Addressing Ghana's Mental Health Crisis: The Stark Reality Of Psychiatric Care Access

Table of Contents
The Scarcity of Mental Health Professionals in Ghana
The foundation of any effective mental healthcare system is a sufficient number of trained professionals. Unfortunately, Ghana faces a severe shortage of psychiatrists, psychologists, and other mental health specialists. This shortage significantly impacts mental healthcare access in Ghana, creating long wait times and limiting the availability of vital services.
Shortage of Psychiatrists and Psychologists
The professional-to-population ratio for psychiatrists and psychologists in Ghana is drastically lower than recommended by the World Health Organization. This disparity means that millions of Ghanaians needing mental health support lack access to qualified professionals.
- Lack of training opportunities: Limited training programs and funding hinder the development of a robust pipeline of mental health professionals.
- Brain drain to other countries: Many trained professionals emigrate to countries offering better working conditions and salaries, exacerbating the shortage within Ghana.
- Unequal distribution of professionals: Most mental health professionals are concentrated in urban areas, leaving rural communities with severely limited access to care. This geographical disparity significantly impacts mental health services Ghana's rural population can access.
Inadequate Training and Supervision
Existing mental health professionals often lack adequate training and ongoing supervision. This deficiency limits their capacity to provide effective and comprehensive care, particularly for complex cases.
- Specific training gaps: There is a need for specialized training in trauma-informed care, addressing the significant impact of trauma on mental health in Ghana.
- Ongoing professional development: Continuous training and updates are crucial to ensure professionals stay abreast of the latest evidence-based treatments and techniques. Continuing professional development is essential for improving the quality of psychiatric care in Ghana.
- Supervision and mentorship: Mentorship programs and regular supervision provide vital support to professionals, improving the quality of care and fostering professional growth.
Limited Access to Mental Healthcare Facilities
Even when mental health professionals are available, accessing facilities remains a considerable hurdle for many Ghanaians. This limitation on mental healthcare access in Ghana stems from both geographical and financial barriers.
Geographic Barriers
Geographic location significantly influences access to mental healthcare services. Individuals in rural and remote areas face insurmountable challenges, impacting their access to psychiatric care in Ghana.
- Long distances to travel: The long distances to the nearest mental health facility, coupled with poor road infrastructure, make accessing care exceedingly difficult.
- Cost of transportation: Transportation expenses can pose a significant financial barrier for many individuals and families.
- Lack of awareness of available services: Many people in rural communities are unaware of the available mental health services, further hindering access.
Financial Barriers
The cost of mental healthcare in Ghana represents another formidable obstacle. Limited insurance coverage and high costs for consultations, medications, and therapies place an immense burden on individuals and families.
- High cost of medications: The price of essential psychiatric medications often prohibits access for those with limited financial means.
- Lack of affordable treatment options: A lack of affordable treatment options and limited access to public mental health funding further exacerbates the problem.
- Burden on families and individuals: The financial burden of mental healthcare can push families into poverty and lead to delayed or forgone treatment.
Stigma and Social Attitudes Towards Mental Illness in Ghana
Deep-rooted cultural beliefs and stigma surrounding mental illness significantly impede help-seeking behaviors and access to care. This stigma deeply affects mental health services Ghana can offer.
Cultural Beliefs and Misconceptions
Harmful cultural beliefs often attribute mental illness to supernatural causes, leading to stigmatization and discrimination against those affected.
- Examples of harmful cultural beliefs: Misconceptions range from attributing mental illness to witchcraft to believing it's a sign of personal weakness.
- Fear of social exclusion: The fear of being ostracized or discriminated against prevents many from seeking help, worsening their condition.
- Discrimination experienced by individuals with mental health issues: Individuals with mental health conditions often face discrimination in employment, social interactions, and healthcare settings.
Lack of Public Awareness and Education
A lack of public awareness and education about mental health perpetuates stigma and hinders help-seeking behavior.
- Need for public awareness campaigns: Comprehensive public awareness campaigns are needed to challenge negative stereotypes and promote understanding.
- Educational initiatives: Integrating mental health education into school curricula can help to destigmatize mental illness from a young age.
- Community outreach programs: Community-based programs can provide crucial information, support, and resources to individuals and families affected by mental illness.
Potential Solutions and Interventions to Address Ghana's Mental Health Crisis
Addressing Ghana's mental health crisis requires a multi-pronged approach involving increased investment, improved training, and strengthened public awareness campaigns. Improving mental healthcare access in Ghana is essential.
Increasing Investment in Mental Healthcare Infrastructure
Greater government investment is crucial to build and equip mental health facilities, particularly in underserved rural areas.
- Specific examples of infrastructure needs: This includes constructing new hospitals, clinics, and community mental health centers.
- Importance of community-based mental health services: Community-based services offer accessible and culturally sensitive care, reducing the need for long journeys to urban centers.
Training and Employing More Mental Health Professionals
Addressing the shortage of mental health professionals requires increased training opportunities and strategies to retain trained individuals within the country.
- Scholarships and grants: Offering scholarships and financial assistance can encourage more individuals to pursue careers in mental health.
- Improved working conditions: Creating better working conditions and providing adequate support for mental health professionals can increase job satisfaction and retention.
- Competitive salaries: Offering competitive salaries can attract and retain skilled professionals within Ghana's healthcare system.
Implementing Comprehensive Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns can effectively reduce stigma and encourage help-seeking behavior.
- Use of media: Utilizing various media channels, such as radio, television, and social media, can reach a wider audience.
- Community events: Organizing community events and workshops can promote dialogue and understanding.
- Educational programs in schools: Integrating mental health education into school curricula can build awareness and understanding from a young age.
Conclusion
The challenges in accessing psychiatric care in Ghana are multifaceted, encompassing a scarcity of professionals, limited access to facilities, and pervasive stigma. Addressing Ghana's mental health crisis requires a collaborative effort involving the government, healthcare professionals, community leaders, and individuals. Tackling the mental health crisis in Ghana demands a comprehensive approach that prioritizes investment in infrastructure, training, and public awareness. By improving mental healthcare access in Ghana, we can build a more supportive and inclusive society that prioritizes the mental wellbeing of all Ghanaians. We urge you to learn more about the organizations working to improve mental healthcare in Ghana and consider supporting their efforts. Together, we can make a difference in tackling this critical issue and ensuring better mental health for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Is Fortnite Down Server Status Update 34 30 Downtime And Patch Notes
May 02, 2025
Is Fortnite Down Server Status Update 34 30 Downtime And Patch Notes
May 02, 2025 -
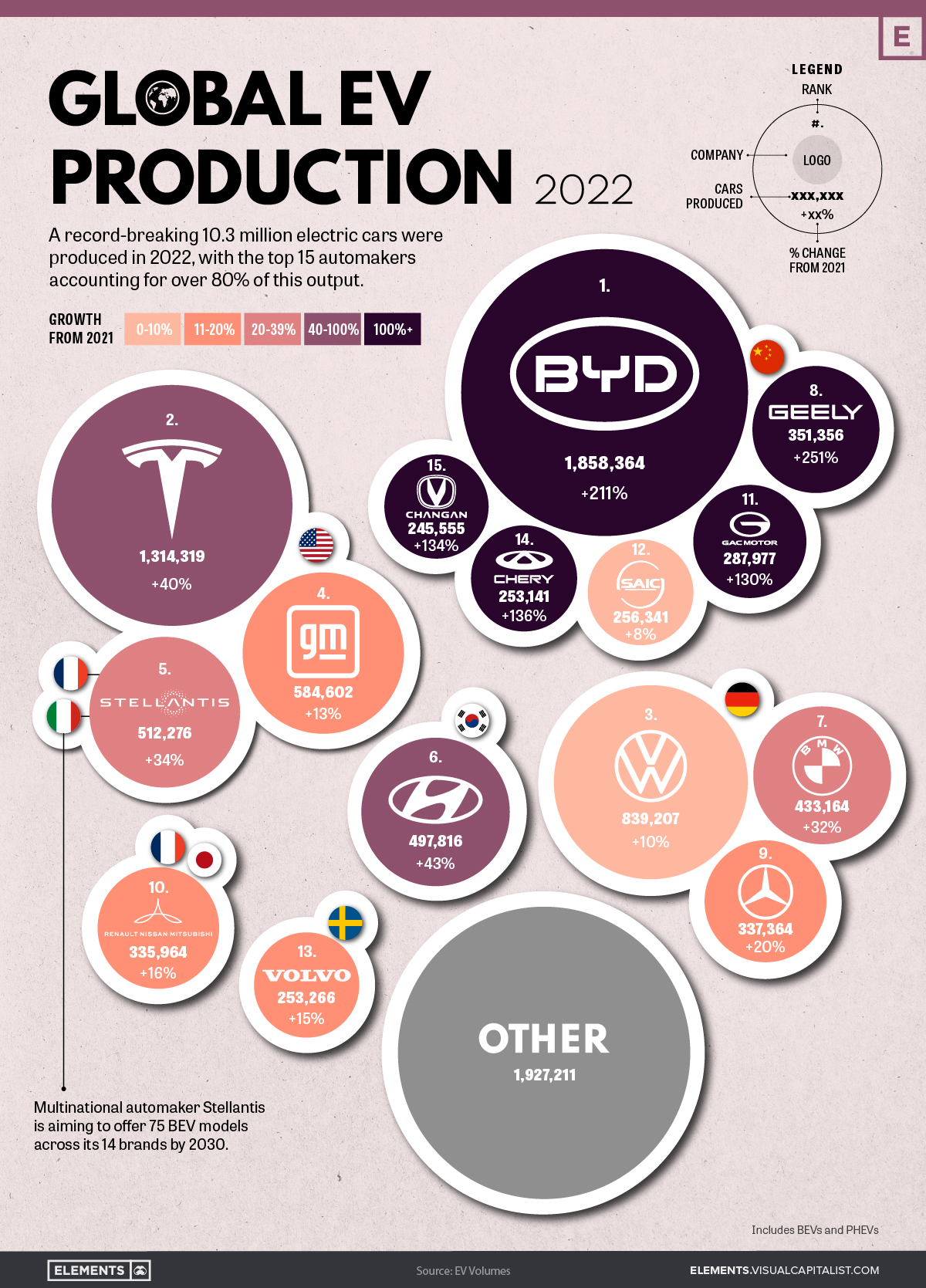 The China Market Navigating The Complexities For Automakers Like Bmw And Porsche
May 02, 2025
The China Market Navigating The Complexities For Automakers Like Bmw And Porsche
May 02, 2025 -
 Fortnites Captain America Freebies A Limited Time Event In The Item Shop
May 02, 2025
Fortnites Captain America Freebies A Limited Time Event In The Item Shop
May 02, 2025 -
 The Xrp Commodity Debate Implications For Investors And The Crypto Market
May 02, 2025
The Xrp Commodity Debate Implications For Investors And The Crypto Market
May 02, 2025 -
 300 5 6 9
May 02, 2025
300 5 6 9
May 02, 2025
