Greenland's Geopolitical Importance: A Look At US-China Tensions
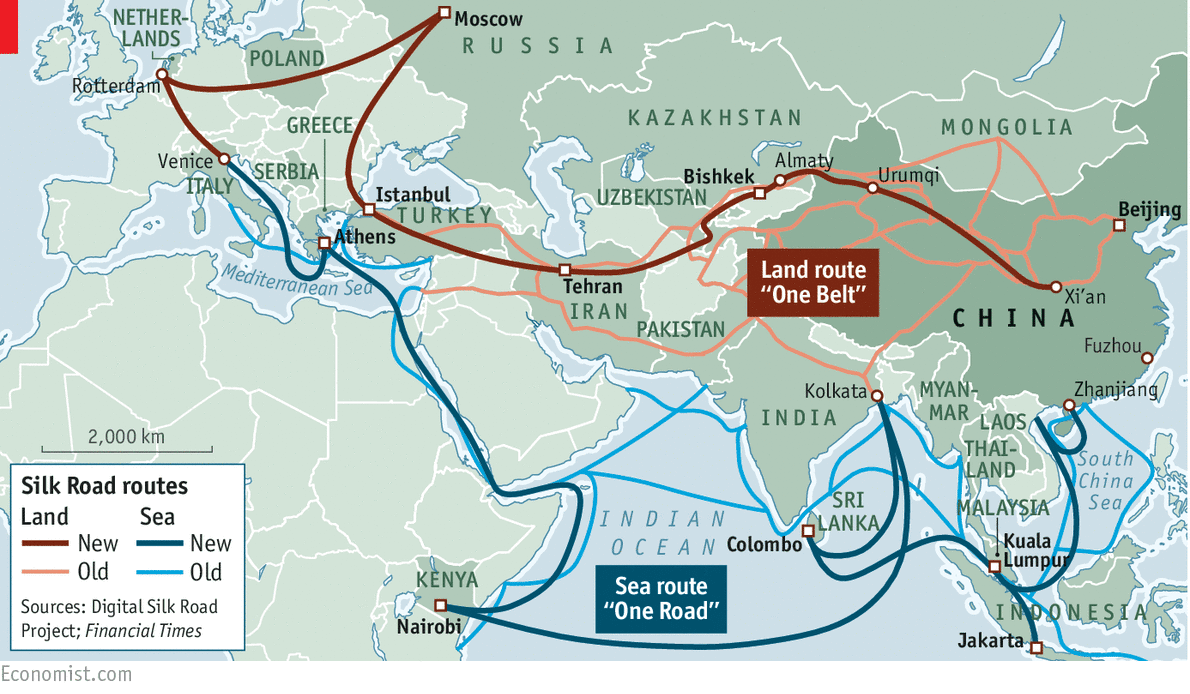
Table of Contents
Greenland's Strategic Location and Resources
Greenland's geopolitical importance stems from its unique geographical location and abundant natural resources, making it a focal point of international interest and competition.
Geographic Significance
Greenland's position between North America and Europe, straddling the Arctic, provides significant strategic advantages. Its location offers unparalleled opportunities for:
- Shorter flight times: Greenland's location allows for significantly reduced flight times between North America and Europe, making it a potential hub for transatlantic air travel and military operations.
- Potential for new shipping lanes (Northern Sea Route): The melting Arctic ice is opening up new navigable shipping lanes, significantly shortening trade routes between Asia and Europe. Greenland's coastal areas are poised to become crucial transit points along these routes.
- Enhanced surveillance capabilities: Greenland's location provides excellent opportunities for establishing surveillance systems, monitoring maritime traffic, and enhancing national security for nations with interests in the Arctic region.
These factors contribute to Greenland's growing importance as a key player in Arctic geopolitics, enhancing its Arctic strategic location and solidifying its geographical advantage.
Abundant Natural Resources
Beyond its strategic location, Greenland possesses vast reserves of valuable natural resources that are attracting significant international attention. These include:
- Rare earth element mining: Greenland holds substantial deposits of rare earth elements, crucial for modern technologies like smartphones, wind turbines, and electric vehicles. Control over these resources offers significant economic and technological leverage.
- Potential energy independence for nations: Significant deposits of oil and gas reserves offer the potential for energy independence for various nations, reducing their reliance on volatile global energy markets.
- Economic opportunities: The exploitation of these resources promises significant economic opportunities for Greenland, potentially transforming its economy and improving the living standards of its population.
The presence of these Greenland's natural resources, especially rare earth elements, is a major driver of the growing geopolitical competition in the Arctic, highlighting Greenland's economic potential and its importance in the global mineral resource market.
US Interests and Engagement in Greenland
The United States has a long-standing interest in Greenland, driven by strategic considerations and historical ties.
Historical Ties and Strategic Partnerships
The US presence in Greenland dates back decades, with significant investments in infrastructure and collaborative projects. Key aspects include:
- Thule Air Base: The Thule Air Base, a crucial US military installation, plays a vital role in North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) operations and provides strategic surveillance capabilities across the Arctic.
- Scientific research collaborations: The US and Greenland have engaged in extensive scientific collaborations, focusing on climate change research, environmental monitoring, and geological surveys.
- Economic aid programs: The US has provided economic aid and support to Greenland, fostering economic development and strengthening bilateral ties.
These historical ties and strategic partnerships solidify US-Greenland relations and underscore the American influence in Greenland.
Countering Chinese Influence
The US views China's growing interest in Greenland with concern, perceiving it as a potential threat to its strategic interests in the Arctic. The US's concerns include:
- Concerns over Chinese investment in infrastructure: Chinese investment in Greenland's infrastructure, such as ports and airports, raises concerns about potential dual-use capabilities and the expansion of Chinese influence.
- Resource extraction: Chinese companies' involvement in resource extraction projects in Greenland raises concerns about potential environmental damage and the potential transfer of critical resources to China.
- Potential military expansion: The US is concerned about the potential for China to use its economic leverage in Greenland to establish a military presence in the Arctic.
These concerns highlight the US-China rivalry in the Arctic and the growing focus on Greenland security concerns within the broader context of great power competition.
China's Growing Influence in Greenland
China's increasing engagement with Greenland is driven by its broader Arctic strategy and its desire to secure resources and expand its global influence.
Economic Investments and Infrastructure Projects
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has extended its reach to the Arctic, with proposals for significant infrastructure development in Greenland. These include:
- Port development: China has expressed interest in developing port facilities in Greenland, improving connectivity and facilitating trade.
- Mining investments: Chinese companies have invested in mining projects in Greenland, aiming to secure access to valuable resources.
- Potential for increased trade and connectivity: Improved infrastructure supported by Chinese investment could lead to increased trade and connectivity between Greenland, China, and other parts of the world.
These initiatives demonstrate China's Belt and Road Initiative's impact in the Arctic and its increasing investment in Greenland infrastructure development.
Geopolitical Ambitions and Strategic Objectives
China's growing presence in the Arctic is not merely economic; it reflects broader geopolitical ambitions:
- Access to natural resources: China aims to secure access to Greenland's valuable natural resources to support its growing economy and technological development.
- Expansion of global trade routes: China seeks to leverage Greenland's strategic location to expand its global trade routes and strengthen its economic connectivity.
- Potential military capabilities: While not explicitly stated, some analysts suggest that China's long-term goals include the potential development of military capabilities in the Arctic region.
These factors underscore China's Arctic strategy and its broader geopolitical ambitions, highlighting Greenland's role in Chinese strategy and its importance to China's future economic and political influence.
Greenland's Self-Determination and Navigating Great Power Competition
Greenland faces the complex challenge of balancing its desire for economic development with its strategic autonomy and national security in the face of growing great power competition.
Balancing Competing Interests
Greenland must carefully navigate its relationship with both the US and China, ensuring it does not become overly reliant on any single power. Key considerations include:
- Need for transparent governance: Maintaining transparent and accountable governance is crucial to ensuring that development projects benefit the Greenlandic people and do not compromise national security.
- Diversification of partnerships: Greenland needs to diversify its partnerships, reducing its dependence on any single nation and ensuring access to diverse sources of investment and support.
- Environmental sustainability: Balancing economic development with environmental sustainability is vital for Greenland's long-term well-being and the preservation of its unique Arctic ecosystem.
These challenges highlight Greenland's sovereignty and its difficult task of balancing economic development with its national security interests.
The Role of International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential for managing the competing interests in the Arctic and preventing the escalation of tensions between major powers. This requires:
- Arctic Council: The Arctic Council provides a crucial platform for dialogue and cooperation among Arctic states, including Greenland, on issues such as environmental protection and sustainable development.
- International environmental agreements: Strengthening and enforcing international environmental agreements is vital for protecting the fragile Arctic ecosystem from the impacts of resource extraction and climate change.
- Promoting dialogue and cooperation: Encouraging dialogue and cooperation between the US, China, and other stakeholders is critical for preventing misunderstandings and resolving disputes peacefully.
These considerations underscore the vital role of Arctic governance and international cooperation in the Arctic, promoting responsible Arctic development and minimizing the risk of conflict.
Conclusion
Greenland's geopolitical importance is undeniable, and the competition between the US and China highlights the strategic significance of this Arctic nation. The struggle for influence over Greenland’s resources and territory underscores the increasing tensions in the Arctic region. Understanding the complexities of Greenland's geopolitical importance is crucial for navigating the future of Arctic cooperation and preventing potential conflicts. Further research and informed discussion are essential to shaping a sustainable and secure future for Greenland and the Arctic. We need to continue to monitor the developments in Greenland's geopolitical importance closely.

Featured Posts
-
 Us Tariffs A Convenient Excuse For Gms Reduced Canadian Presence
May 08, 2025
Us Tariffs A Convenient Excuse For Gms Reduced Canadian Presence
May 08, 2025 -
 Nba Playoffs Alex Carusos Historic Performance In Thunders Game 1
May 08, 2025
Nba Playoffs Alex Carusos Historic Performance In Thunders Game 1
May 08, 2025 -
 Rogue Exiles Explained Path Of Exile 2
May 08, 2025
Rogue Exiles Explained Path Of Exile 2
May 08, 2025 -
 John Fetterman Rebuts Ny Magazine Report On His Fitness For Office
May 08, 2025
John Fetterman Rebuts Ny Magazine Report On His Fitness For Office
May 08, 2025 -
 Understanding The Impact Of Liberation Day Tariffs On Stock Prices
May 08, 2025
Understanding The Impact Of Liberation Day Tariffs On Stock Prices
May 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Tri Poljupca Deandre Dzordan Otkriva Zasto On I Nikola Jokic Tako Cine
May 08, 2025
Tri Poljupca Deandre Dzordan Otkriva Zasto On I Nikola Jokic Tako Cine
May 08, 2025 -
 Deandre Dzordan I Nikola Jokic Objasnjenje Za Trostruki Poljubac
May 08, 2025
Deandre Dzordan I Nikola Jokic Objasnjenje Za Trostruki Poljubac
May 08, 2025 -
 Deandre Dzordan Zasto Se Ljubi Sa Jokicem Tri Puta Bobi Marjanovic Krivac
May 08, 2025
Deandre Dzordan Zasto Se Ljubi Sa Jokicem Tri Puta Bobi Marjanovic Krivac
May 08, 2025 -
 De Andre Jordan Makes Nba History In Thrilling Nuggets Bulls Matchup
May 08, 2025
De Andre Jordan Makes Nba History In Thrilling Nuggets Bulls Matchup
May 08, 2025 -
 New Trailer For Stephen Kings The Long Walk Adaptation
May 08, 2025
New Trailer For Stephen Kings The Long Walk Adaptation
May 08, 2025
