Another Month Of Rising Grocery Prices: Outpacing Inflation
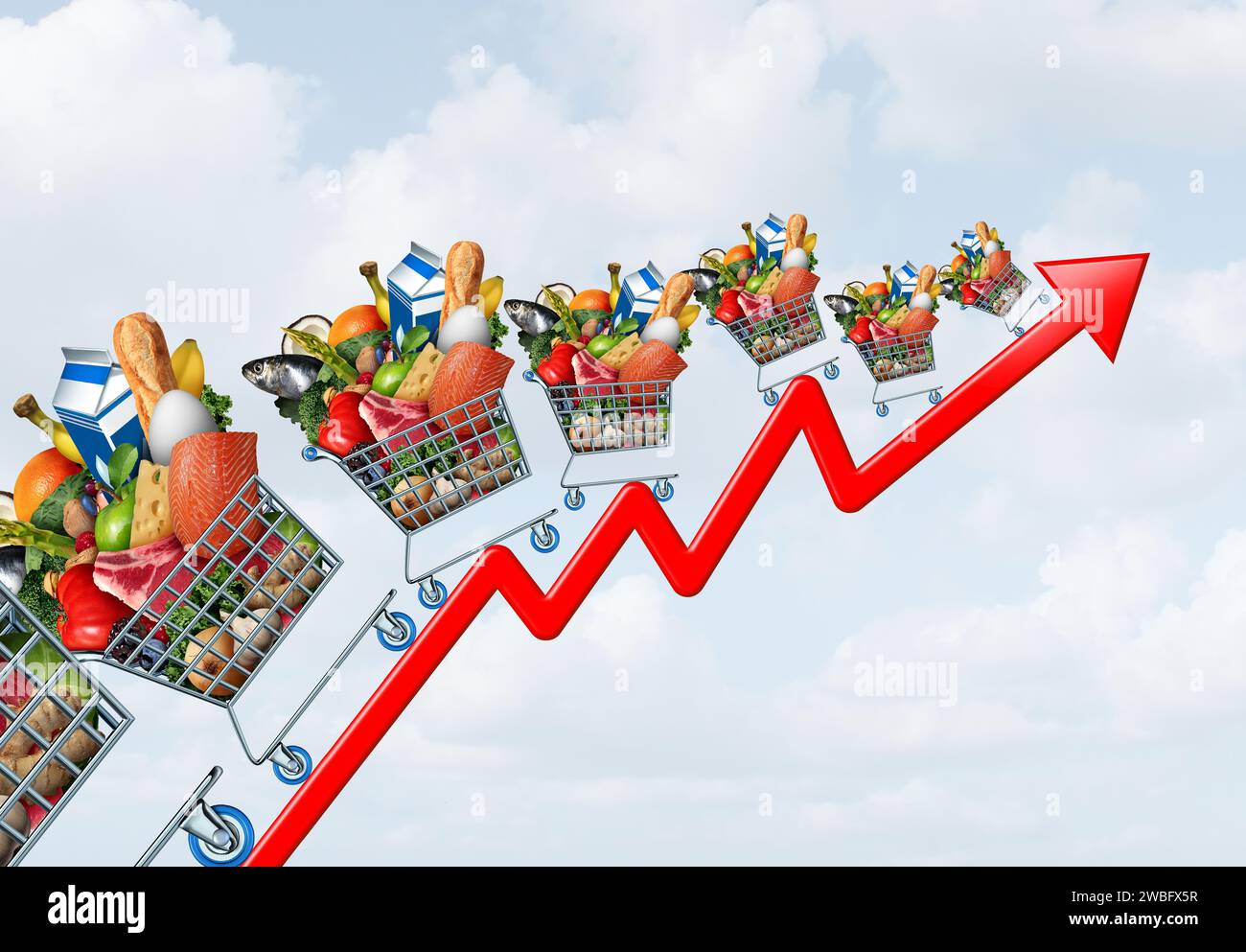

Table of Contents
H2: Key Drivers Behind Soaring Grocery Prices
The surge in grocery prices isn't a single event but a consequence of several interconnected factors. Understanding these drivers is crucial to comprehending the ongoing crisis.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: The lingering effects of the pandemic continue to plague global supply chains. Delays in transportation, port congestion, and labor shortages throughout the supply chain lead to reduced availability of goods and increased prices. This is particularly true for imported goods, impacting everything from coffee and chocolate to certain fruits and vegetables.
-
Energy Costs: The sharp rise in energy prices, including fuel and electricity, significantly impacts every stage of food production and distribution. From powering farm equipment to transporting goods across vast distances, increased energy costs directly translate to higher food prices. This effect is magnified by the reliance on fossil fuels throughout the agricultural industry.
-
Labor Shortages: Across the agricultural and food processing sectors, labor shortages are rampant. This lack of workers leads to increased labor costs, which are inevitably passed on to consumers in the form of higher grocery prices. Competition for skilled workers further exacerbates the issue.
-
Climate Change: Extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves, are increasingly disrupting agricultural production. These events decimate crops, leading to reduced yields and subsequently higher prices for affected produce. The long-term effects of climate change pose a significant threat to global food security.
-
Fertilizer Prices: The cost of fertilizers, essential for crop growth, has skyrocketed. This increase is attributed to various factors, including disruptions to global supply chains and the rising cost of natural gas, a key component in fertilizer production. Higher fertilizer costs directly translate into higher food production costs.
-
Transportation and Packaging Costs: The cost of transporting food from farms to processing plants and then to supermarkets has significantly increased due to higher fuel prices and driver shortages. Similarly, the cost of packaging materials, such as cardboard and plastic, has also risen, adding to the final price of goods.
-
Import Costs and Global Market Fluctuations: Global market fluctuations and dependence on imported goods further contribute to price instability. Changes in international trade policies and currency exchange rates can dramatically impact the domestic cost of imported food items.
H2: Which Grocery Items Are Seeing the Biggest Price Increases?
Several grocery staples have experienced particularly steep price hikes recently. Precise figures vary by region and retailer, but some consistent trends emerge:
-
Eggs: Egg prices have soared due to factors including avian flu outbreaks affecting poultry populations and rising feed costs.
-
Meat: Beef, pork, and poultry prices have all risen due to increased feed costs, labor shortages, and higher transportation expenses.
-
Dairy: Milk, cheese, and yogurt prices have also seen notable increases, reflecting the rise in feed costs for dairy cows and the increased cost of processing and distribution.
-
Bread: The price of wheat, a key ingredient in bread, has increased due to various factors including global supply chain disruptions and unfavorable weather conditions in key wheat-producing regions.
-
Produce: Fruits and vegetables, particularly those heavily reliant on fertilizer and impacted by extreme weather, have shown considerable price increases.
[Insert a chart or graph here visually representing price increases for these items].
H2: The Impact on Consumers and the Economy
The relentless rise in grocery prices has a profound impact on consumers and the broader economy:
-
Consumer Spending: Rising grocery costs force consumers to cut back on other expenses, dampening overall consumer spending and economic growth.
-
Household Budgets: Many families, particularly those with low incomes, are experiencing significant financial strain, as a larger portion of their income is now allocated to food.
-
Food Insecurity: The increased cost of food is driving a rise in food insecurity, affecting vulnerable populations and leading to potential health and social problems.
-
Economic Hardship: The cumulative effect of rising grocery prices, alongside other inflationary pressures, can lead to economic hardship for individuals and families, potentially increasing poverty rates.
H3: Strategies for Managing Rising Grocery Costs
While the overall situation is challenging, there are strategies consumers can employ to mitigate the impact of rising grocery costs:
-
Meal Planning: Carefully planning meals ahead of time helps reduce food waste and ensures you're buying only what you need.
-
Couponing and Sales: Take advantage of coupons, sales, and loyalty programs to save money on groceries.
-
Buying in Bulk (When Appropriate): Purchasing non-perishable items in bulk can offer cost savings, but be mindful of storage space and potential spoilage.
-
Reducing Food Waste: Properly storing food and using leftovers creatively can significantly reduce food waste and save money.
-
Exploring Alternative Food Sources: Consider shopping at farmers' markets or community gardens for fresher, sometimes cheaper produce, depending on location.
3. Conclusion
Another month has passed, and rising grocery prices continue to outpace overall inflation, placing an immense burden on consumers and the economy. The underlying drivers are complex and multifaceted, encompassing supply chain disruptions, energy costs, labor shortages, climate change, and global market dynamics. Specific items such as eggs, meat, dairy, and produce are experiencing the most dramatic price increases. To alleviate the financial strain, consumers can employ strategies such as meticulous meal planning, utilizing coupons, and minimizing food waste. Staying informed about the latest trends in rising grocery prices and taking proactive steps to manage your food budget effectively is crucial in navigating this challenging economic climate. Consider exploring resources available to those experiencing food insecurity in your area. Stay informed and adapt your strategies as needed to protect your family’s financial wellbeing during this period of high food inflation.

Featured Posts
-
 Ing Groups 2024 Form 20 F Filing A Comprehensive Overview
May 22, 2025
Ing Groups 2024 Form 20 F Filing A Comprehensive Overview
May 22, 2025 -
 The Evolving World Of Gumball A Teaser
May 22, 2025
The Evolving World Of Gumball A Teaser
May 22, 2025 -
 Stijgende Huizenprijzen Ondanks Economische Tegenvallers Abn Amro Analyse
May 22, 2025
Stijgende Huizenprijzen Ondanks Economische Tegenvallers Abn Amro Analyse
May 22, 2025 -
 L Incroyable Architecture Toscane De La Petite Italie De L Ouest
May 22, 2025
L Incroyable Architecture Toscane De La Petite Italie De L Ouest
May 22, 2025 -
 Stijgende Vraag Naar Occasions Impact Op Abn Amros Verkoopcijfers
May 22, 2025
Stijgende Vraag Naar Occasions Impact Op Abn Amros Verkoopcijfers
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Philadelphia Fuel Costs Consistent 6 Cent Rise Predicted
May 22, 2025
Philadelphia Fuel Costs Consistent 6 Cent Rise Predicted
May 22, 2025 -
 Gas Buddy Virginia Gasoline Prices Fall This Week
May 22, 2025
Gas Buddy Virginia Gasoline Prices Fall This Week
May 22, 2025 -
 Philly Gas Prices Continue Upward Trend Average Rises 6 Cents
May 22, 2025
Philly Gas Prices Continue Upward Trend Average Rises 6 Cents
May 22, 2025 -
 Major Route 581 Delays Box Truck Crash Investigation
May 22, 2025
Major Route 581 Delays Box Truck Crash Investigation
May 22, 2025 -
 Route 581 Traffic Stopped Following Box Truck Crash
May 22, 2025
Route 581 Traffic Stopped Following Box Truck Crash
May 22, 2025
