Revitalizing Scotland's Coast: The Role Of Seagrass Planting Bids
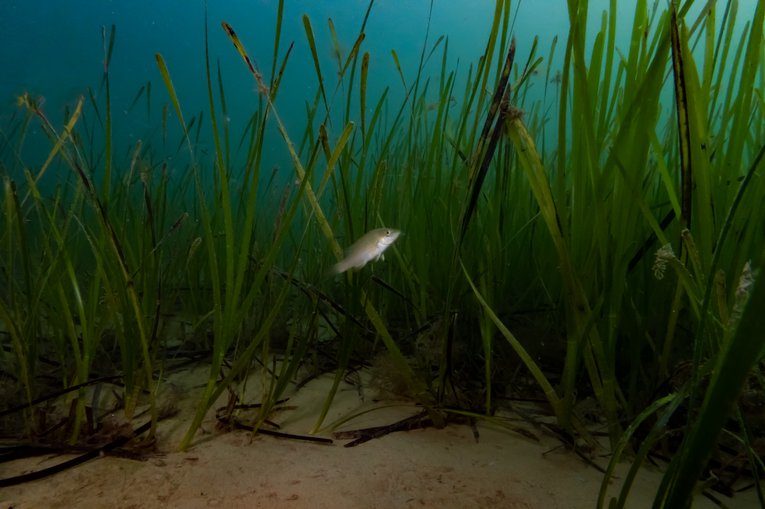

Table of Contents
- The Ecological Importance of Seagrass
- Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation
- Biodiversity Hotspots
- Coastal Protection
- The Role of Seagrass Planting Bids in Restoration
- Funding and Investment
- Community Engagement and Collaboration
- Monitoring and Evaluation
- Challenges and Opportunities for Seagrass Planting Bids in Scotland
- Site Selection and Suitability
- Invasive Species and Disease
- Future Research and Innovation
- Conclusion
The Ecological Importance of Seagrass
Seagrass meadows are far more than just underwater plants; they are complex and incredibly valuable ecosystems. Their importance to the health of Scotland's coastal waters cannot be overstated.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation
Seagrass meadows are remarkably effective carbon sinks, absorbing atmospheric CO2 at a rate significantly exceeding that of terrestrial forests. Through photosynthesis, seagrass captures CO2 and stores it in their tissues and sediments. This process, known as "blue carbon" sequestration, plays a vital role in mitigating climate change. In the Scottish context, restoring and protecting seagrass meadows could contribute substantially to the nation's carbon reduction targets.
- Studies show that seagrass can sequester up to 35 times more carbon per unit area than tropical rainforests.
- Restoring even a small percentage of Scotland's lost seagrass could significantly reduce our carbon footprint.
- Successful seagrass restoration projects can be incorporated into national and international carbon offsetting schemes, generating further funding for conservation efforts.
Biodiversity Hotspots
Seagrass beds act as vital nurseries and habitats for a wide array of marine species. These underwater meadows provide food, shelter, and breeding grounds for commercially important fish like cod and haddock, as well as numerous invertebrates, crustaceans, and marine mammals.
- Seagrass supports populations of commercially important fish, boosting fishing yields and supporting local economies.
- Numerous invertebrate species, including shellfish and worms, rely on seagrass for survival, contributing to the overall health of the marine food web.
- Seagrass meadows provide crucial habitats for threatened species such as seahorses and various seabird species that depend on the fish found within them.
Coastal Protection
Seagrass beds provide a natural buffer against coastal erosion and storm damage. Their dense root systems stabilize sediments, reducing the impact of waves and currents on shorelines. This natural coastal defense mechanism offers a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to artificial structures.
- Seagrass reduces wave energy by up to 70%, protecting coastal communities and infrastructure from erosion.
- In areas of Scotland experiencing significant coastal erosion, seagrass restoration can be a highly effective and cost-efficient solution.
- The long-term cost savings associated with seagrass protection compared to traditional methods like seawalls are considerable, making it an attractive option for sustainable coastal management.
The Role of Seagrass Planting Bids in Restoration
Securing funding for large-scale seagrass restoration is crucial, and this is where seagrass planting bids come into play. These bids are competitive applications for funding from various sources, enabling vital projects to proceed.
Funding and Investment
Successful seagrass planting bids are instrumental in securing crucial funding for large-scale restoration projects. Various sources of funding exist, including:
- Government grants from bodies like NatureScot and the EU's LIFE Programme.
- Funding from environmental charities and organizations such as The Marine Conservation Society.
- Investment from private sector companies committed to environmental sustainability.
Successful bids often detail the potential ecological and economic benefits of the project, demonstrating a strong return on investment for funders.
Community Engagement and Collaboration
Effective seagrass restoration requires collaboration. Successful projects often involve:
- Strong partnerships between scientists, local communities, and government agencies.
- Community-led initiatives, empowering local stakeholders and fostering environmental stewardship.
- Citizen science programs, enabling community members to participate in monitoring and data collection.
This collaborative approach ensures project sustainability and strengthens local support for conservation efforts.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Comprehensive monitoring and evaluation are crucial for the long-term success of seagrass planting initiatives. Successful bids will include:
- Detailed plans for monitoring seagrass growth, survival rates, and overall ecosystem health.
- Regular data collection using techniques such as underwater surveys and remote sensing.
- Analysis of collected data to inform future restoration efforts and adaptive management strategies.
This rigorous approach ensures that valuable lessons are learned, contributing to more efficient and effective seagrass restoration in the future.
Challenges and Opportunities for Seagrass Planting Bids in Scotland
While the potential benefits of seagrass restoration are significant, several challenges must be addressed.
Site Selection and Suitability
Careful site selection is crucial for successful seagrass planting. Factors to consider include:
- Water quality: Suitable sites must have good water clarity and minimal pollution.
- Sediment type: Seagrass thrives in specific sediment types that provide suitable anchorage.
- Light availability: Adequate sunlight penetration is essential for photosynthesis.
Identifying suitable sites requires extensive surveys and environmental assessments.
Invasive Species and Disease
Invasive species and diseases pose a significant threat to newly planted seagrass beds. Strategies to mitigate this risk include:
- Careful site selection to avoid areas with known invasive species.
- Monitoring for invasive species and disease outbreaks.
- Implementing control measures to manage and eradicate invasive species.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the long-term success of seagrass restoration projects.
Future Research and Innovation
Continued research and innovation are essential to improve seagrass planting techniques and address ongoing challenges. Future research priorities include:
- Developing more resilient seagrass varieties that are better adapted to changing environmental conditions.
- Improving planting methods to increase survival rates and reduce costs.
- Exploring new technologies for monitoring and managing seagrass meadows.
Investment in research and development is vital for the long-term success of seagrass restoration efforts in Scotland.
Conclusion
Seagrass planting bids are vital for the successful restoration and protection of Scotland's precious coastal ecosystems. By securing funding, fostering community engagement, and employing innovative techniques, these bids offer a powerful pathway towards a healthier and more resilient coastline. Investing in seagrass planting bids is an investment in Scotland's future, contributing to climate change mitigation, biodiversity enhancement, and sustainable coastal management. Let's continue to support and expand the vital work of seagrass planting bids and ensure the health and vitality of Scotland's coasts for generations to come. Learn more about how you can contribute to seagrass planting initiatives and make a difference today.

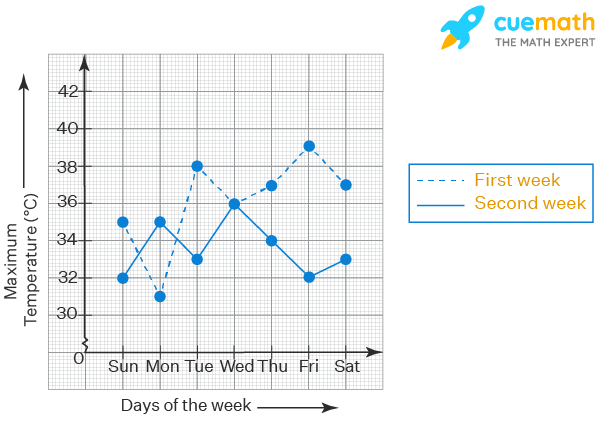 Gold Market Update Analyzing Two Consecutive Weeks Of Losses 2025
Gold Market Update Analyzing Two Consecutive Weeks Of Losses 2025
 Stanley Cup Playoffs Us Viewership Trends And International Influence
Stanley Cup Playoffs Us Viewership Trends And International Influence
 Sydney Sweeney And Jonathan Davino Wedding Plans Delayed Official Statement And Fan Reactions
Sydney Sweeney And Jonathan Davino Wedding Plans Delayed Official Statement And Fan Reactions
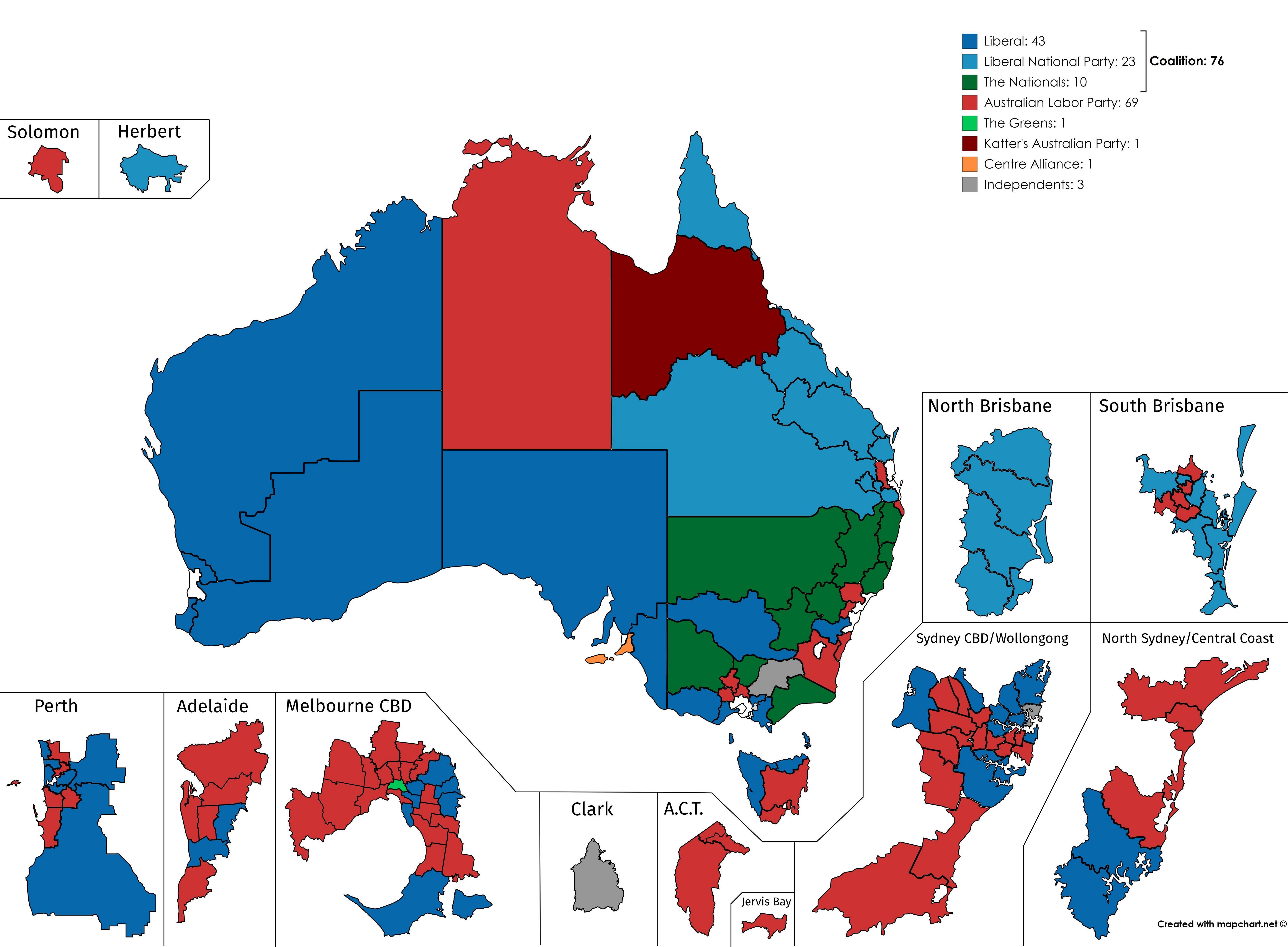 Australian Election Results Analyzing The Global Political Landscape
Australian Election Results Analyzing The Global Political Landscape
 Eurovision Concerns Grow As Tynnas Voice Faces Scrutiny
Eurovision Concerns Grow As Tynnas Voice Faces Scrutiny
