China's Soybean Supply Crisis: Sinograin's Auction Response
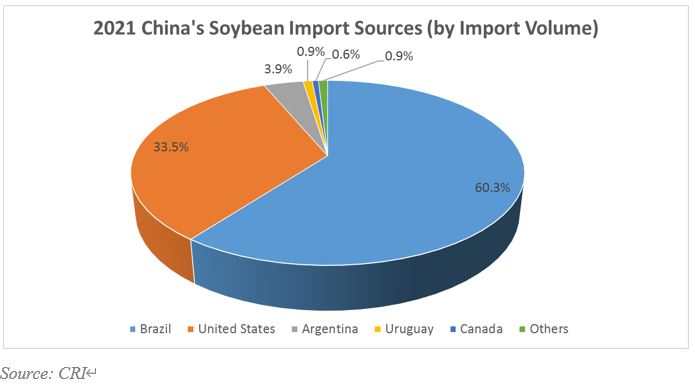
Table of Contents
The Severity of China's Soybean Supply Shortfall
China, the world's largest soybean importer, faces a severe soybean deficit driven by a confluence of factors. Poor harvests, exacerbated by climate change and extreme weather events, have significantly reduced domestic production. Simultaneously, a burgeoning demand from a growing population and expanding livestock sector has strained the supply chain. Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes have further complicated the situation, restricting access to key global soybean markets.
- Reduced Domestic Production: Years of suboptimal harvests have resulted in a consistent shortfall in domestic soybean production, forcing China to rely heavily on imports to meet its needs.
- Increased Demand: Rapid economic growth and a rising middle class have led to increased consumption of soybean-based products, driving up demand and intensifying the pressure on the supply chain.
- Price Volatility: The interplay of these factors has created significant price volatility in the soybean market, impacting consumers, livestock farmers, and the overall economy. Food inflation is a significant concern.
- Geopolitical Factors: Trade tensions and sanctions can disrupt established import channels, further exacerbating the soybean shortage and increasing reliance on less stable supply sources.
The impact ripples through the entire economy. Livestock farmers face higher feed costs, impacting meat and dairy prices. Consumers experience increased food costs, impacting their household budgets. The overall effect is a threat to food security and economic stability. Keywords like soybean deficit, China soybean imports, soybean prices, agricultural production, and food inflation help to highlight the gravity of the situation.
Sinograin's Auction Strategy as a Response Mechanism
Sinograin, a key player in China's agricultural market, has employed auction strategies as a primary mechanism to stabilize soybean markets and mitigate the crisis. Its role involves managing state reserves and releasing soybeans through a system of auctions designed to regulate supply and influence prices.
- Auction Types: Sinograin utilizes a combination of open auctions and negotiated sales to reach a wide range of buyers, including soybean processors and feed mills.
- Volume and Impact: The volume of soybeans released through these auctions directly influences market prices, attempting to curb price volatility and ensure a stable supply. The scale of these interventions is considerable.
- Target Audience: The auctions are strategically targeted at key players in the soybean processing and livestock industries, ensuring that the released soybeans reach those who need them most efficiently.
- State Reserves: The strategic release of soybeans from state reserves acts as a buffer against supply shocks, providing a safety net during times of crisis.
The use of auctions allows Sinograin to achieve a degree of transparency and market efficiency, while still maintaining control over the strategic release of state reserves. This approach aims to prevent hoarding and price gouging, benefiting both businesses and consumers. Keywords like Sinograin soybean auctions, state reserves, market intervention, price stabilization, and soybean supply management are crucial for defining this aspect of the crisis response.
Effectiveness of Sinograin's Auction Response: An Assessment
Assessing the effectiveness of Sinograin's auction response requires a nuanced examination. While the auctions have undoubtedly played a role in moderating price spikes and ensuring some degree of supply stability, challenges remain.
- Price Impact: Analysis of soybean prices before, during, and after the auctions reveals a degree of price moderation, although the impact varies depending on market conditions and the volume of soybeans released.
- Limitations: The auctions haven't entirely eliminated price volatility. Furthermore, the scale of the deficit makes complete resolution through auctions alone challenging.
- Challenges: Factors beyond Sinograin's control, such as global market dynamics and geopolitical factors, continue to influence prices and supply.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing Sinograin's response to previous crises and alternative strategies offers valuable insights into best practices and potential improvements.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of Sinograin's intervention is a mixed bag. While the auctions offer a degree of market regulation, the underlying structural issues require a broader, long-term solution. Keywords like auction effectiveness, market impact, price volatility, supply chain resilience, and policy implications are central to this critical assessment.
Future Implications and Potential Solutions for China's Soybean Dependence
Addressing China's long-term soybean dependence requires a multi-pronged approach focused on both increasing domestic production and diversifying import sources.
- Technological Advancements: Investing in research and development to improve soybean cultivation techniques and develop higher-yielding, climate-resilient varieties is crucial.
- Import Diversification: Reducing reliance on a single source of soybean imports through strategic partnerships and trade agreements with multiple countries would mitigate risks.
- Government Policies: Supportive government policies incentivizing domestic soybean production, including subsidies, tax breaks, and improved infrastructure, are essential.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration with other countries to secure stable and reliable soybean supplies is a crucial part of a comprehensive solution.
China needs to strive for greater soybean self-sufficiency to safeguard its food security. Keywords like soybean self-sufficiency, agricultural technology, import diversification, food security policy, and international cooperation highlight the pathway towards a more resilient future.
Conclusion: Understanding China's Soybean Supply Crisis and the Role of Sinograin's Auctions
China's soybean supply crisis is a complex challenge stemming from a combination of reduced domestic production, increased demand, and external factors. Sinograin's auction response, while playing a role in mitigating price volatility and ensuring some supply stability, hasn't fully addressed the underlying structural issues. Long-term solutions demand increased domestic production through technological advancements and policy support, coupled with a diversification of import sources and strengthened international collaborations. Understanding this dynamic interplay between domestic policy, global markets, and the role of Sinograin is crucial for addressing China’s soybean supply challenges and ensuring food security. Stay informed about China's evolving soybean market and Sinograin's response to future supply crises by following [link to relevant resources] or by exploring resources on food security and global agricultural markets.

Featured Posts
-
 Pokemon Tcg Pocket Celebrates 6 Months New Missions And Rayquaza Ex
May 29, 2025
Pokemon Tcg Pocket Celebrates 6 Months New Missions And Rayquaza Ex
May 29, 2025 -
 Crooks Office365 Hacking Spree Millions In Losses For Executives
May 29, 2025
Crooks Office365 Hacking Spree Millions In Losses For Executives
May 29, 2025 -
 Man Utd Transfer News Dominant Free Agent Joins The Race
May 29, 2025
Man Utd Transfer News Dominant Free Agent Joins The Race
May 29, 2025 -
 Unforeseen Success Pcc Community Markets 2024 Financial Performance
May 29, 2025
Unforeseen Success Pcc Community Markets 2024 Financial Performance
May 29, 2025 -
 Nba Mathurins 28 Points Power Pacers Past Nets In Overtime
May 29, 2025
Nba Mathurins 28 Points Power Pacers Past Nets In Overtime
May 29, 2025
