Indonesia Reserve Drop: Rupiah Depreciation Impacts Foreign Exchange Holdings

Table of Contents
Understanding the Rupiah's Depreciation
The weakening of the Rupiah against major currencies like the US dollar is a multi-faceted issue. Several key factors are at play:
-
Global Interest Rate Hikes: The aggressive interest rate hikes implemented by central banks worldwide, particularly the US Federal Reserve, to combat inflation have drawn capital away from emerging markets like Indonesia. Investors seek higher returns in developed economies, leading to a decrease in demand for the Rupiah and subsequently, its devaluation. This currency devaluation impacts the Rupiah exchange rate negatively.
-
Inflationary Pressures: Global inflation, driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions and energy price volatility, erodes the purchasing power of the Rupiah and puts downward pressure on its value. Higher inflation makes Indonesian exports less competitive, further weakening the Rupiah exchange rate.
-
Capital Flows and Investor Sentiment: Shifting investor sentiment and reduced capital inflows into Indonesia also contribute to the Rupiah's depreciation. Geopolitical uncertainties and concerns about global economic growth can cause investors to pull their funds from emerging markets, increasing selling pressure on the Rupiah. This impacts emerging market currency values globally.
These factors collectively contribute to the downward pressure on the Rupiah exchange rate, necessitating a closer examination of its effects on Indonesia's economic stability.
The Direct Impact on Foreign Exchange Holdings
The depreciation of the Rupiah directly translates to a reduction in the value of Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves held in other currencies. When the Rupiah weakens, the equivalent value of these foreign currency reserves in Rupiah terms decreases. This reserve depletion can be substantial, limiting the government's capacity to intervene in the foreign exchange market or manage external debt effectively. Data illustrating this correlation between Rupiah performance and reserve levels is crucial for understanding the severity of the situation. (Insert relevant charts and graphs here illustrating the correlation between Rupiah depreciation and the drop in foreign exchange reserves). The implications are significant for managing balance of payments and ensuring sufficient resources to cover import costs.
Indirect Impacts on the Indonesian Economy
The decline in foreign exchange reserves has far-reaching consequences for the Indonesian economy:
-
Increased Inflation: A weaker Rupiah makes imports more expensive, contributing to inflationary pressures. This can erode purchasing power and impact consumer spending. The inflation rate becomes a key concern.
-
Reduced Investment: Uncertainty surrounding the Rupiah's value can deter foreign investment, hindering economic growth. Lower investor confidence leads to capital outflows, further exacerbating the situation.
-
Slower Economic Growth: The combined effects of inflation, reduced investment, and decreased consumer confidence can lead to a slowdown in overall economic growth. This creates a negative feedback loop impacting economic stability.
The Indonesian government needs to carefully manage these indirect impacts to prevent a deeper economic downturn.
Government Measures and Policy Responses
The Indonesian government has implemented several measures to address the Rupiah's depreciation and protect its foreign exchange reserves:
-
Monetary Policy Adjustments: Bank Indonesia has adjusted interest rates to attract foreign investment and stabilize the Rupiah. Raising interest rates makes Indonesian assets more attractive to foreign investors, potentially increasing demand for the Rupiah. This is a key aspect of monetary policy.
-
Fiscal Policy Measures: The government is implementing fiscal policies aimed at boosting economic growth and reducing the current account deficit. Stimulating domestic demand and promoting export-oriented industries can help improve the Rupiah's value. This is a vital component of fiscal policy.
-
Foreign Exchange Market Interventions: While potentially costly, the government might intervene in the foreign exchange market to support the Rupiah and manage volatility. However, such government intervention needs to be carefully calibrated to avoid unintended consequences. These interventions are part of broader economic stimulus efforts.
Conclusion: Safeguarding Indonesia's Foreign Exchange Reserves – A Call to Action
The depreciation of the Rupiah has significantly impacted Indonesia's foreign exchange holdings, creating challenges for economic stability. Maintaining sufficient Indonesia foreign exchange reserves is critical for managing external debt, financing imports, and maintaining investor confidence. The government's response through monetary and fiscal policies is crucial, but continued vigilance is necessary. The future outlook depends on global economic conditions, investor sentiment, and the effectiveness of government policies.
Further research and open discussion on strategies to strengthen the Rupiah and bolster foreign exchange holdings are vital. We must continue monitoring Rupiah depreciation and its effect on foreign exchange holdings to ensure Indonesia's economic resilience. Understanding the interplay between global economic forces and domestic policies is paramount for safeguarding Indonesia's economic future.

Featured Posts
-
 Us Deportations To El Salvador Concerns Over Due Process And Judicial Oversight
May 10, 2025
Us Deportations To El Salvador Concerns Over Due Process And Judicial Oversight
May 10, 2025 -
 Exploring Alternative Canola Suppliers Chinas Post Canada Approach
May 10, 2025
Exploring Alternative Canola Suppliers Chinas Post Canada Approach
May 10, 2025 -
 Is Trumps Transgender Military Ban Fair Examining The Arguments
May 10, 2025
Is Trumps Transgender Military Ban Fair Examining The Arguments
May 10, 2025 -
 Dakota Johnson El Exito Del Bolso Hereu Entre Las Celebrities
May 10, 2025
Dakota Johnson El Exito Del Bolso Hereu Entre Las Celebrities
May 10, 2025 -
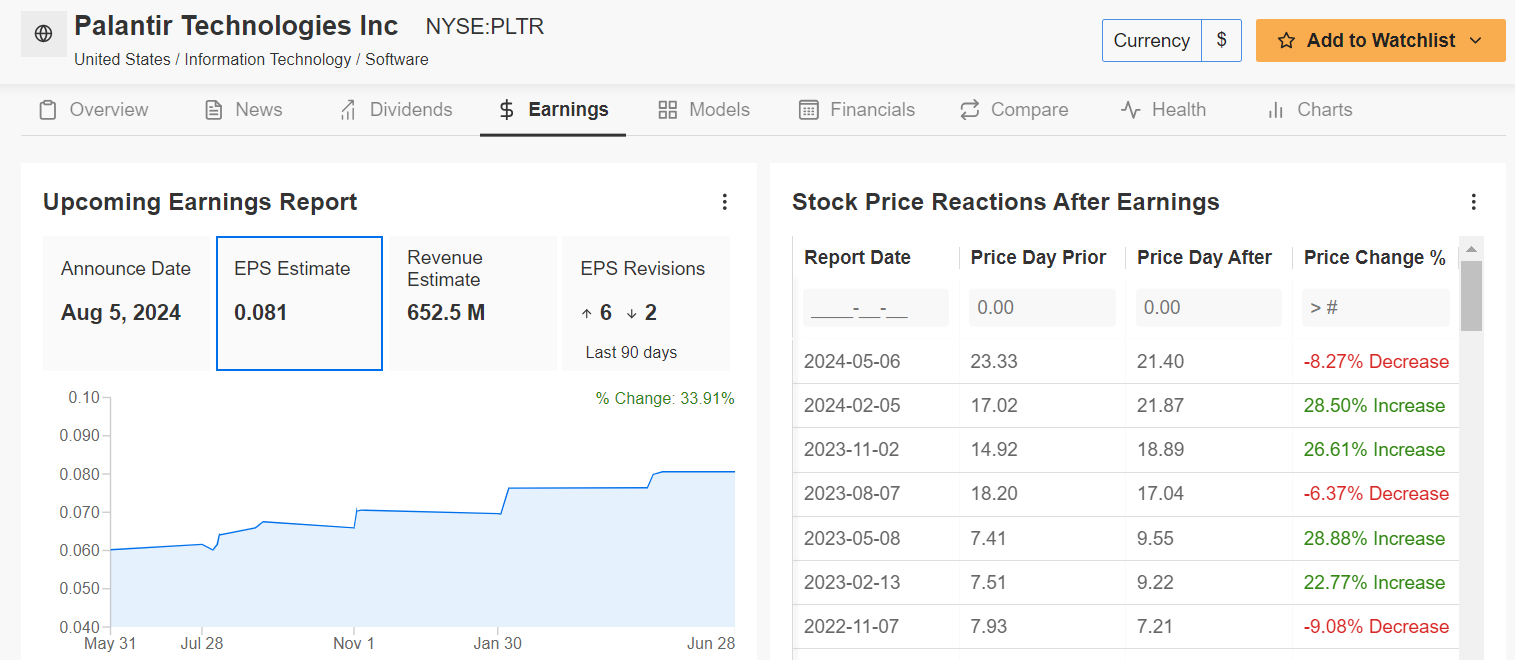 Should You Buy Palantir Stock Before May 5 A Pre Earnings Analysis
May 10, 2025
Should You Buy Palantir Stock Before May 5 A Pre Earnings Analysis
May 10, 2025
