Pilbara Mining And Environmental Concerns: A Clash Between Rio Tinto And Andrew Forrest

Table of Contents
Rio Tinto's Mining Practices and Environmental Impact
Rio Tinto's Operational Footprint in the Pilbara: Rio Tinto's Pilbara operations represent some of the largest iron ore mining activities globally. Their extensive network of mines, railways, and ports consumes vast resources. For instance, their water usage is substantial, and their energy consumption contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Precise figures vary yearly, but reports consistently indicate a considerable environmental footprint.
- Scale of Operations: Multiple large-scale mines across the Pilbara region.
- Resource Consumption: High water demand for processing ore, significant reliance on fossil fuels for energy.
- Environmental Impact: Large-scale land clearing, greenhouse gas emissions exceeding those of smaller operations, and dust generation impacting air quality. Specific data on these impacts should be sourced from Rio Tinto's sustainability reports and independent analyses for accuracy.
Environmental Mitigation Strategies Employed by Rio Tinto: Rio Tinto has publicly committed to various sustainability goals, including reducing its carbon footprint and improving water management. These initiatives involve investing in renewable energy sources, implementing water recycling programs, and engaging in biodiversity conservation projects. However, the effectiveness of these strategies remains a subject of ongoing debate.
- Renewable Energy Investments: Shifting towards renewable energy sources but still heavily reliant on fossil fuels.
- Water Management: Implementing water recycling, but the overall water footprint remains substantial.
- Criticism from NGOs: Environmental organizations continue to express concerns about the scale of Rio Tinto's operations and the impact on biodiversity and Indigenous heritage.
Case Studies of Environmental Incidents Involving Rio Tinto: The destruction of the Juukan Gorge rock shelters in 2020 stands as a stark example of the environmental controversies surrounding Rio Tinto's Pilbara operations. This incident highlighted significant failings in community consultation and environmental protection protocols, leading to significant regulatory fines and widespread public condemnation. Other incidents, though perhaps less publicized, contribute to a broader narrative of environmental challenges associated with large-scale mining in the Pilbara.
Andrew Forrest's Advocacy for Sustainable Pilbara Mining
Forrest's Critique of Existing Mining Practices: Andrew Forrest, through his company Fortescue Metals Group, has been a vocal critic of what he considers inadequate environmental performance within the Pilbara mining sector. He argues that existing practices are not sufficiently sustainable and calls for more stringent environmental regulations and a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
- Call for stricter regulation: Forrest advocates for stronger government oversight and enforcement of environmental standards.
- Emphasis on responsible mining: He stresses the importance of minimizing environmental damage and respecting Indigenous heritage.
Forrest's Proposed Solutions and Initiatives: Forrest's Fortescue Future Industries (FFI) is a key element of his approach. FFI is heavily invested in developing green hydrogen technologies as a means to decarbonize the mining industry and beyond. This ambitious project aims to displace fossil fuels with renewable energy sources, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Green hydrogen production: FFI aims to create a global green hydrogen industry, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Renewable energy integration: A focus on integrating renewable energy sources into mining operations.
The Effectiveness and Challenges of Forrest's Approach: While Forrest's vision is ambitious, its success hinges on several factors. The economic viability of green hydrogen technology is crucial, as is overcoming technological limitations and securing policy support. Industry-wide collaboration is also vital for achieving significant change.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Pilbara Mining
The contrasting approaches of Rio Tinto and Andrew Forrest highlight the inherent tension between economic development and environmental protection in the Pilbara. Rio Tinto's focus on mitigating its impact, while acknowledging past failings, needs to accelerate towards full decarbonization and zero-impact operations. Forrest's advocacy for radical change, exemplified by FFI, presents a compelling alternative vision. The future of Pilbara mining hinges on a commitment to responsible environmental stewardship. Sustainable Pilbara mining requires a holistic approach that integrates economic realities with ambitious environmental goals. The ongoing dialogue surrounding Pilbara mining and environmental concerns must continue, demanding innovative solutions and ensuring the region's future prosperity is achieved without sacrificing its unique environment. Stay informed about the ongoing debate and demand sustainable practices from mining companies operating in the Pilbara; the future of this remarkable region depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Experience Hellfest Concerts Au Noumatrouff Mulhouse
May 22, 2025
Experience Hellfest Concerts Au Noumatrouff Mulhouse
May 22, 2025 -
 Coldplays Top Performance Blending Music Light And Powerful Messages
May 22, 2025
Coldplays Top Performance Blending Music Light And Powerful Messages
May 22, 2025 -
 Core Weave Stock A Deep Dive Into Current Market Activity
May 22, 2025
Core Weave Stock A Deep Dive Into Current Market Activity
May 22, 2025 -
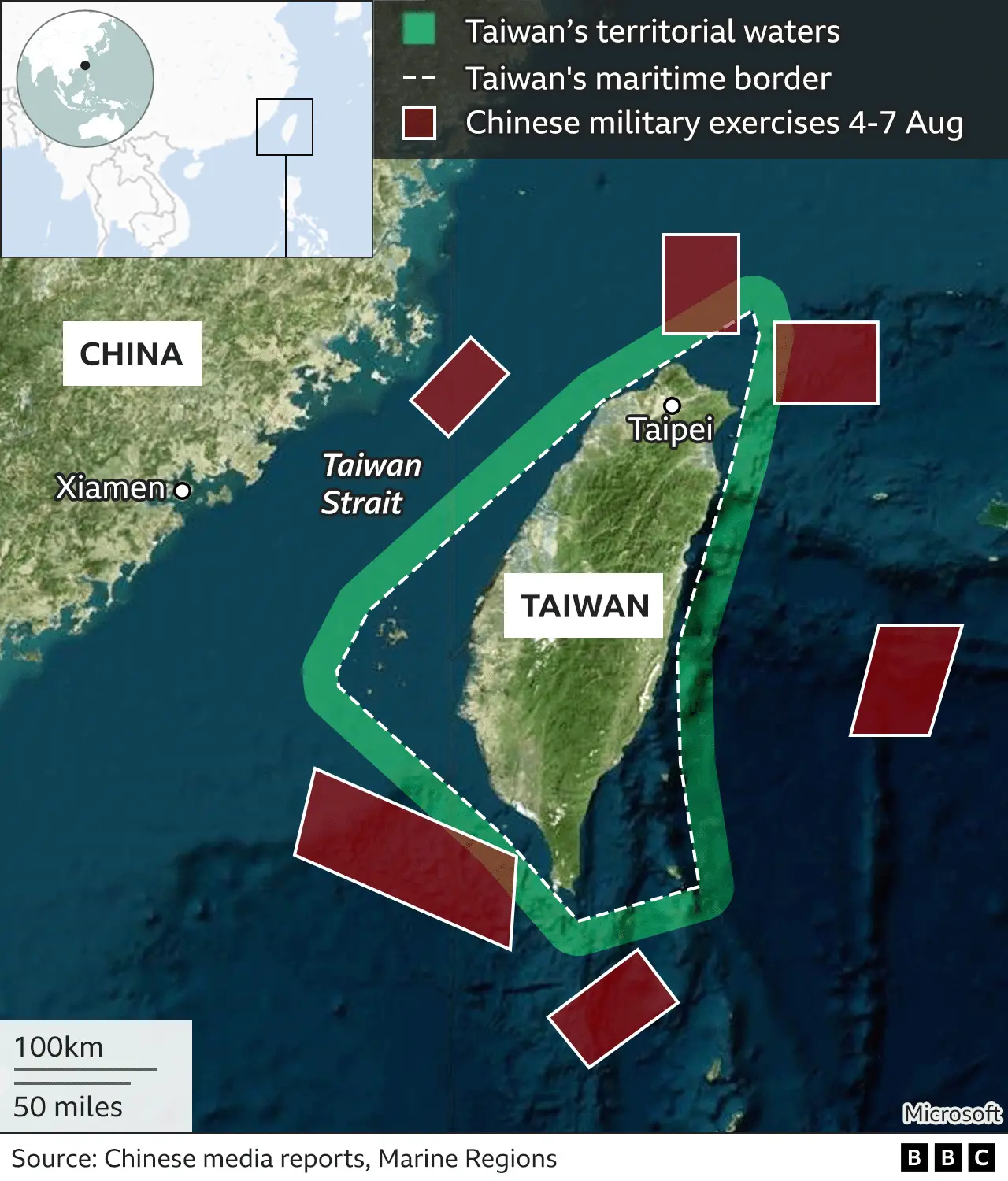 Chinas Military Drills Switzerland Issues Strong Reprimand
May 22, 2025
Chinas Military Drills Switzerland Issues Strong Reprimand
May 22, 2025 -
 Jim Cramers Lone Wolf Prediction Core Weave Crwv As The Ai Infrastructure Star
May 22, 2025
Jim Cramers Lone Wolf Prediction Core Weave Crwv As The Ai Infrastructure Star
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Wide Gas Price Range In Columbus 2 83 3 31 Gallon
May 22, 2025
Wide Gas Price Range In Columbus 2 83 3 31 Gallon
May 22, 2025 -
 Solve Nyt Wordle 1368 March 18 Hints And The Answer
May 22, 2025
Solve Nyt Wordle 1368 March 18 Hints And The Answer
May 22, 2025 -
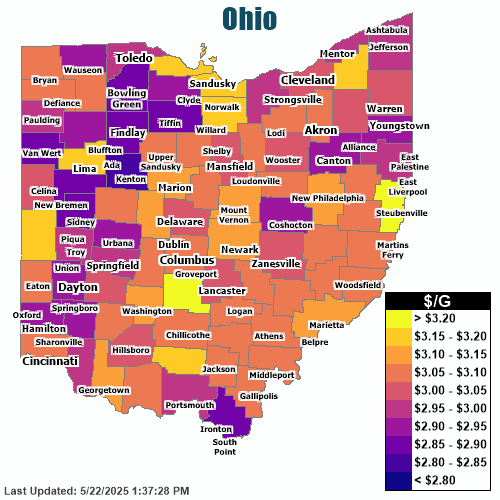 Columbus Gas Station Prices Vary By 48 Cents
May 22, 2025
Columbus Gas Station Prices Vary By 48 Cents
May 22, 2025 -
 Wordle 367 March 17th Hints Clues And Answer
May 22, 2025
Wordle 367 March 17th Hints Clues And Answer
May 22, 2025 -
 Columbus Gas Prices 2 83 To 3 31 Per Gallon
May 22, 2025
Columbus Gas Prices 2 83 To 3 31 Per Gallon
May 22, 2025
