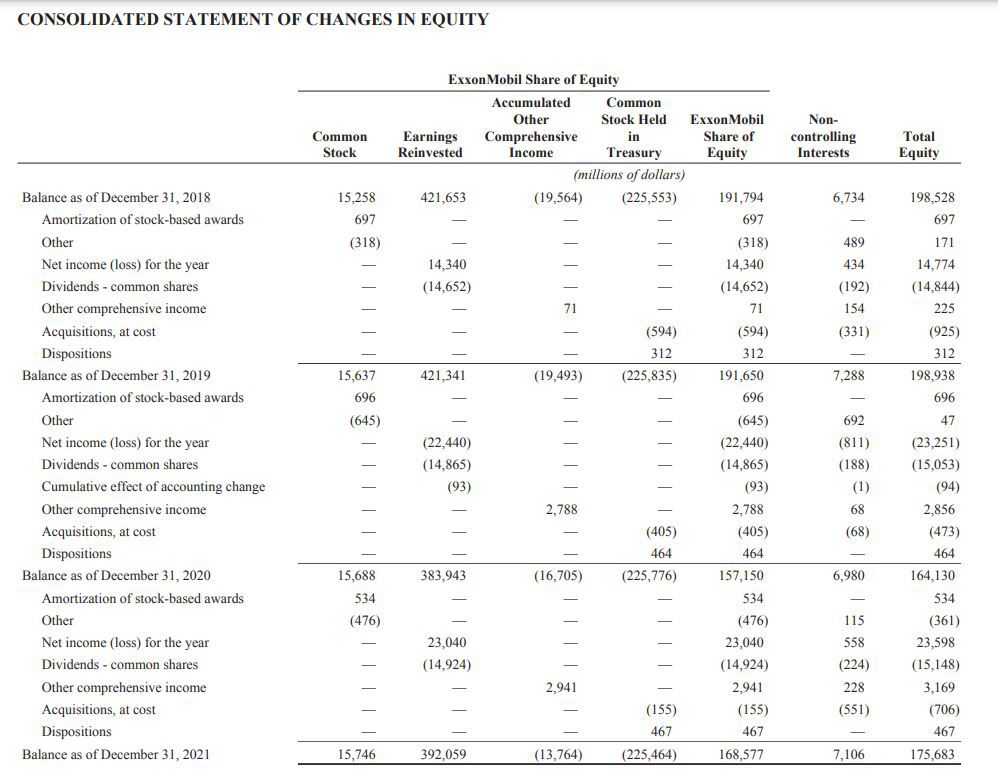 Decoding Xs Financials Post Musk Debt Sale Analysis
Apr 28, 2025
Decoding Xs Financials Post Musk Debt Sale Analysis
Apr 28, 2025 -
 The Changing Face Of X A Look At The Financials Following Musks Debt Sale
Apr 28, 2025
The Changing Face Of X A Look At The Financials Following Musks Debt Sale
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Analysis Of Musks X Debt Sale Impact On Company Finances
Apr 28, 2025
Analysis Of Musks X Debt Sale Impact On Company Finances
Apr 28, 2025 -
 New X Financials How Musks Debt Sale Reshaped The Company
Apr 28, 2025
New X Financials How Musks Debt Sale Reshaped The Company
Apr 28, 2025
