Federal Reserve Holds Steady: Assessing Inflation And Employment Data

Table of Contents
The Federal Reserve's recent decision to hold interest rates steady has sent ripples through the financial markets. This move comes amidst a complex economic landscape, with inflation showing signs of cooling but employment remaining robust. This article delves into the key data points influencing the Fed's decision and explores the potential implications for investors and the broader economy. We'll assess the current state of inflation and employment, examining the interplay between these crucial economic indicators and the Federal Reserve's monetary policy.
Inflation Data: A Cooling Trend?
CPI and PPI Figures: A Detailed Look
The latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) data offer crucial insights into the state of inflation. Let's examine the numbers:
- CPI: The July CPI showed a year-over-year increase of X%, down from Y% in June. This deceleration is a positive sign, suggesting that inflation might be peaking. Core inflation (excluding volatile food and energy prices) also showed a decrease, indicating a broader cooling trend.
- PPI: The Producer Price Index, which measures inflation at the wholesale level, also registered a slowdown, increasing by Z% year-over-year. This suggests that inflationary pressures are easing throughout the supply chain.
These figures, while encouraging, don't tell the whole story. We need to look at the underlying trends to fully understand the direction of inflation. For example, while overall inflation is cooling, specific sectors like housing and certain energy sources continue to show persistent price increases.
Impact of Supply Chain Issues on Inflation
Global supply chain disruptions have played a significant role in fueling inflation over the past few years. While some improvements have been observed, the situation remains complex:
- Easing Bottlenecks: Port congestion and transportation delays are gradually easing, though not uniformly across all sectors.
- Geopolitical Factors: The ongoing war in Ukraine, along with other geopolitical tensions, continue to impact global commodity prices and supply chains, creating uncertainty.
- Resilient Demand: Strong consumer demand continues to put pressure on supply, contributing to higher prices for some goods and services.
Federal Reserve's Inflation Target and Current Progress
The Federal Reserve has set an inflation target of 2%. Currently, inflation remains above this target.
- Progress Towards the Target: While the recent slowdown in inflation is encouraging, the Fed is likely to maintain a cautious approach, given the persistent inflationary pressures in certain sectors.
- Future Inflation Trajectories: The path of future inflation will depend on several factors, including the evolution of global supply chains, energy prices, and wage growth. The Fed will closely monitor these factors to guide its monetary policy decisions.
Employment Data: A Strong Labor Market
The labor market continues to exhibit strength, presenting a complex challenge for the Federal Reserve in its fight against inflation.
Unemployment Rate and Labor Force Participation
The unemployment rate has remained remarkably low, currently standing at X%. This indicates a tight labor market with strong demand for workers.
- Low Unemployment: The persistently low unemployment rate suggests that the economy is operating near full employment.
- Labor Force Participation: While labor force participation has shown some improvement, it remains below pre-pandemic levels. This suggests that there is still some untapped potential within the workforce.
Wage Growth and Inflationary Pressures
Strong wage growth can contribute to inflationary pressures as businesses pass increased labor costs onto consumers.
- Wage Growth Trends: Wage growth has remained elevated, reflecting the tight labor market.
- Wage-Price Spiral Risk: The Fed is monitoring the risk of a wage-price spiral, where rising wages lead to higher prices, which in turn lead to further wage increases. Containing this risk is crucial.
Job Openings and Labor Shortages
The number of job openings remains high, indicating continued labor shortages across various sectors.
- High Job Openings: This reflects strong demand for labor, further contributing to wage pressures.
- Impact on Wages: The mismatch between available workers and job openings is driving up wages, which is feeding into inflation.
The Federal Reserve's Decision and Future Outlook
The Federal Reserve's decision to hold interest rates steady reflects a careful balancing act.
Rationale Behind Holding Interest Rates Steady
The Fed likely opted to hold rates steady to assess the impact of previous rate hikes and to closely monitor the incoming economic data.
- Assessing the Impact: The lagged effects of monetary policy mean that the full impact of previous rate hikes is yet to be fully realized.
- Data Dependency: The Fed is emphasizing its data dependency, meaning that future decisions will be guided by incoming information on inflation and employment.
Potential Future Rate Adjustments
The path of future interest rate adjustments remains uncertain. However, several scenarios are possible.
- Further Rate Hikes: If inflation remains stubbornly high, further interest rate increases are likely.
- Rate Cuts: If inflation cools significantly and economic growth slows down, the Fed might consider rate cuts to stimulate the economy.
- Holding Steady: The Fed may also choose to hold rates steady for an extended period, carefully monitoring economic data.
Implications for Investors and the Economy
The Fed's decision to hold rates steady will have far-reaching consequences.
- Stock Market: Holding rates steady might provide some relief to equity markets, but uncertainty remains.
- Bond Market: Bond yields could react depending on expectations regarding future rate adjustments.
- Housing Market: The impact on the housing market will depend on various factors, including overall economic conditions and borrowing costs.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve's decision to hold interest rates steady reflects a careful assessment of current economic conditions. While inflation shows signs of cooling, a robust employment market presents a complex challenge. The interplay between inflation and employment will continue to shape the Fed's future monetary policy decisions.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving economic landscape and the Federal Reserve's response. Continue to monitor inflation and employment data to make informed financial decisions. Regularly check back for updates on Federal Reserve actions and their impact on the economy. Understanding the Federal Reserve's policies is crucial for navigating the complexities of the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 The Impact Of Trumps Policies On Greenlands Relationship With Denmark
May 09, 2025
The Impact Of Trumps Policies On Greenlands Relationship With Denmark
May 09, 2025 -
 The Unlikely Rise From Wolves Rejection To European Footballing Success
May 09, 2025
The Unlikely Rise From Wolves Rejection To European Footballing Success
May 09, 2025 -
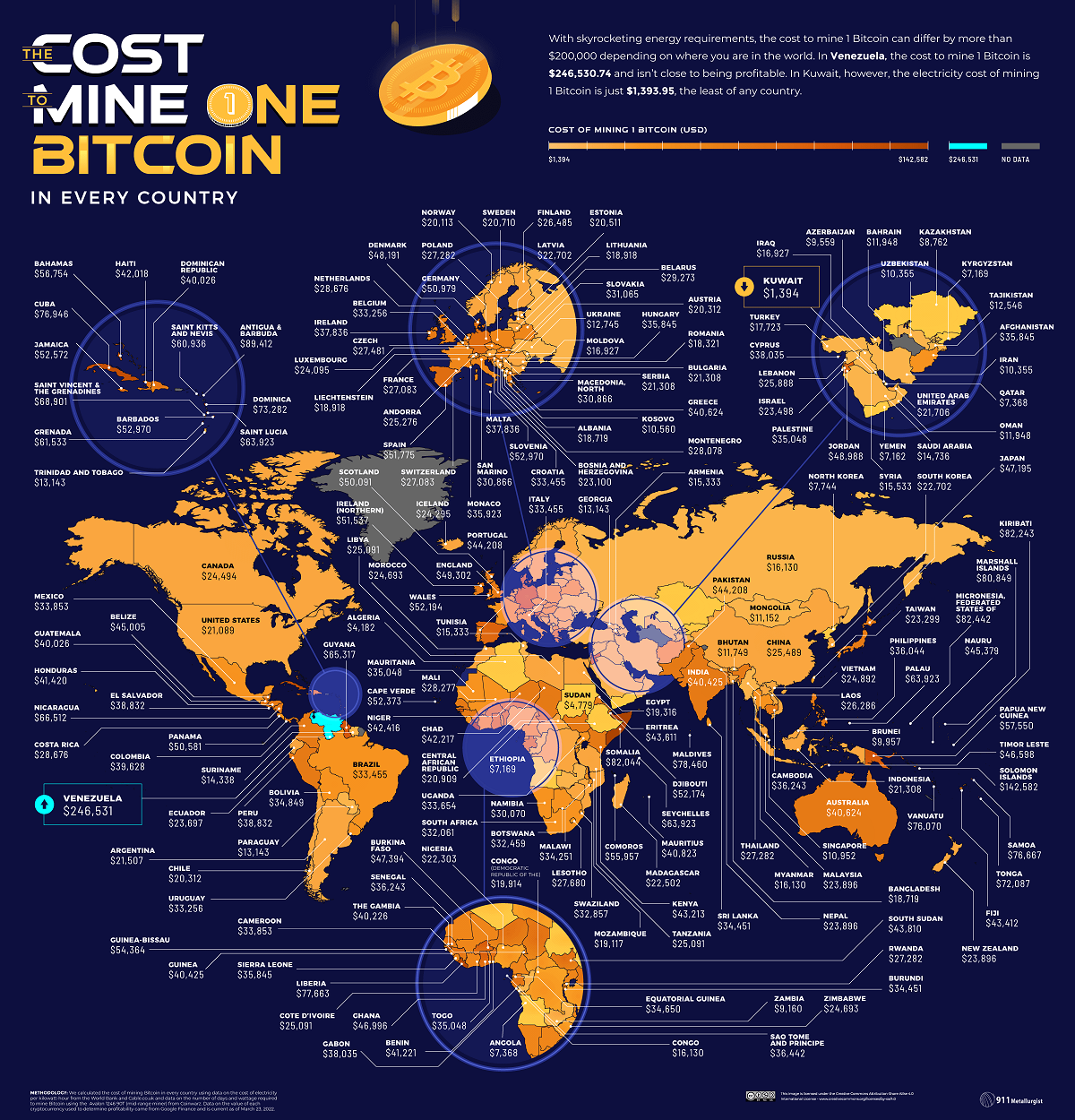 Recent Bitcoin Mining Activity Causes And Implications
May 09, 2025
Recent Bitcoin Mining Activity Causes And Implications
May 09, 2025 -
 Nyt Strands Game 374 Solutions And Hints For March 12
May 09, 2025
Nyt Strands Game 374 Solutions And Hints For March 12
May 09, 2025 -
 Formacioni Ideal I Gjysmefinaleve Te Liges Se Kampioneve Yjet E Psg Se Shkelqejne
May 09, 2025
Formacioni Ideal I Gjysmefinaleve Te Liges Se Kampioneve Yjet E Psg Se Shkelqejne
May 09, 2025
