Addressing Investor Concerns: BofA's Take On Stretched Stock Market Valuations
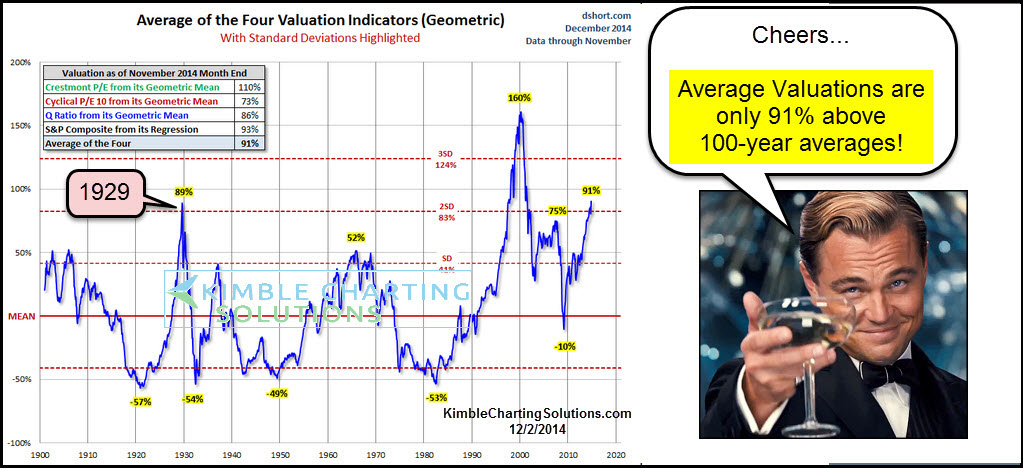
Table of Contents
BofA's Key Concerns Regarding High Valuations
BofA's assessment of current market valuations utilizes traditional metrics like price-to-earnings ratios (P/E), alongside other valuation multiples, to paint a picture of potential overvaluation. Their analysis suggests a level of concern, highlighting several key issues. The firm isn't necessarily predicting an immediate crash, but rather flagging potential risks investors should be aware of when dealing with stretched valuations.
- High P/E ratios compared to historical averages: BofA likely points to current P/E ratios exceeding historical averages by a significant margin, indicating that stocks may be priced higher than their fundamentals justify. This suggests reduced potential for future growth, at least relative to the current price.
- Potential overvaluation in specific sectors: Certain sectors, particularly those that have experienced rapid growth in recent years, might exhibit particularly high valuations. This concentration of risk within specific sectors should be cause for investor caution. Overvalued stocks in these sectors become extremely susceptible to market corrections.
- Concerns regarding interest rate hikes and their impact on valuations: Rising interest rates increase borrowing costs for companies, potentially impacting their profitability and thus, justifying a lower stock valuation. BofA likely factored in the Federal Reserve's monetary policy and its implications for future earnings.
- The role of quantitative easing and its effect on asset prices: Years of quantitative easing (QE) have injected significant liquidity into the market, potentially inflating asset prices including stocks. A reversal or slowdown of QE can lead to a reassessment of valuations.
- Specific examples cited by BofA (hypothetical): For instance, BofA might cite the technology sector as exhibiting particularly high valuations, possibly using examples of specific companies with elevated P/E multiples compared to their historical norms or industry peers.
Potential Risks Associated with Overvalued Stocks
Investing in an overvalued market carries significant risks. While market timing is notoriously difficult, understanding these risks is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Increased risk of market corrections or crashes: Overvalued markets are inherently unstable and prone to sharp corrections. A sudden shift in investor sentiment or an unexpected economic event can trigger a significant sell-off.
- Lower potential for future returns: Stocks purchased at inflated prices offer lower potential for future returns compared to those bought at more reasonable valuations. The potential for capital appreciation is inherently limited when stocks are already trading at a premium.
- The impact of inflation on real returns: Inflation erodes purchasing power, reducing the real return on investments. High valuations are particularly problematic during inflationary periods because they limit the upside while maintaining the downside.
- The importance of diversification to mitigate risk: Diversification across various asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) can help reduce the overall portfolio risk. This is especially crucial in a market environment characterized by stretched stock market valuations.
- Specific examples of past market corrections: Referencing past market corrections like the dot-com bubble or the 2008 financial crisis can effectively highlight the potential consequences of investing in significantly overvalued markets.
BofA's Recommendations for Investors
BofA's recommendations likely emphasize a cautious approach, focusing on risk management and diversification.
- Diversification across asset classes: Spreading investments across different asset classes helps mitigate risk. BofA might recommend allocating a portion of the portfolio to bonds, real estate, or other less correlated assets.
- Focus on value investing and identifying undervalued stocks: Rather than chasing high-growth stocks, investors should seek companies trading below their intrinsic value. This requires fundamental analysis to identify undervalued opportunities.
- Considering defensive investments: Defensive stocks in sectors less sensitive to economic downturns can provide stability during market corrections. Utilities, consumer staples, and healthcare are often considered defensive sectors.
- Regular portfolio rebalancing: Periodically adjusting the portfolio's asset allocation to maintain the desired risk level is essential. Rebalancing involves selling some assets that have outperformed and buying others that have underperformed.
- The importance of a long-term investment horizon: A long-term perspective helps weather short-term market fluctuations. Investors with a longer time horizon are better positioned to ride out market corrections and benefit from long-term growth.
Analyzing Sector-Specific Valuations
BofA’s analysis likely delves into specific sectors. While specific examples depend on the actual BofA report, we can hypothesize:
- Examples of overvalued sectors (e.g., technology): The technology sector, known for its rapid growth and innovation, might be identified as potentially overvalued due to high P/E ratios and elevated growth expectations.
- Examples of undervalued sectors (e.g., energy or financials): Conversely, sectors like energy or financials, depending on market conditions, might be highlighted as relatively undervalued, presenting potential opportunities for investors.
- Rationale behind BofA's sector-specific assessments: These assessments likely consider factors like industry growth prospects, earnings potential, and prevailing market sentiment for each sector.
Considering Macroeconomic Factors
Macroeconomic factors significantly influence stock valuations and investor decisions.
- The effect of inflation on corporate earnings: High inflation can squeeze corporate profit margins, leading to lower earnings and potentially impacting stock valuations.
- The impact of interest rate increases on bond yields and stock valuations: Rising interest rates can make bonds more attractive, diverting investment away from stocks and potentially impacting valuations.
- Geopolitical risks and their potential market impact: Global uncertainties can create volatility in the markets, impacting investor confidence and potentially triggering market corrections.
Conclusion
BofA's analysis highlights concerns regarding stretched stock market valuations, emphasizing the potential risks of investing in an overvalued market. Their recommendations focus on diversification, value investing, and a long-term investment approach. Understanding both valuation metrics and macroeconomic factors is crucial for navigating this complex environment. By considering these insights regarding stretched stock market valuations, investors can make more informed decisions and better manage their portfolio risk. Don't wait – take control of your investment portfolio today by addressing concerns related to stretched stock market valuations. Learn more about navigating the current market by researching BofA's full report and developing a well-diversified investment strategy.

Featured Posts
-
 A Day In Chicago History Remembering Picassos First American Exhibition
May 28, 2025
A Day In Chicago History Remembering Picassos First American Exhibition
May 28, 2025 -
 Lagardes Strategy Elevating The Euros Global Standing Through Eur Usd
May 28, 2025
Lagardes Strategy Elevating The Euros Global Standing Through Eur Usd
May 28, 2025 -
 Arsenal Eye Surprise Luis Diaz Bid
May 28, 2025
Arsenal Eye Surprise Luis Diaz Bid
May 28, 2025 -
 Alejandro Garnacho Transfer Chelseas Interest And Manchester Uniteds Stance
May 28, 2025
Alejandro Garnacho Transfer Chelseas Interest And Manchester Uniteds Stance
May 28, 2025 -
 Cek Cuaca Bandung 22 April 2024 Peringatan Hujan Siang
May 28, 2025
Cek Cuaca Bandung 22 April 2024 Peringatan Hujan Siang
May 28, 2025
