Economists Forecast Bank Of Canada Rate Cuts Due To Tariff-Related Job Losses

Table of Contents
<meta name="description" content="Analysis of economists' predictions for Bank of Canada interest rate cuts, driven by concerns over tariff-induced job losses in Canada's economy. Learn about the potential impact on Canadian businesses and consumers.">
The Canadian economy is facing significant headwinds, with economists widely predicting that the Bank of Canada will soon implement interest rate cuts. This anticipated monetary policy shift is a direct response to substantial job losses stemming from escalating global tariffs and their ripple effects across various sectors of the Canadian economy. This article will delve into the reasons behind these forecasts, examining the impact of tariffs on key industries and the potential consequences for Canadian businesses and consumers. We'll explore the Bank of Canada's likely response, and analyze the potential positive and negative impacts of the predicted rate cuts.
<h2>Tariff Impact on Canadian Employment</h2>
Escalating tariffs have had a demonstrably negative impact on Canadian employment, particularly within key sectors heavily reliant on international trade. The resulting job losses are a major contributing factor to the predicted Bank of Canada rate cuts.
<h3>Manufacturing Sector Job Losses</h3>
The Canadian manufacturing sector has been severely impacted by tariffs, leading to a significant decline in jobs. Increased import costs and reduced export opportunities have forced many manufacturers to cut production and lay off workers.
- Specific sectors affected: The automotive industry, lumber production, and steel manufacturing have experienced substantial job losses.
- Statistics on job losses: Recent reports indicate a [Insert Statistic - e.g., 5%] decline in manufacturing jobs in the past year, directly attributable to tariff-related challenges. (Source: [Insert Reliable Source]).
- Government support measures: The Canadian government has implemented some support programs, such as [Insert Examples - e.g., wage subsidies, retraining initiatives], but these measures have not fully offset the job losses.
<h3>Impact on the Agricultural Sector</h3>
Canadian agricultural exports, a cornerstone of the Canadian economy, have also suffered due to tariffs imposed by trading partners. This has resulted in reduced export volumes, lower prices for farmers, and consequent job losses across the agricultural value chain.
- Specific products affected: The dairy, canola, and pork industries have been particularly hard hit by retaliatory tariffs.
- Data on reduced exports and job losses: [Insert Statistics - e.g., Exports of canola have decreased by X% leading to Y job losses in the agricultural sector.] (Source: [Insert Reliable Source]).
- Trade diversification strategies: The government and industry are exploring trade diversification strategies to reduce reliance on specific markets and mitigate the impact of future tariff increases.
<h3>Ripple Effects Across the Economy</h3>
Job losses in the manufacturing and agricultural sectors aren't isolated incidents; they trigger a ripple effect across the broader Canadian economy. The consequences are far-reaching and contribute significantly to the economic slowdown.
- Decreased consumer spending: Job insecurity leads to reduced consumer confidence and spending, weakening aggregate demand.
- Reduction in business investment: Uncertainty surrounding the economic outlook discourages businesses from investing, further hindering growth.
- Potential impact on the housing market: A weakening economy and reduced consumer confidence can negatively affect the housing market, leading to price corrections or slower growth.
<h2>The Bank of Canada's Response: Predicted Rate Cuts</h2>
In response to the economic slowdown and significant job losses, economists widely predict that the Bank of Canada will lower interest rates. This monetary policy response aims to stimulate economic activity and mitigate the negative impacts of tariffs.
<h3>Stimulating Economic Growth</h3>
Lower interest rates are intended to incentivize borrowing and investment, boosting economic growth. This is a classic tool in monetary policy to counteract economic downturns.
- Monetary policy tools: The Bank of Canada will likely lower its key interest rate, making borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers.
- Past instances: Historically, the Bank of Canada has lowered interest rates during periods of economic weakness to stimulate growth; [Insert example of a previous rate cut and its impact].
<h3>Balancing Inflation and Employment</h3>
The Bank of Canada faces the challenge of balancing its inflation target with the need to stimulate employment growth. Aggressive rate cuts risk fueling inflation, while insufficient cuts may fail to adequately boost the economy.
- Inflation levels and forecasts: Current inflation is [Insert data on current inflation rates], and forecasts suggest [Insert future inflation projections].
- Risks of overly aggressive rate cuts: Rapidly lowering interest rates could lead to increased inflation and potentially destabilize the financial markets.
<h2>Potential Consequences of Rate Cuts</h2>
The predicted Bank of Canada rate cuts will have a multifaceted impact on the Canadian economy, presenting both potential benefits and risks.
<h3>Positive Impacts</h3>
Lower interest rates can stimulate the economy in several ways:
- Stimulated economic growth and job creation: Cheaper borrowing costs can encourage businesses to invest and expand, leading to job creation in certain sectors.
- Potential increase in consumer spending and confidence: Lower interest rates can make borrowing more attractive for consumers, potentially boosting spending and confidence.
<h3>Negative Impacts</h3>
However, there are potential downsides to aggressive rate cuts:
- Risk of higher inflation: If economic growth is too rapid in response to lower interest rates, inflation could rise, eroding purchasing power.
- Potential for increased household debt levels: Lower interest rates could encourage increased borrowing, potentially leading to higher household debt levels.
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
The anticipated Bank of Canada rate cuts are a direct response to the substantial job losses triggered by escalating tariffs and their subsequent impact on the Canadian economy. While these cuts aim to stimulate economic growth and cushion the negative impacts, it's crucial to carefully monitor the potential consequences, including inflation and increased debt levels. Understanding the multifaceted impact of these economic factors is critical for businesses and consumers alike. The interplay between tariffs, job losses, and monetary policy is complex, and its full ramifications will unfold over time.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving economic situation and the Bank of Canada's response to tariff-related job losses. Continue to follow our analysis for the latest updates on Bank of Canada rate cuts and their implications for the Canadian economy. Understanding these changes is crucial for navigating the current economic landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Snow Whites Dismal Debut Analyzing The Box Office Failure
May 14, 2025
Snow Whites Dismal Debut Analyzing The Box Office Failure
May 14, 2025 -
 Fda Recall Investigating The Walmart Canned Bean Issue
May 14, 2025
Fda Recall Investigating The Walmart Canned Bean Issue
May 14, 2025 -
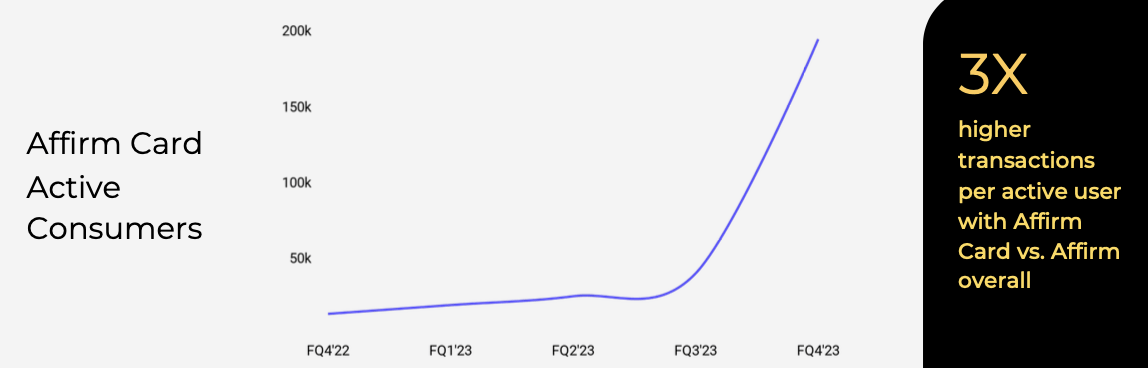 Trumps Trade War A Crushing Blow To Fintech Ipos Including Affirm Afrm
May 14, 2025
Trumps Trade War A Crushing Blow To Fintech Ipos Including Affirm Afrm
May 14, 2025 -
 Tommy Fury Speeding Fine After Molly Mae Hague Split
May 14, 2025
Tommy Fury Speeding Fine After Molly Mae Hague Split
May 14, 2025 -
 Recent Walmart Canned Bean Recall Causes And Effects
May 14, 2025
Recent Walmart Canned Bean Recall Causes And Effects
May 14, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Klarna Us Ipo 24 Revenue Growth Detailed In Filing
May 14, 2025
Klarna Us Ipo 24 Revenue Growth Detailed In Filing
May 14, 2025 -
 Klarnas Us Ipo Filing 24 Revenue Surge Revealed
May 14, 2025
Klarnas Us Ipo Filing 24 Revenue Surge Revealed
May 14, 2025 -
 E Toro Aims For 500 Million In New Ipo Funding Round
May 14, 2025
E Toro Aims For 500 Million In New Ipo Funding Round
May 14, 2025 -
 500 Million Ipo E Toros Renewed Pursuit Of Public Listing
May 14, 2025
500 Million Ipo E Toros Renewed Pursuit Of Public Listing
May 14, 2025 -
 E Toros 500 Million Ipo Push A Deep Dive
May 14, 2025
E Toros 500 Million Ipo Push A Deep Dive
May 14, 2025
