Fungal Infections: A Growing Threat Of Antibiotic Resistance
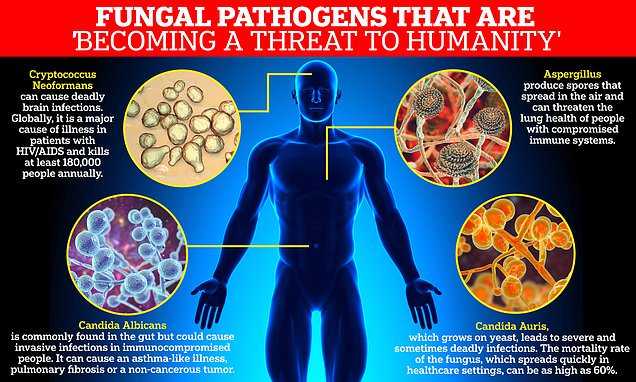
Table of Contents
The Rise of Antifungal Resistance
The development of antifungal resistance is a complex process, mirroring the mechanisms seen in bacterial antibiotic resistance. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial to developing effective countermeasures.
Understanding Antifungal Resistance Mechanisms
Fungi employ several strategies to evade the effects of antifungal drugs. These mechanisms include:
- Target modification: Fungi alter the structure of the drug's target site, preventing the drug from binding effectively. This is particularly relevant for azoles, which target ergosterol synthesis in fungal cell membranes. Mutations in the target enzyme (e.g., lanosterol 14α-demethylase for azoles) can significantly reduce drug efficacy.
- Efflux pumps: Fungi can actively pump antifungal drugs out of their cells, reducing intracellular drug concentrations. This mechanism contributes to multi-drug resistance, as efflux pumps often target multiple classes of antifungals.
- Altered cell wall synthesis: Some fungi develop resistance by altering the composition or synthesis of their cell walls, reducing the drug's ability to penetrate and damage the fungal cell. This mechanism is particularly important for echinocandins, which target cell wall synthesis.
Specific mechanisms vary depending on the antifungal drug class. Azole resistance, for instance, often involves mutations in the CYP51A gene encoding the target enzyme. Echinocandin resistance frequently results from mutations in FKS genes, encoding proteins involved in cell wall synthesis. Polyene resistance, meanwhile, can arise from modifications to the fungal cell membrane. Genetic mutations play a crucial role, often arising spontaneously or being acquired through horizontal gene transfer. Environmental factors, including exposure to antifungal agents in agriculture and healthcare settings, can also significantly influence the selection and spread of resistant strains.
Contributing Factors to the Rise of Antifungal Resistance
Several interconnected factors contribute to the alarming rise in antifungal resistance.
Overuse and Misuse of Antifungal Drugs
Inappropriate use of antifungal drugs in both healthcare and agriculture plays a major role in driving resistance. This includes:
- Prophylactic use: The routine use of antifungals to prevent infections, even in the absence of clear indications, contributes significantly to resistance development.
- Broad-spectrum use: Employing broad-spectrum antifungals indiscriminately, rather than targeting specific fungal pathogens, selects for resistant strains.
- Inadequate treatment duration: Incomplete treatment courses allow surviving fungal cells to recover and potentially develop resistance.
- Self-medication: Easy access to antifungals without prescription leads to misuse and contributes to the emergence of resistance.
- Agricultural use: The widespread use of antifungals in agriculture to protect crops further fuels the development and spread of resistant fungal strains. These strains can subsequently transfer resistance genes to human pathogens.
- Lack of new drug development: The limited pipeline of new antifungal drugs exacerbates the problem, leaving fewer options to treat resistant infections.
Impact of Antifungal Resistance on Public Health
The consequences of antifungal resistance are severe and far-reaching.
Increased Morbidity and Mortality
Resistant fungal infections translate to:
- Increased morbidity: Longer hospital stays, increased treatment costs, and prolonged illness significantly impact patients' quality of life.
- Increased mortality: Untreatable fungal infections can lead to death, particularly among vulnerable populations.
- Impact on vulnerable populations: Immunocompromised individuals, such as cancer patients, organ transplant recipients, and those with HIV/AIDS, are particularly susceptible to severe and fatal outcomes from resistant fungal infections.
- Emergence of deadly pathogens: Candida auris, a multi-drug resistant fungus, highlights the potential for devastating outbreaks with high mortality rates. Its ability to persist in hospital environments and spread easily presents a significant public health challenge.
- Economic burden: The treatment of resistant fungal infections is costly, placing a significant burden on healthcare systems worldwide.
Strategies to Combat Antifungal Resistance
Addressing the challenge of antifungal resistance requires a multi-pronged approach.
Developing New Antifungal Drugs and Therapies
The development of novel antifungal agents with new mechanisms of action is paramount:
- Research and development: Increased investment in research is vital to identify and develop novel antifungal drug candidates.
- Drug repurposing: Exploring the potential of existing drugs for antifungal activity can accelerate the development process.
- Alternative therapies: Investigating alternative approaches like phage therapy and immunotherapy offers promising avenues for combating resistant fungal infections.
Improving Infection Prevention and Control
Strengthening infection prevention and control (IPC) measures is equally important:
- Hand hygiene: Strict adherence to hand hygiene protocols remains a cornerstone of infection control.
- Sterilization techniques: Employing appropriate sterilization techniques for medical equipment prevents fungal contamination.
- Environmental cleaning: Regular and thorough cleaning of hospital and healthcare environments is crucial for minimizing fungal spread.
- Surveillance and rapid diagnostic testing: Effective surveillance programs and rapid diagnostic tests are critical for early detection and appropriate treatment of fungal infections.
- Antifungal stewardship: Implementing antifungal stewardship programs in healthcare settings promotes responsible antifungal use and minimizes resistance development.
Conclusion
The growing threat of antifungal resistance poses a significant and escalating challenge to global health. The overuse and misuse of antifungals, coupled with a lack of new drug development, has fueled the emergence of multi-drug resistant fungal pathogens, leading to increased morbidity and mortality, particularly among vulnerable populations. Combating this threat requires a concerted effort focusing on developing novel antifungal agents, strengthening infection prevention and control measures, and promoting responsible antifungal use. Understanding and addressing the growing threat of fungal infections is crucial for safeguarding global health. Let's work together to combat antifungal resistance and protect vulnerable populations from the devastating consequences of these increasingly resistant infections.

Featured Posts
-
 Canadas Mark Carney Rebuffed Trumps Attempts To Influence Policy
May 08, 2025
Canadas Mark Carney Rebuffed Trumps Attempts To Influence Policy
May 08, 2025 -
 Inter Milan Vs Fc Barcelona Watch The Champions League Live
May 08, 2025
Inter Milan Vs Fc Barcelona Watch The Champions League Live
May 08, 2025 -
 Inter Milan Triumphs Over Bayern Munich In First Leg Of Champions League Tie
May 08, 2025
Inter Milan Triumphs Over Bayern Munich In First Leg Of Champions League Tie
May 08, 2025 -
 The Future Of Xrp The Impact Of Sec Decisions And Etf Applications
May 08, 2025
The Future Of Xrp The Impact Of Sec Decisions And Etf Applications
May 08, 2025 -
 Sms Dolandiriciligi Sikayetler Neden Artti Ve Nasil Korunabilirsiniz
May 08, 2025
Sms Dolandiriciligi Sikayetler Neden Artti Ve Nasil Korunabilirsiniz
May 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Aktuelle Lotto 6aus49 Ergebnisse Ziehung Vom 12 April 2025
May 08, 2025
Aktuelle Lotto 6aus49 Ergebnisse Ziehung Vom 12 April 2025
May 08, 2025 -
 Lotto 6aus49 Alle Zahlen Vom 19 April 2025
May 08, 2025
Lotto 6aus49 Alle Zahlen Vom 19 April 2025
May 08, 2025 -
 Xrp Price Prediction After A 400 Increase Where To Next
May 08, 2025
Xrp Price Prediction After A 400 Increase Where To Next
May 08, 2025 -
 Lotto 6aus49 Ziehung Vom 12 April 2025 Alle Ergebnisse
May 08, 2025
Lotto 6aus49 Ziehung Vom 12 April 2025 Alle Ergebnisse
May 08, 2025 -
 400 And Climbing Analyzing Xrps Future Price Trajectory
May 08, 2025
400 And Climbing Analyzing Xrps Future Price Trajectory
May 08, 2025
