Post-Pandemic Fiscal Stimulus: ECB Highlights Inflationary Impact
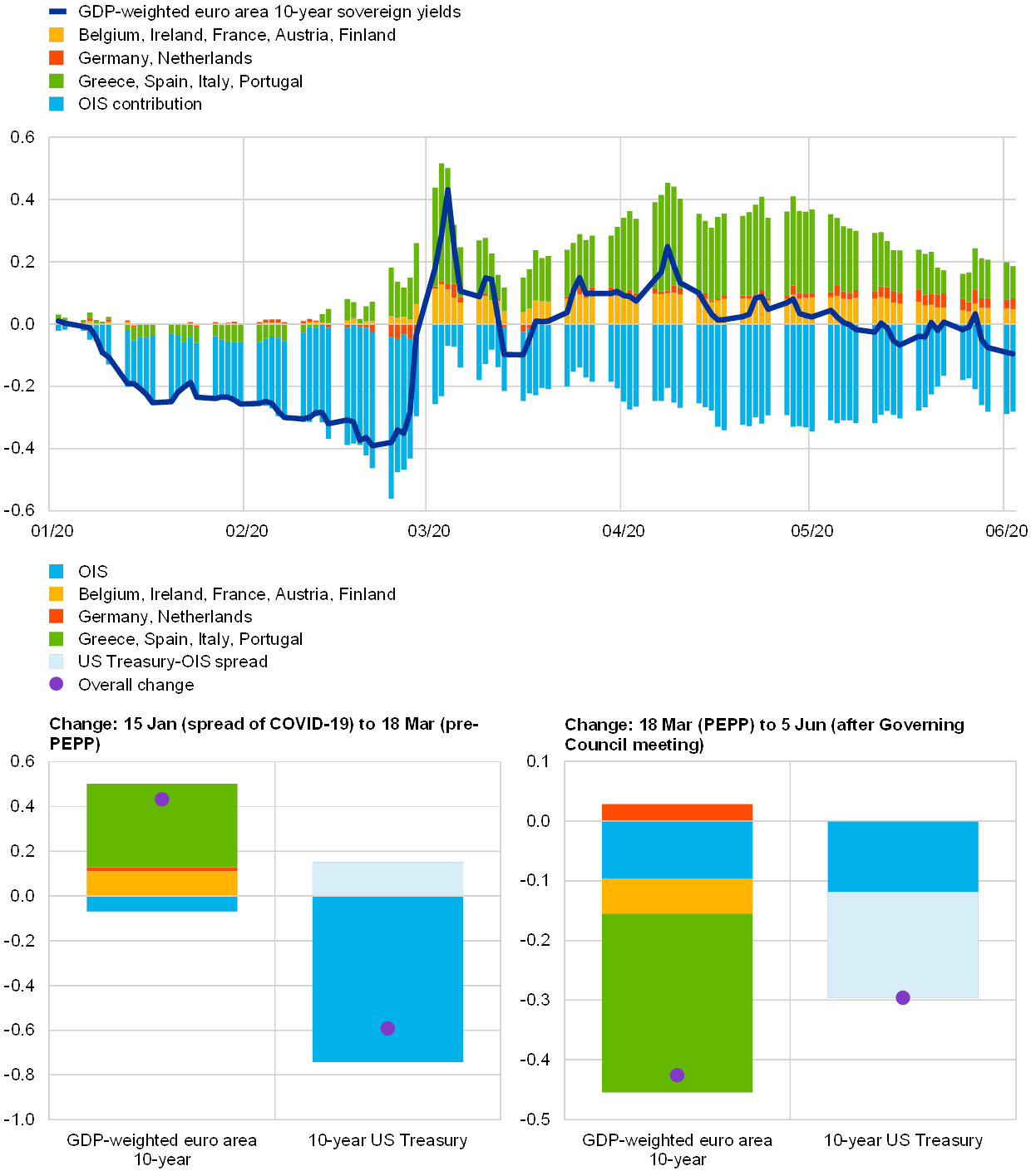
Table of Contents
The ECB's Role in Managing Post-Pandemic Inflation
The ECB's primary mandate is to maintain price stability within the Eurozone. The surge in inflation following the pandemic forced the ECB to adopt a more restrictive monetary policy. Initially, the ECB maintained extremely low interest rates and engaged in quantitative easing (QE) to support economic recovery. However, as inflation soared beyond its 2% target, the ECB shifted gears.
The ECB employed several monetary policy tools to combat inflation:
- Interest Rate Hikes: The ECB significantly raised its key interest rates, increasing borrowing costs for banks and businesses. This aimed to curb lending and reduce aggregate demand.
- Quantitative Tightening (QT): The ECB began reducing its balance sheet by allowing maturing bonds to roll off without replacement. This decreased the money supply and further tightened monetary conditions.
The effectiveness of these measures remains a subject of ongoing debate.
- Effectiveness: While interest rate hikes have shown some success in curbing inflation, their impact has been uneven across Eurozone countries and sectors. The effectiveness of QT is still unfolding.
- Challenges: The ECB faces the difficult task of balancing inflation control with the need to support economic growth. Aggressive monetary tightening risks triggering a recession.
- Unintended Consequences: Higher interest rates can negatively impact investment, employment, and overall economic activity. The ECB's actions need careful calibration to avoid exacerbating these risks.
- ECB Statements: The ECB's monthly bulletins and press conferences provide insights into its evolving strategy in managing inflation and its assessments of the risks.
Analyzing the Direct Impact of Stimulus Packages on Inflation
Eurozone governments implemented various fiscal stimulus measures, including:
- Increased Government Spending: Significant investments were made in healthcare, social support programs, and infrastructure projects.
- Reduced Taxation: Tax cuts and deferrals were introduced to boost disposable income and stimulate consumption.
This surge in government spending and reduced taxation fueled demand-pull inflation, driving up prices as demand outpaced supply. Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the pandemic, further aggravated inflationary pressures.
- Examples: The German Konjunkturpaket and the French plan de relance are prime examples of substantial stimulus packages implemented. Their impact on inflation can be quantitatively assessed through econometric models.
- Statistical Data: Data from Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union, reveals a strong correlation between the timing and scale of stimulus packages and subsequent increases in inflation rates.
- Sectoral Impact: Energy and food prices experienced particularly sharp increases, impacting household budgets significantly.
- Inflation Rate Comparisons: Inflation rates varied across Eurozone countries, reflecting differences in the structure of their economies, the scale of stimulus measures, and the extent of supply chain disruptions.
The Interaction Between Fiscal and Monetary Policy in the Eurozone
Coordinating fiscal and monetary policies across the diverse economies of the Eurozone presents significant challenges. Ideally, fiscal and monetary authorities should work in tandem: fiscal policy stimulating the economy in times of recession and monetary policy keeping inflation under control. However, in practice, achieving such coordination has proven difficult.
- Coordination Challenges: Different Eurozone countries face varying economic conditions, necessitating tailored fiscal responses that may conflict with the ECB's overarching monetary policy goals.
- Conflicts: Fiscal stimulus aimed at boosting growth can clash with monetary tightening aimed at controlling inflation, leading to policy dilemmas.
- Examples: The differing approaches to fiscal stimulus adopted by various member states and the ensuing impact on inflation highlight the coordination issues. Analysis of past successful coordinated policies versus those leading to conflicting outcomes can reveal valuable lessons.
- Policy Improvements: Enhanced communication and data-sharing between fiscal authorities and the ECB, along with clearer policy frameworks, could improve coordination. Political constraints, such as national sovereignty concerns, remain major hurdles.
Long-Term Implications of Post-Pandemic Fiscal Stimulus on the Eurozone Economy
Persistently high inflation has far-reaching consequences.
-
Impact on Investment and Savings: High inflation erodes the real value of savings and discourages investment.
-
Economic Growth: Sustained high inflation can lead to uncertainty, dampening economic growth and potentially triggering stagflation (a combination of high inflation and slow economic growth).
-
Future Fiscal Policy: The experience of post-pandemic inflation has prompted a reassessment of the design and implementation of future fiscal stimulus packages, with a focus on sustainability and avoiding excessive demand-pull pressures.
-
Inflation Predictions: Forecasting future inflation rates remains uncertain, but various models and economic indicators suggest that inflation, though easing, may remain above the ECB’s target for some time.
-
Long-term Consequences: The long-term economic consequences may include slower potential growth, increased income inequality, and increased public debt.
-
Policy Recommendations: Long-term sustainable economic policies should prioritize investments that enhance productivity, improve supply-side flexibility, and mitigate climate change.
Conclusion: Understanding the Lasting Effects of Post-Pandemic Fiscal Stimulus
The post-pandemic fiscal stimulus in the Eurozone, while necessary for mitigating the immediate economic impact of COVID-19, significantly contributed to inflationary pressures. The ECB's response, involving interest rate hikes and quantitative tightening, aims to control inflation but faces the challenge of balancing this with the need for economic growth. The interaction between fiscal and monetary policies has been complex and highlights the need for better coordination. The long-term economic implications of this period of high inflation remain to be seen, but it is clear that it poses substantial challenges for the Eurozone's economic future. To fully understand the lasting effects, further research into post-pandemic fiscal stimulus and its various impacts on the Eurozone economy is essential. We encourage you to explore the ECB's publications and other credible economic resources to stay informed about the ongoing developments in the ECB's monetary policy and its influence on inflation within the Eurozone.

Featured Posts
-
 Suspecting Adult Adhd Your Guide To Next Steps
Apr 29, 2025
Suspecting Adult Adhd Your Guide To Next Steps
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Top India Fund Manager Dsp Sounds Warning On Stocks
Apr 29, 2025
Top India Fund Manager Dsp Sounds Warning On Stocks
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Murder Conviction After Deadly Teen Rock Throwing Game
Apr 29, 2025
Murder Conviction After Deadly Teen Rock Throwing Game
Apr 29, 2025 -
 20 000 Demonstrate A Powerful Display For Transgender Equality
Apr 29, 2025
20 000 Demonstrate A Powerful Display For Transgender Equality
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Culture Departments Canoe Awakening An Annual Tradition
Apr 29, 2025
The Culture Departments Canoe Awakening An Annual Tradition
Apr 29, 2025
