Wildfires Intensify: Global Forest Loss Hits Unprecedented Levels

Table of Contents
- The Escalating Threat of Wildfires
- Climate Change as a Primary Driver
- Human Activities Exacerbate the Problem
- Devastating Consequences of Global Forest Loss
- Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Disruption
- Economic and Social Impacts
- Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
- Strengthening Forest Management Practices
- Addressing Climate Change
- Community Engagement and Resilience
- Conclusion
The Escalating Threat of Wildfires
Climate Change as a Primary Driver
The link between climate change and the increase in wildfires is undeniable. Rising global temperatures create longer, hotter, and drier summers, leading to increased wildfire frequency and intensity. Drought conditions severely dehydrate vegetation, turning forests into tinderboxes easily ignited by lightning strikes or human carelessness.
For example, regions like Australia and California have experienced increasingly severe and widespread wildfires in recent years, directly linked to prolonged periods of drought and extreme heat exacerbated by climate change.
Key climate change impacts contributing to wildfires include:
- Longer and hotter summers: Extended periods of high temperatures dry out vegetation, creating ideal conditions for fire spread.
- Increased lightning strikes: Warmer temperatures can lead to more frequent and intense thunderstorms, increasing the risk of lightning-ignited wildfires.
- Drier vegetation: Reduced rainfall and increased evaporation due to higher temperatures leave forests vulnerable to ignition.
Human Activities Exacerbate the Problem
While climate change is a major driver, human activities significantly exacerbate the wildfire problem. Deforestation, unsustainable land management practices, and human-caused ignitions all contribute to increased wildfire risk.
Illegal logging removes natural firebreaks and creates dense, flammable underbrush. Unsustainable agricultural practices, including slash-and-burn agriculture, often lead to uncontrolled fires that spread rapidly. Careless disposal of cigarettes and unattended campfires are common causes of human-ignited wildfires.
Examples of human activities increasing wildfire risk include:
- Illegal logging: Removing trees reduces forest resilience and creates fuel for wildfires.
- Agricultural burning: Uncontrolled agricultural fires frequently escape and devastate surrounding areas.
- Improper disposal of cigarettes: A leading cause of human-caused wildfires.
Devastating Consequences of Global Forest Loss
Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Disruption
Wildfires cause catastrophic biodiversity loss. The destruction of habitats leads to the displacement and death of countless plant and animal species, pushing many towards extinction. Ecosystem services provided by forests are also severely disrupted.
The loss of forests impacts crucial processes such as carbon sequestration, water regulation, and soil erosion control, further exacerbating climate change and threatening human livelihoods.
Specific examples of endangered species threatened by wildfires and habitat loss include:
- Koala (Australia): Wildfires have devastated koala habitats, leading to significant population declines.
- Giant Panda (China): Wildfires threaten bamboo forests, the primary food source for giant pandas.
- Orangutan (Indonesia): Deforestation and wildfires linked to palm oil production are destroying orangutan habitats.
Economic and Social Impacts
The economic costs associated with wildfires are staggering, encompassing wildfire suppression efforts, property damage, loss of timber resources, and disrupted tourism. The social impacts are equally severe.
Wildfires displace communities, forcing evacuations and causing significant hardship. Smoke inhalation leads to respiratory illnesses, and the psychological toll of losing homes and livelihoods is substantial.
Examples of the economic and social costs of wildfires include:
- California (USA): Billions of dollars in property damage and suppression costs annually.
- Australia: Significant economic losses in tourism and agriculture following devastating bushfires.
- Amazon Rainforest (South America): Loss of biodiversity and vital ecosystem services impacting global climate regulation and indigenous communities.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Strengthening Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forest management is crucial for wildfire mitigation. This involves techniques such as controlled burns to reduce fuel loads, forest thinning to create firebreaks, and improved forest health monitoring.
Early warning systems using advanced technology and improved fire suppression strategies, including better training and equipment for firefighters, are essential for effective response.
Effective forest management practices for wildfire mitigation include:
- Controlled burns: Reducing fuel loads by carefully managing low-intensity fires.
- Forest thinning: Removing dense undergrowth to create firebreaks.
- Improved firebreaks: Creating barriers to prevent wildfire spread.
Addressing Climate Change
The most critical long-term strategy is addressing climate change by drastically reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This requires global cooperation, policy changes promoting renewable energy, and investment in climate-resilient infrastructure.
Individual actions, like reducing carbon footprints and supporting sustainable practices, are equally important.
Actions to reduce carbon emissions include:
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources: Solar, wind, and geothermal energy.
- Improving energy efficiency: Reducing energy consumption in buildings and transportation.
- Sustainable transportation: Promoting public transit, cycling, and walking.
Community Engagement and Resilience
Community engagement is paramount in wildfire preparedness and response. Education and awareness campaigns can empower communities to reduce their wildfire risk through preventative measures, and robust evacuation plans are vital.
Actions communities can take to improve wildfire resilience include:
- Creating defensible space around homes: Removing flammable vegetation.
- Developing community wildfire protection plans: Establishing evacuation routes and communication strategies.
- Participating in wildfire preparedness training: Learning fire safety and evacuation procedures.
Conclusion
The escalating frequency and intensity of wildfires are causing unprecedented levels of global forest loss, with devastating consequences for biodiversity, economies, and human well-being. The interconnectedness of climate change, human activities, and the wildfire threat demands immediate and comprehensive action. We must implement robust mitigation and adaptation strategies, including sustainable forest management, aggressive climate change mitigation, and enhanced community resilience. To prevent further devastating wildfires and protect our planet's forests, we must act now. Learn more about wildfire mitigation strategies and support organizations dedicated to combating forest loss and climate change.
 Ardisson Vs Baffie Une Querelle De Cons Et Machos
Ardisson Vs Baffie Une Querelle De Cons Et Machos
 I Naomi Kampel Kai Oi Eksotikes Tis Diakopes Stis Maldives Fotografies Me Mpikini
I Naomi Kampel Kai Oi Eksotikes Tis Diakopes Stis Maldives Fotografies Me Mpikini
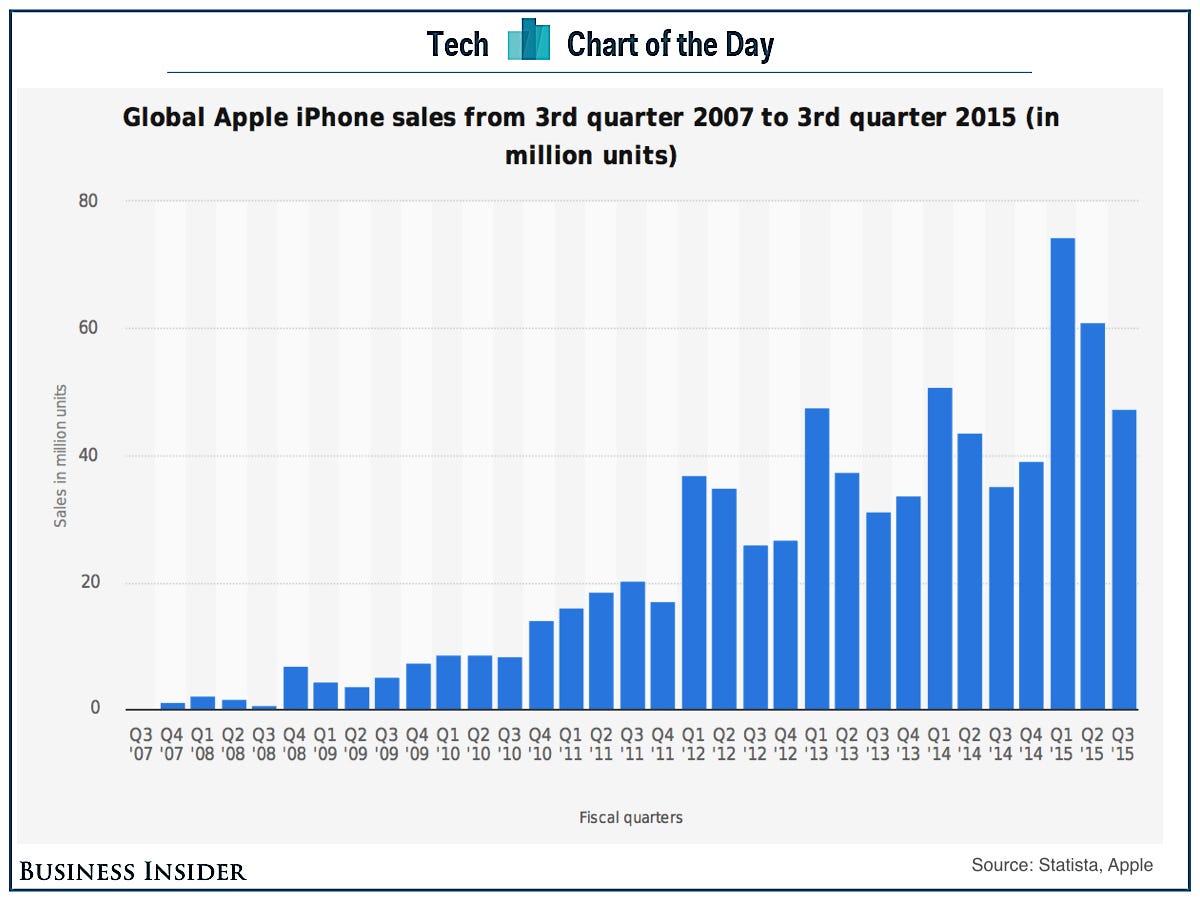 Apple Stock Q2 Earnings I Phone Sales Fuel Growth
Apple Stock Q2 Earnings I Phone Sales Fuel Growth
 Svadby Na Kharkovschine Bolee 600 Brakov Za Mesyats
Svadby Na Kharkovschine Bolee 600 Brakov Za Mesyats
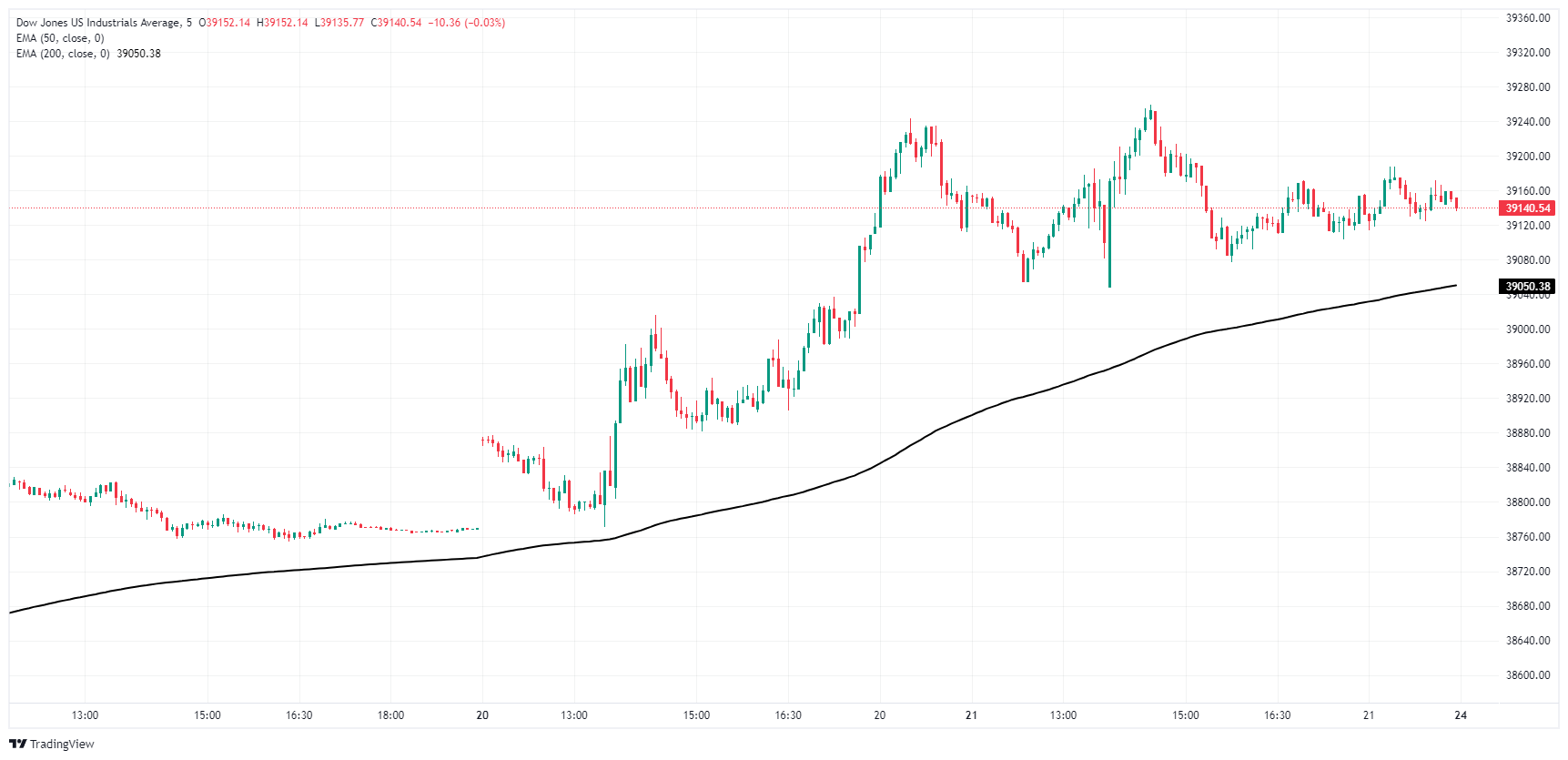 Pmi Beats Expectations Supporting Dow Joness Measured Climb
Pmi Beats Expectations Supporting Dow Joness Measured Climb
