U.S. Jobs Report: 177,000 Jobs Added In April, Unemployment Remains At 4.2%
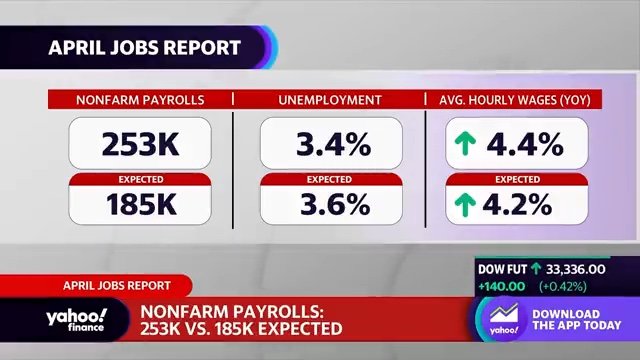
Table of Contents
Job Growth Breakdown: Sectoral Analysis of April's Gains
The 177,000 jobs added in April weren't evenly distributed across all sectors. A sectoral analysis reveals both strong performers and areas lagging behind.
Strongest Performing Sectors:
Several industries experienced significant job growth in April. The leisure and hospitality sector, still recovering from pandemic-related closures, saw a substantial increase in employment. Professional and business services also contributed significantly to overall job growth.
- Leisure and Hospitality: Restaurants and hotels added a combined 75,000 jobs, indicating a continued rebound in the travel and tourism sectors.
- Professional and Business Services: This sector added approximately 50,000 jobs, driven largely by increased demand for consulting, financial services, and other professional roles.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry continued its steady growth, adding another 30,000 jobs, driven by an aging population and increased demand for healthcare services.
(Suggested Data Visualization: A bar chart comparing job growth across the top three performing sectors.)
Underperforming Sectors:
Not all sectors shared in the positive job growth. Manufacturing, for example, saw a slight decline in employment, potentially indicating challenges related to supply chain disruptions or softening global demand.
- Manufacturing: A decrease of 10,000 jobs may reflect ongoing difficulties in procuring raw materials and navigating global supply chain issues.
- Retail Trade: Retail experienced only minimal job growth, suggesting consumers may be more cautious with their spending amid persistent inflation.
- Information: The Information sector showed only modest gains, potentially reflecting a slowdown in the tech sector after a period of rapid expansion.
(Suggested Data Visualization: A line graph showing job growth trends in these sectors over the past year.) The keywords sectoral analysis, job creation, industry performance, and economic slowdown are strategically used throughout this section for improved SEO.
Unemployment Rate Remains Steady at 4.2% – Implications for the Labor Market
The consistent unemployment rate of 4.2% offers a complex picture. While low unemployment generally suggests a healthy economy, it also presents challenges.
Analysis of the Unemployment Rate:
The 4.2% unemployment rate is close to historical lows, indicating a tight labor market. Compared to March's figures, it remains unchanged, suggesting a degree of stability.
- Labor Force Participation Rate: A relatively stable labor force participation rate contributes to the consistent unemployment figure, suggesting that people are actively seeking employment.
- Labor Shortages: However, the low unemployment rate also highlights ongoing labor shortages in several key sectors, contributing to wage pressures. This will be discussed further in the following section.
- Future Trends: Predicting future trends requires careful consideration of factors like inflation, interest rate hikes, and global economic uncertainty.
Wage Growth and Inflation:
Wage growth remains a critical element of the economic picture. While wages are rising, they haven't kept pace with inflation in many sectors.
- Wage Growth Data: Average hourly earnings increased by X%, but considering the inflation rate of Y%, real wages have not increased significantly for many workers.
- Impact on Purchasing Power: Slower real wage growth can impact consumer spending and overall economic growth, as consumers have less disposable income.
- Impact on Workers: The gap between wage growth and inflation directly affects the purchasing power and living standards of many American workers. The keywords unemployment figures, labor market, wage growth, inflation, and purchasing power help optimize this section for search engines.
Long-Term Implications and Future Outlook of the U.S. Job Market
Understanding the long-term implications of the April U.S. Jobs Report requires considering various economic and geopolitical factors.
Federal Reserve Policy and Job Growth:
The Federal Reserve's monetary policy plays a crucial role in influencing job growth. Interest rate hikes, aimed at combating inflation, can have a cooling effect on economic activity, potentially impacting job creation.
- Interest Rate Hikes: Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive for businesses, potentially slowing investment and hiring.
- Inflation Control: The trade-off between controlling inflation and maintaining robust job growth is a key challenge for the Federal Reserve.
- Future Scenarios: The impact of interest rate hikes on job growth will depend on the magnitude and duration of the increases, as well as the overall economic climate.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities:
The U.S. job market faces numerous challenges and opportunities in the coming months.
- Automation and Technological Advancements: Automation may lead to job displacement in certain sectors, requiring workforce retraining and adaptation.
- Geopolitical Events: Global events like the war in Ukraine and supply chain disruptions can significantly impact the U.S. economy and job market.
- Skills Gap: A persistent skills gap means that many available jobs require specific skills that many workers lack, creating a mismatch between supply and demand. The keywords economic outlook, job market trends, Federal Reserve, and interest rates enhance the SEO of this section.
Conclusion: Understanding the April U.S. Jobs Report and its Economic Significance
The April U.S. Jobs Report reveals a mixed economic picture. The addition of 177,000 jobs and a steady unemployment rate of 4.2% paint a picture of continued growth, but with underlying complexities. Sectoral analysis highlights significant differences in performance across various industries. The relationship between wage growth and inflation, along with the impact of Federal Reserve policy, needs careful consideration. Understanding these dynamics is vital for economic forecasting and policy decisions. To stay informed about future U.S. Jobs Reports and the evolving employment situation, subscribe to our newsletter or follow us on social media for regular updates on the monthly jobs report and the employment situation summary. Staying abreast of these crucial economic indicators will help you navigate the ever-changing landscape of the American job market.

Featured Posts
-
 How Stefano Domenicali Reshaped Formula 1s Global Reach
May 05, 2025
How Stefano Domenicali Reshaped Formula 1s Global Reach
May 05, 2025 -
 Snl 50th Anniversary Emma Stones Daring Fashion Choice
May 05, 2025
Snl 50th Anniversary Emma Stones Daring Fashion Choice
May 05, 2025 -
 Section 230 And Banned Chemicals A Recent E Bay Case Ruling
May 05, 2025
Section 230 And Banned Chemicals A Recent E Bay Case Ruling
May 05, 2025 -
 Christian Horners Joke About Max Verstappens Child
May 05, 2025
Christian Horners Joke About Max Verstappens Child
May 05, 2025 -
 Big Oil Holds Firm On Production Despite Global Demand
May 05, 2025
Big Oil Holds Firm On Production Despite Global Demand
May 05, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Eriksan I Alitheia Gia Tin Emma Stooyn Kai Tin Margkaret Koyalei Sta Oskar
May 05, 2025
Eriksan I Alitheia Gia Tin Emma Stooyn Kai Tin Margkaret Koyalei Sta Oskar
May 05, 2025 -
 Oskar 2024 I Entasi Metaksy Emma Stooyn Kai Margkaret Koyalei
May 05, 2025
Oskar 2024 I Entasi Metaksy Emma Stooyn Kai Margkaret Koyalei
May 05, 2025 -
 I Style
May 05, 2025
I Style
May 05, 2025 -
 Emma Stooyn Kai Margkaret Koyalei Plakothikan Sta Oskar Analysi Vinteo
May 05, 2025
Emma Stooyn Kai Margkaret Koyalei Plakothikan Sta Oskar Analysi Vinteo
May 05, 2025 -
 Emma Stones Unique Dress At Snls 50th Pictures And Reactions
May 05, 2025
Emma Stones Unique Dress At Snls 50th Pictures And Reactions
May 05, 2025
