Wildfires Drive Unprecedented Global Forest Loss: A Record Year
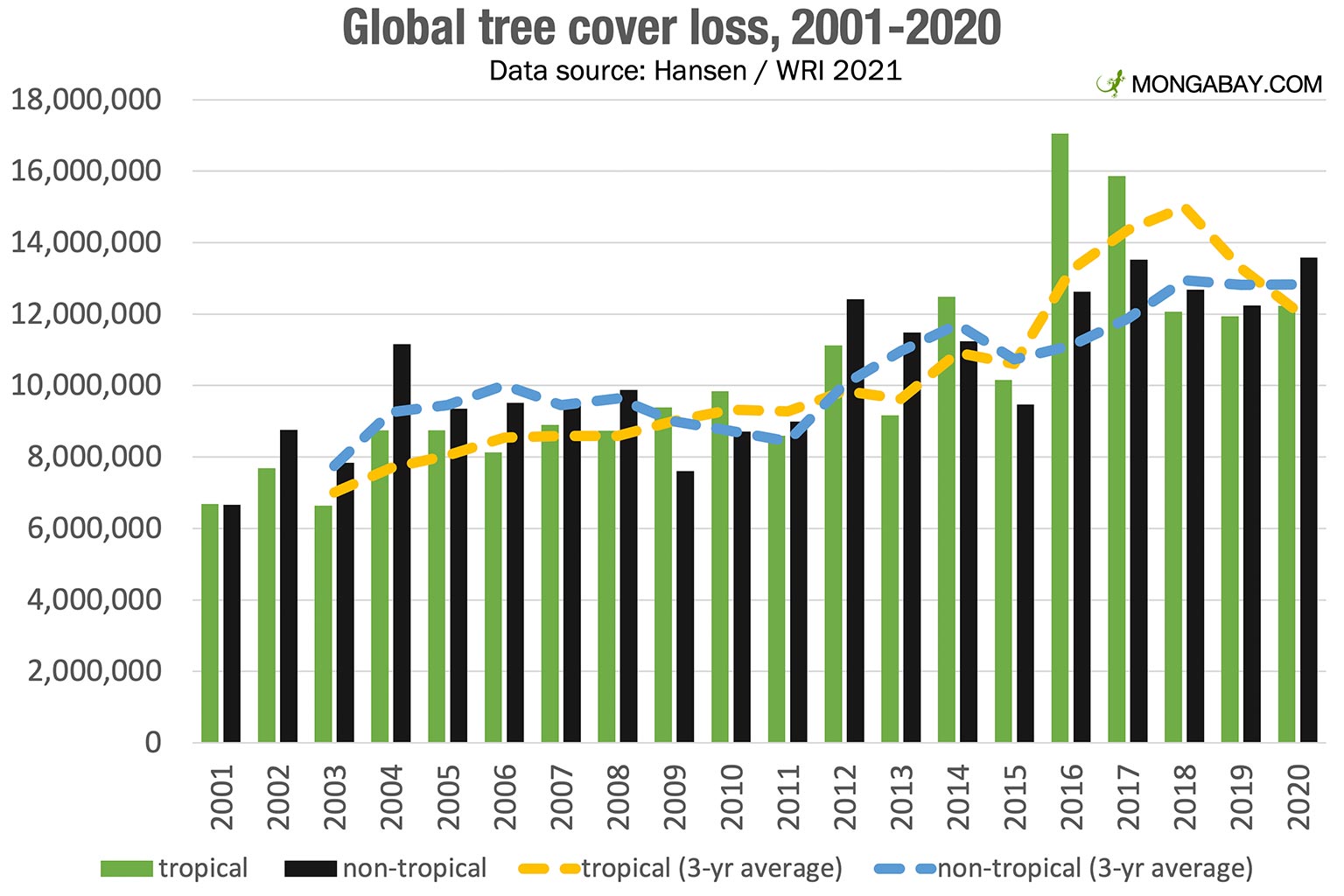
Table of Contents
H2: The Devastating Impact of 2023 Wildfires on Global Forests
H3: Geographic Distribution of Wildfires
The 2023 wildfire season scorched vast swathes of the globe, impacting regions already vulnerable to deforestation and climate change. The scale of destruction was truly unprecedented.
- Canada: Experienced its worst wildfire season on record, with millions of hectares burned and significant impacts on air quality across North America. [Cite source: e.g., Canadian government wildfire statistics]
- Australia: Continued to grapple with devastating bushfires, impacting biodiversity hotspots and releasing significant amounts of carbon emissions. [Cite source: e.g., CSIRO bushfire reports]
- Siberia: Suffered extensive wildfires across vast stretches of boreal forest, contributing to significant carbon emissions and threatening unique ecosystems. [Cite source: e.g., NASA FIRMS data]
- Amazon Rainforest: While not experiencing the scale of loss seen in previous years, the Amazon still saw significant wildfire activity fueled by deforestation and drought, threatening its vital role in global climate regulation. [Cite source: e.g., INPE deforestation data]
- California, USA: Experienced intense wildfires fueled by drought and high temperatures, leading to widespread destruction of property and ecosystems. [Cite source: e.g., Cal Fire statistics]
H3: Causes of Increased Wildfire Activity
The dramatic increase in wildfire activity is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors.
- Climate Change: Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and increased frequency of heatwaves create ideal conditions for wildfire ignition and spread. Drier vegetation acts as kindling, leading to faster and more intense fires. [Cite source: IPCC reports]
- Deforestation: The removal of trees reduces the natural barriers to wildfire spread and leaves behind dry, flammable underbrush. This is particularly problematic in already dry regions. [Cite source: FAO deforestation statistics]
- Human Negligence: Human activities, including unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, and power lines, are significant causes of wildfire ignition. [Cite source: National Park Service wildfire statistics]
- Unusual Weather Patterns: Extreme weather events, such as unusually strong winds and lightning storms, can exacerbate wildfire conditions and accelerate their spread. [Cite source: NOAA weather data]
H2: Ecological Consequences of Unprecedented Forest Loss
H3: Biodiversity Loss
The destruction of forests through wildfires has profound consequences for biodiversity.
- Habitat Loss: Wildfires destroy crucial habitats for countless plant and animal species, leading to population declines and extinctions.
- Endangered Species: Many endangered species, already vulnerable to habitat loss and climate change, are further threatened by wildfires. For example, koala populations in Australia suffered significant losses during recent bushfires. [Cite source: relevant conservation organizations]
- Ecosystem Disruption: Wildfires disrupt intricate ecological relationships, impacting the balance of ecosystems and their ability to provide crucial services. The long-term recovery of burned areas can take decades, even centuries.
H3: Carbon Emissions and Climate Change
Wildfires release vast amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
- Positive Feedback Loop: The burning of forests releases stored carbon, contributing to global warming, which in turn creates conditions more favorable for future wildfires. This creates a dangerous positive feedback loop. [Cite source: scientific studies on wildfire carbon emissions]
- Reduced Carbon Sinks: The destruction of forests reduces the planet's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, further accelerating climate change.
H2: Economic and Social Impacts of Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
H3: Economic Losses
The economic costs of wildfires are staggering.
- Property Damage: Wildfires cause extensive damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure, leading to billions of dollars in losses.
- Tourism and Recreation: The destruction of forests impacts tourism and recreation industries, resulting in significant economic losses for local communities.
- Timber Industry: Wildfires destroy valuable timber resources, impacting the forestry industry and related jobs.
H3: Social and Health Impacts
Wildfires have severe social and health consequences.
- Displacement and Evacuation: Wildfires force people to evacuate their homes, causing displacement and disruption to their lives.
- Air Quality: Smoke from wildfires significantly impacts air quality, leading to respiratory problems and other health issues.
- Mental Health: Experiencing a wildfire can have profound psychological impacts on individuals and communities, leading to stress, anxiety, and trauma.
H2: Mitigation and Prevention Strategies for Future Wildfires
H3: Forest Management Practices
Effective forest management is crucial in mitigating wildfire risks.
- Controlled Burns: Prescribed burns, conducted under carefully controlled conditions, can help reduce the accumulation of flammable material and prevent large-scale wildfires.
- Reforestation: Planting trees in deforested areas helps restore forests and reduce wildfire risks.
- Forest Thinning: Reducing the density of trees in forests can make them less susceptible to intense wildfires.
H3: Combating Climate Change
Addressing climate change is paramount to mitigating the long-term causes of increased wildfire activity.
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are essential to slowing climate change and reducing the frequency and intensity of wildfires.
- Renewable Energy Transition: Shifting to renewable energy sources is crucial in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is vital in addressing climate change and wildfire prevention on a global scale.
3. Conclusion:
The unprecedented global forest loss driven by wildfires in 2023 underscores the urgent need for collective action. The ecological, economic, and social consequences are profound and far-reaching. Combating wildfires requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing improved forest management practices, aggressive efforts to combat climate change, and international cooperation. We must all play a part in preventing global forest loss and addressing wildfire-driven forest loss. Support conservation organizations, advocate for climate action, and promote sustainable forestry practices to protect our planet's precious forests for future generations. Let's work together to mitigate the devastating impacts of wildfires and build a more resilient future.

Featured Posts
-
 Incidents Techniques Aux Studios De La Rtbf
May 26, 2025
Incidents Techniques Aux Studios De La Rtbf
May 26, 2025 -
 Otkrovennye Foto Naomi Kempbell Zakhvatyvayuschaya Fotosessiya Dlya Glyantsa
May 26, 2025
Otkrovennye Foto Naomi Kempbell Zakhvatyvayuschaya Fotosessiya Dlya Glyantsa
May 26, 2025 -
 Hells Angels Member Craig Mc Ilquham Sunday Memorial Service Details
May 26, 2025
Hells Angels Member Craig Mc Ilquham Sunday Memorial Service Details
May 26, 2025 -
 Jeu De Gestion Cycliste Rtbf Et Le Tour De France Une Collaboration Unique
May 26, 2025
Jeu De Gestion Cycliste Rtbf Et Le Tour De France Une Collaboration Unique
May 26, 2025 -
 Tadej Pogacars Tour Of Flanders Strava Data No Flag This Year
May 26, 2025
Tadej Pogacars Tour Of Flanders Strava Data No Flag This Year
May 26, 2025
