WHO Warns: New COVID-19 Variant Fueling Worldwide Case Increase
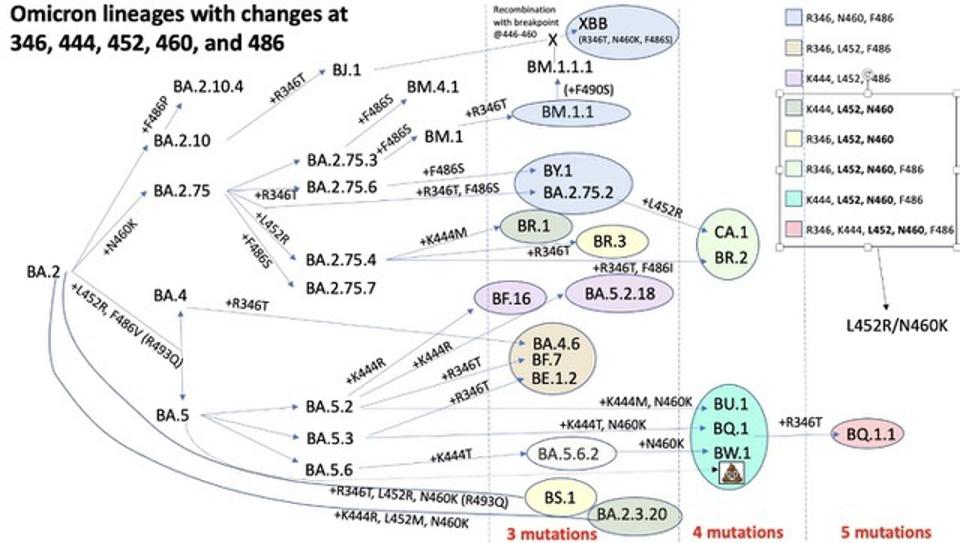
Table of Contents
The Emergence and Characteristics of the New COVID-19 Variant
The new variant, tentatively designated as Omicron subvariant XBB.1.5 (replace with the actual name if known), is causing concern due to its concerning characteristics. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for effective public health responses.
-
Key Genetic Mutations: This variant possesses several key mutations, notably in the spike protein, which is responsible for the virus's ability to infect cells. These mutations are suspected to increase its transmissibility and potentially its ability to evade immunity from previous infections or vaccinations. Further research is ongoing to determine the precise impact of these mutations. [Link to relevant scientific publication].
-
Increased Transmissibility: Preliminary data suggests that XBB.1.5 exhibits significantly higher transmissibility compared to previous variants. This means it can spread more easily from person to person, leading to rapid increases in case numbers. This enhanced transmissibility is a major factor driving the current global surge.
-
Severity and Symptoms: While initial reports suggest that the severity of illness associated with XBB.1.5 may not be significantly different from previous Omicron subvariants, further studies are needed to confirm this. The symptoms generally remain consistent with other COVID-19 variants, including fever, cough, fatigue, and loss of taste or smell. However, individual experiences can vary.
-
Origin and Spread: The origin of XBB.1.5 is currently under investigation, but its rapid spread across multiple continents underscores its ability to circumvent existing immunity and spread efficiently. Understanding its origin and patterns of spread is critical for developing targeted interventions.
Global Impact: Rising Case Numbers and Strain on Healthcare Systems
The emergence of XBB.1.5 has resulted in a noticeable global increase in COVID-19 cases. This surge is placing significant strain on healthcare systems worldwide.
-
Rising Case Numbers: [Insert data and charts showing the global increase in COVID-19 cases since the emergence of the new variant]. The increase is particularly evident in [mention specific regions or countries experiencing significant surges].
-
Strain on Healthcare Systems: Many hospitals in affected regions are experiencing a renewed influx of patients, leading to increased bed occupancy, longer waiting times, and potential shortages of staff and resources. This strain threatens the ability of healthcare systems to provide timely and adequate care for all patients, not only those with COVID-19.
-
Mortality Rate: While the current data suggests that the mortality rate associated with XBB.1.5 may not be drastically higher than previous variants, the sheer number of infections could still result in a significant increase in overall deaths. Continued monitoring is crucial to accurately assess the long-term impact on mortality.
WHO Recommendations and Public Health Measures
In response to the rising case numbers and the threat posed by XBB.1.5, the WHO has issued several key recommendations to mitigate its spread and protect public health.
-
Vaccination and Boosters: Maintaining high vaccination rates and ensuring access to booster shots remains crucial. Vaccination significantly reduces the severity of illness and the risk of hospitalization and death.
-
Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs): The continued importance of NPIs, such as mask-wearing in crowded indoor settings, social distancing, and improved ventilation, cannot be overstated. These measures, alongside vaccination, provide a multi-layered defense against the virus.
-
Testing and Contact Tracing: Prompt and efficient testing and contact tracing remain essential tools for identifying and isolating cases, preventing further spread within communities. Rapid antigen tests can play a significant role in early detection.
-
Improved Hygiene Practices: Maintaining good hand hygiene, regular cleaning of frequently touched surfaces, and respiratory etiquette remain vital for preventing transmission.
Conclusion
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant, tentatively named XBB.1.5, represents a significant challenge to global efforts to control the pandemic. The WHO’s warning underscores the need for continued vigilance and the urgent implementation of recommended public health measures. The increased transmissibility and potential strain on healthcare systems demand a proactive and coordinated response from governments and individuals alike.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the latest developments regarding this new COVID-19 variant and follow the WHO’s guidelines to protect yourself and your community. Take proactive steps to prevent the spread of the virus and contribute to mitigating the global impact of this new COVID-19 variant. Regularly check reliable sources such as the WHO website for updates on the COVID-19 pandemic and new variant information. Your actions can make a difference in controlling the spread of this new COVID-19 variant.

Featured Posts
-
 La Brascada Ingredientes Y Elaboracion Del Bocadillo Valenciano Perfecto
May 31, 2025
La Brascada Ingredientes Y Elaboracion Del Bocadillo Valenciano Perfecto
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguias Revenge Dominant Victory Over Surace In Rematch
May 31, 2025
Munguias Revenge Dominant Victory Over Surace In Rematch
May 31, 2025 -
 Crypto Kidnapping Nypd Detective On Mayor Adams Security Detail Involved Sources Say
May 31, 2025
Crypto Kidnapping Nypd Detective On Mayor Adams Security Detail Involved Sources Say
May 31, 2025 -
 Is Apple Rebranding Its Operating Systems
May 31, 2025
Is Apple Rebranding Its Operating Systems
May 31, 2025 -
 Sanofi Chlamydia Vaccine Candidate Receives Fast Track Designation From Us Fda
May 31, 2025
Sanofi Chlamydia Vaccine Candidate Receives Fast Track Designation From Us Fda
May 31, 2025
