Bank Of Canada Interest Rate: April 2018 And The Trump Tariff Effect
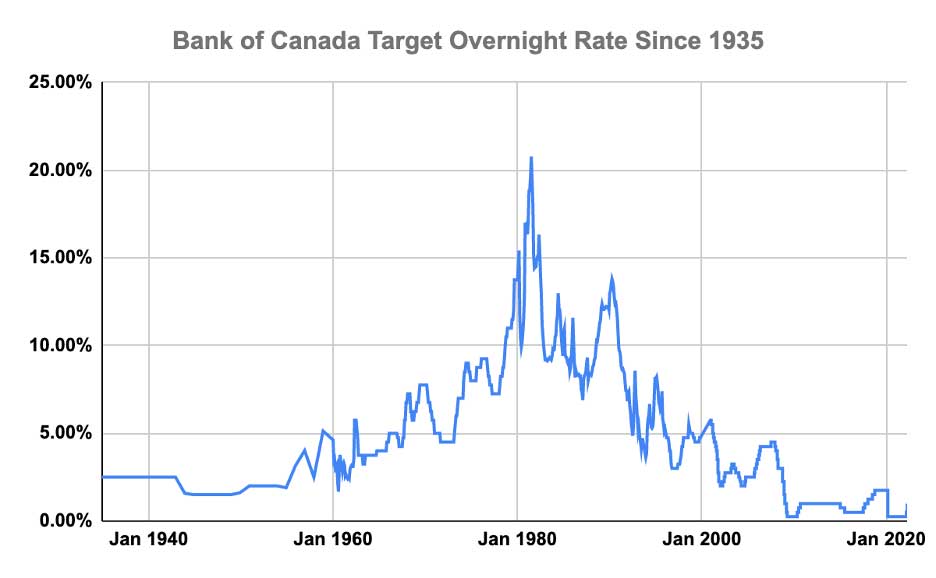
Table of Contents
The Bank of Canada's April 2018 Interest Rate Decision
In April 2018, the Bank of Canada increased its key interest rate by 0.25%, bringing the target for the overnight rate to 1.5%. This interest rate hike, a move in its monetary policy, was driven by several key economic factors. The Bank cited a strengthening Canadian economy, rising inflation, and robust employment numbers as justification for the increase. The decision reflected the Bank's mandate to maintain price stability and foster sustainable economic growth.
- Inflation: Inflation rates in April 2018 were edging closer to the Bank of Canada's target of 2%. Specific data showed a Consumer Price Index (CPI) increase of around 2.2%, signaling inflationary pressures.
- GDP Growth: GDP growth in the months leading up to April 2018 had been positive, indicating a healthy expansion of the Canadian economy. Figures showed a solid growth rate, contributing to the Bank's decision.
- Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate was relatively low in early 2018, suggesting a strong labour market and adding to the case for a rate hike. This contributed to the overall assessment of economic health.
- Inflation Target: The Bank of Canada's unwavering commitment to its 2% inflation target played a significant role in its decision-making process. The slight upward pressure on inflation prompted the adjustment.
The Impact of Trump Tariffs on the Canadian Economy
The implementation of Trump tariffs in 2018 introduced significant uncertainty into the global trading landscape, including for Canada. These tariffs, particularly those targeting key Canadian exports like lumber and aluminum, posed a substantial threat to certain sectors of the Canadian economy.
- Affected Industries: The lumber and aluminum industries were directly impacted, facing increased trade barriers and potentially reduced demand from the United States, a key trading partner.
- Trade Data: Trade data following the tariff implementation showed a negative impact on Canadian exports to the US in these affected sectors. This contraction in trade directly affected economic growth.
- Inflationary Pressures: Increased import costs, stemming from retaliatory tariffs and disruptions to global supply chains, contributed to inflationary pressures within the Canadian economy.
- Export Impact: Reduced demand for Canadian exports resulted in slower growth and potential job losses in affected industries.
The Bank of Canada's Response to Tariff Uncertainty
The Bank of Canada acknowledged the uncertainty created by the Trump tariffs in its communications. Its April 2018 decision was made with this uncertainty in mind, balancing the positive domestic economic indicators with the potential downside risks associated with the trade dispute.
- Bank of Canada Statements: Public statements from Bank officials highlighted the ongoing monitoring of the tariff situation and its potential impact on the Canadian economy. These statements emphasized the Bank's readiness to adjust monetary policy if necessary.
- Contingency Planning: While specific contingency plans weren't publicly detailed, the Bank undoubtedly factored potential negative economic fallout from escalating trade tensions into its decision-making.
- Communication Strategy: The Bank's communication strategy aimed to convey a sense of cautious optimism, acknowledging the risks but maintaining a confident outlook on the underlying strength of the Canadian economy.
Alternative Economic Scenarios and their Impact on the Interest Rate
It's crucial to consider alternative scenarios to fully understand the April 2018 interest rate decision. Had the Trump tariffs not been implemented, the Bank of Canada might have reacted differently.
- Economic Indicators Comparison: A comparison of economic indicators with and without the tariff impact would likely show a more robust growth trajectory without the trade uncertainties introduced by the tariffs.
- Other Influencing Factors: Other factors, such as oil prices (a significant component of the Canadian economy), the housing market's performance, and consumer confidence, all contributed to the overall economic picture and influenced the Bank’s decision.
- Alternative Interest Rate Scenarios: Without the added uncertainty of the tariffs, the Bank might have opted for a smaller rate increase or even maintained the status quo, depending on the assessment of these other factors.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada's April 2018 interest rate hike, while reflecting positive domestic economic indicators like strong employment and GDP growth, was also made against a backdrop of significant uncertainty caused by the newly implemented Trump tariffs. The tariffs' potential negative impact on Canadian trade and inflation played a role in the Bank’s decision-making process. Understanding the interplay between global trade policies and the Bank of Canada interest rate is crucial for navigating the complexities of the Canadian economy. Stay informed about future Bank of Canada interest rate announcements and their implications for your financial planning. Further research into the Bank of Canada's monetary policy and its response to global economic events is encouraged to better understand the Bank of Canada interest rate and its influence on the Canadian economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Riot Fest 2025 The Unmissable Lineup Featuring Green Day Blink 182 And Weird Al Yankovic
May 03, 2025
Riot Fest 2025 The Unmissable Lineup Featuring Green Day Blink 182 And Weird Al Yankovic
May 03, 2025 -
 Loyle Carner New Music Fatherhood And Glastonbury 2024
May 03, 2025
Loyle Carner New Music Fatherhood And Glastonbury 2024
May 03, 2025 -
 Fortnite Chapter 6 Season 2 Launch Delayed Extended Downtime Causes Player Frustration
May 03, 2025
Fortnite Chapter 6 Season 2 Launch Delayed Extended Downtime Causes Player Frustration
May 03, 2025 -
 Farage Reaches Agreement With Nat West Over Account Closure
May 03, 2025
Farage Reaches Agreement With Nat West Over Account Closure
May 03, 2025 -
 Unprecedented Financial Crisis Hits Bbc After 1bn Income Fall
May 03, 2025
Unprecedented Financial Crisis Hits Bbc After 1bn Income Fall
May 03, 2025
