The Powell Fed's Calculated Risk: Interest Rate Cuts And The Trump Administration's Demands
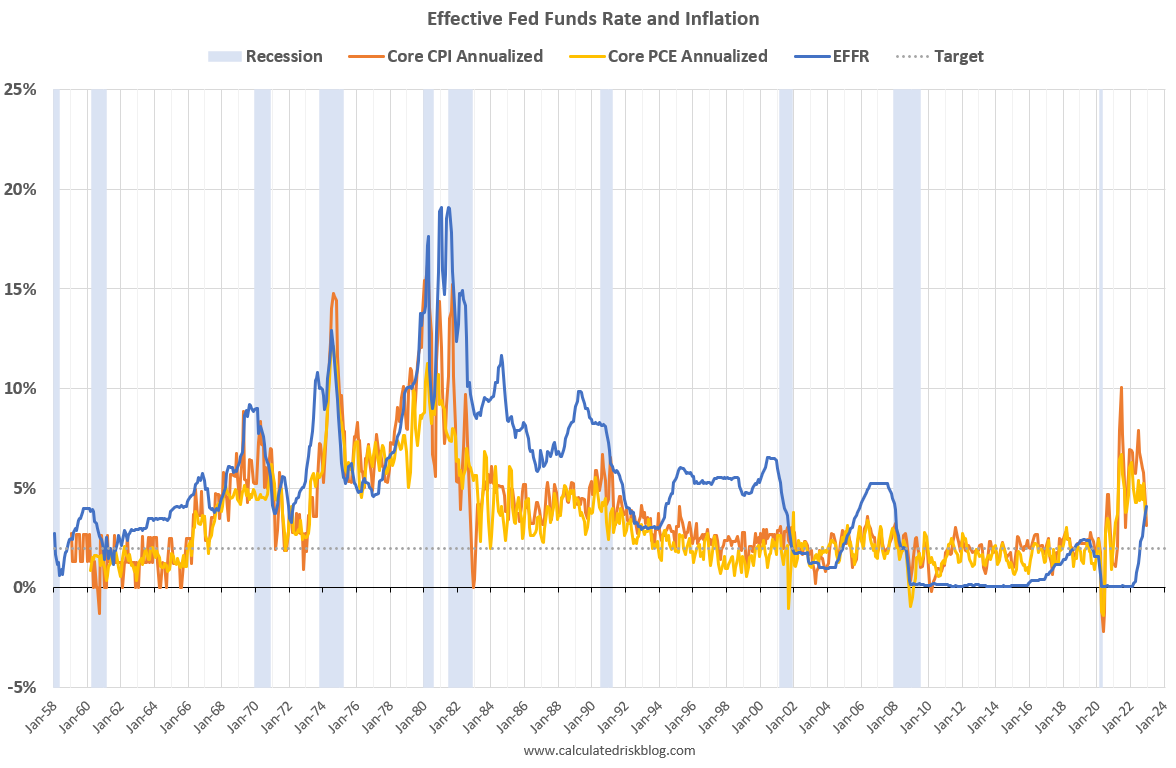
Table of Contents
The Economic Context Leading to Interest Rate Cuts
The decision to lower interest rates wasn't made in a vacuum. Several significant economic factors contributed to the pressure on the Powell Fed.
Slowing Economic Growth and Trade Wars
By late 2018, the US economy showed signs of slowing growth. The escalating US-China trade war introduced significant uncertainty, impacting businesses and consumer confidence. GDP growth, once robust, began to decelerate.
- Decreasing consumer confidence: Uncertainty surrounding trade tariffs led to reduced consumer spending and investment.
- Rising trade deficits: The trade war exacerbated existing trade imbalances, putting further pressure on the economy.
- Uncertainty in the business sector: Businesses delayed investment decisions due to the unpredictable trade environment, leading to reduced capital expenditure.
Keywords: GDP growth, inflation, unemployment, trade war, economic slowdown, consumer confidence, trade deficit, capital expenditure. Data from this period would show a clear decline in these key economic indicators, supporting the argument for intervention. For example, GDP growth figures could be cited to illustrate the slowing momentum.
Inflationary Pressures and the Fed's Dual Mandate
The Federal Reserve operates under a dual mandate: maintaining price stability and achieving maximum employment. While stimulating growth through lower interest rates seemed necessary given the slowing economy, concerns about inflation remained.
- Analysis of inflation data: Inflation data at the time needs to be examined to determine whether it was genuinely a threat or remained within the Fed's target range.
- The Fed's inflation target: The Fed's target inflation rate typically hovers around 2%. Any deviation from this target requires careful consideration.
- Potential risks of runaway inflation: Lowering interest rates too aggressively could risk igniting inflation, eroding purchasing power and potentially destabilizing the economy.
Keywords: Inflation target, dual mandate, price stability, maximum employment, inflation risk, monetary policy. Examining the inflation rate alongside GDP growth provides context for the Fed's decision-making process.
Political Pressure and the Trump Administration's Demands
The economic context was further complicated by intense political pressure from the Trump administration.
Public Criticism and Tweets
President Trump frequently criticized Chairman Powell and the Fed's monetary policy decisions via public statements and social media.
- Examples of Trump's public statements: Specific examples of Trump's criticism should be cited, demonstrating the level and nature of his pressure.
- Market reactions to his comments: Analyzing market reactions – shifts in stock prices, bond yields, etc. – reveals the impact of these statements on investor confidence and market volatility.
- Analysis of the political influence on the Fed: The degree to which the Fed's independence was compromised by this political pressure is a critical aspect requiring careful examination.
Keywords: Trump administration, political pressure, Fed independence, market volatility, tweet, public statement. This section requires factual evidence to support the claim of political interference.
The Search for Economic Stimulus
The Trump administration's desire for lower interest rates was partly driven by a need for economic stimulus before the 2020 election.
- Discussion of the administration's economic goals: The administration's economic policies and their underlying goals should be explained.
- The role of interest rates in achieving those goals: The administration likely viewed lower interest rates as a tool to boost economic growth and improve their chances in the upcoming election.
- Potential conflicts with long-term economic stability: The pursuit of short-term economic gains through interest rate cuts could conflict with long-term economic stability.
Keywords: Economic stimulus, election cycle, monetary policy, economic growth, political economy. The potential for short-term gains at the expense of long-term stability is a crucial point to emphasize.
Assessing the Effectiveness of the Powell Fed's Interest Rate Cuts
The effectiveness of the Powell Fed's interest rate cuts is a complex issue with both short-term and long-term implications.
Short-Term Effects on Economic Growth
The immediate impact of the rate cuts on key economic indicators needs to be evaluated.
- Changes in investment: Did investment increase following the rate cuts, signaling business confidence?
- Consumer spending: Did consumer spending rise, indicating increased disposable income?
- Employment growth: Did employment rates improve, indicating positive effects on the labor market? Economic data from this period should be referenced.
Keywords: Interest rate cuts, economic indicators, consumer spending, investment, employment growth, monetary policy effectiveness. Statistical analysis of these indicators is necessary to evaluate the short-term success of the rate cuts.
Potential Long-Term Risks and Side Effects
Lowering interest rates for an extended period can lead to several potential negative consequences.
- Asset bubbles: Prolonged low interest rates can inflate asset prices, creating unsustainable bubbles that could burst and trigger economic downturns.
- Increased national debt: Lower interest rates may encourage increased borrowing by both the government and businesses, leading to an unsustainable rise in national debt.
- Reduced future policy flexibility: Once interest rates are very low, the Fed has limited room to maneuver if future economic crises arise.
Keywords: Asset bubbles, national debt, monetary policy risks, long-term economic consequences, interest rate risk. A discussion of alternative policy options that might have been pursued should also be included.
Conclusion
The Powell Fed's response to the Trump administration's demands for interest rate cuts involved a calculated risk balancing short-term economic stimulus with potential long-term risks. While the rate cuts may have provided a temporary boost to economic growth, their long-term effects remain uncertain and warrant ongoing analysis. The episode highlights the delicate balance between the Fed's independence and political pressures, offering valuable lessons for navigating future economic challenges. Understanding the complexities of the Powell Fed interest rate cuts is crucial for comprehending current economic trends and anticipating future monetary policy decisions. Further research into the lasting impacts of these decisions is needed to fully grasp their implications. Continue exploring the intricacies of Powell Fed interest rate cuts and their effects on the US economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Thursday April 17 2025 Daily Lotto Results
May 07, 2025
Thursday April 17 2025 Daily Lotto Results
May 07, 2025 -
 Is John Wick 5 Really Necessary A Call For Caution
May 07, 2025
Is John Wick 5 Really Necessary A Call For Caution
May 07, 2025 -
 The Karate Kids Impact On Pop Culture And Martial Arts Training
May 07, 2025
The Karate Kids Impact On Pop Culture And Martial Arts Training
May 07, 2025 -
 Cleveland Cavaliers Vs San Antonio Spurs Injury Report March 27th Fox Sports 980 Wone
May 07, 2025
Cleveland Cavaliers Vs San Antonio Spurs Injury Report March 27th Fox Sports 980 Wone
May 07, 2025 -
 The Celebrity Who Wants To Be A Millionaire Special Format Rules And Notable Moments
May 07, 2025
The Celebrity Who Wants To Be A Millionaire Special Format Rules And Notable Moments
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Assessing The Overvaluation Of The Canadian Dollar A Call To Action
May 08, 2025
Assessing The Overvaluation Of The Canadian Dollar A Call To Action
May 08, 2025 -
 Andor Showrunner Almost Reveals Rogue One Recut Secrets
May 08, 2025
Andor Showrunner Almost Reveals Rogue One Recut Secrets
May 08, 2025 -
 The Canadian Dollars Strength Risks And Opportunities
May 08, 2025
The Canadian Dollars Strength Risks And Opportunities
May 08, 2025 -
 Canadian Dollars High Value Economic Experts Sound The Alarm
May 08, 2025
Canadian Dollars High Value Economic Experts Sound The Alarm
May 08, 2025 -
 Savage Land Showdown Rogue 2 Preview Featuring Ka Zar
May 08, 2025
Savage Land Showdown Rogue 2 Preview Featuring Ka Zar
May 08, 2025
