Why The Fed Is Lagging Behind On Interest Rate Cuts
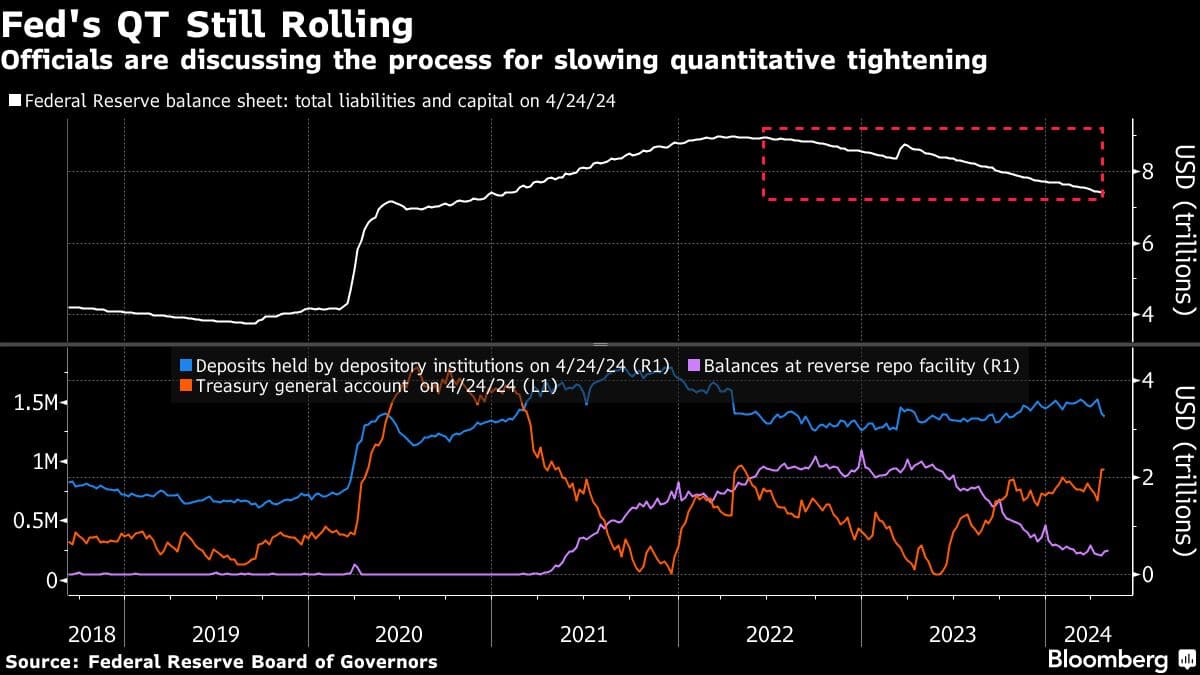
Table of Contents
Persistent Inflationary Pressures
While headline inflation has shown some signs of cooling, core inflation—a measure that excludes volatile food and energy prices—remains stubbornly high. This persistent inflationary pressure is a key reason why the Fed hesitates to initiate interest rate cuts. Several factors contribute to this stickiness. Wage growth, fueled by a tight labor market, continues to outpace productivity gains, creating upward pressure on prices. Furthermore, lingering supply chain disruptions, although easing, still contribute to elevated costs for businesses, which are passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Sticky inflation in the services sector: Inflation in services, which accounts for a significant portion of the consumer price index (CPI), remains elevated, indicating that inflationary pressures are deeply entrenched in the economy.
- Wage growth exceeding productivity gains: This wage-price spiral, where rising wages lead to higher prices, which in turn necessitate further wage increases, creates a challenging dynamic for the Fed.
- Lingering supply chain bottlenecks: Though improving, persistent supply chain issues continue to impact the availability and cost of goods, hindering the return to pre-pandemic price levels.
These factors contribute to the ongoing challenge of controlling core inflation and explain why the Fed remains cautious about prematurely cutting interest rates, despite the headline inflation numbers appearing more encouraging.
Fear of Reigniting Inflation
The Fed's cautious approach is largely driven by a deep-seated fear of prematurely cutting interest rates and reigniting inflationary pressures. The memory of the 1970s stagflationary period, characterized by high inflation and slow economic growth, serves as a stark warning. Once inflationary momentum takes hold, it proves exceedingly difficult to reverse course.
- Risk of a repeat of the 1970s stagflation: The potential for a repeat of this disastrous economic scenario is a major concern influencing the Fed's decision-making process.
- Difficulty in reversing inflationary momentum once established: The longer inflation persists, the greater the risk that it becomes embedded in inflation expectations, making it even harder to control.
- Importance of maintaining credibility in combating inflation: The Fed's credibility in managing inflation is paramount. Prematurely cutting rates could undermine this credibility and make future inflation-fighting efforts even more challenging.
The Fed prioritizes maintaining its credibility and avoiding a resurgence of inflation, even if it means accepting a slower economic recovery in the short term.
Data Dependency and Lagging Indicators
Monetary policy operates with inherent time lags. Changes in interest rates don't immediately translate into noticeable shifts in the economy. This data dependency and the prevalence of lagging indicators add significant complexity to the Fed's decision-making process. Interpreting economic data accurately and promptly is crucial but challenging.
- Employment data lags behind economic activity: Employment figures often lag behind broader economic trends, making it difficult to assess the true state of the economy in real-time.
- Inflation data can be volatile and subject to revision: Inflation data is frequently revised, making it difficult for the Fed to make precise assessments of its effectiveness.
- The Fed’s reliance on a range of lagging indicators: The Fed relies heavily on lagging indicators, which only provide a retrospective view of economic activity, hindering their ability to respond swiftly to emerging economic changes.
This lag between policy adjustments and their impact on the economy necessitates a cautious approach, further delaying potential interest rate cuts.
The Role of Quantitative Tightening (QT)
Quantitative tightening (QT), the process of reducing the Fed's balance sheet by allowing assets to mature without reinvestment, further complicates the picture. QT contributes to tighter monetary conditions, effectively raising longer-term interest rates and reducing liquidity in the market. Coordinating interest rate cuts with QT presents a significant challenge.
- QT reduces the money supply: By reducing the money supply, QT reinforces the effects of interest rate hikes, further slowing down economic activity.
- QT's impact on longer-term interest rates: QT exerts upward pressure on longer-term interest rates, impacting borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
- Challenges in managing QT alongside interest rate adjustments: The interplay between QT and interest rate adjustments requires careful calibration to avoid unintended consequences.
The complexities of managing QT simultaneously with interest rate decisions add another layer to the challenges the Fed faces in determining the appropriate timing for interest rate cuts.
Conclusion
The Fed's perceived lag in implementing interest rate cuts stems from a confluence of factors: persistent inflationary pressures, a justifiable fear of reigniting inflation, the inherent limitations of data dependency and lagging indicators, and the added complexity of quantitative tightening. The Fed faces a delicate balancing act, attempting to control inflation without triggering a significant economic downturn. Understanding the complexities behind the Fed's approach to interest rate cuts is crucial for navigating the current economic climate. Stay informed on the latest developments in monetary policy and the implications of potential Fed interest rate cuts. Continue following our analysis for insightful commentary on future Fed decisions and their impact on your investments.

Featured Posts
-
 Bondis Record Fentanyl Seizure A Major Blow To Us Drug Trade
May 09, 2025
Bondis Record Fentanyl Seizure A Major Blow To Us Drug Trade
May 09, 2025 -
 High Potential Abc Episode Air Date Whens The Next One
May 09, 2025
High Potential Abc Episode Air Date Whens The Next One
May 09, 2025 -
 Rio Ferdinands Champions League Prediction Who Wins
May 09, 2025
Rio Ferdinands Champions League Prediction Who Wins
May 09, 2025 -
 Finding The Right Leader Thailands Hunt For A New Bank Of Thailand Governor
May 09, 2025
Finding The Right Leader Thailands Hunt For A New Bank Of Thailand Governor
May 09, 2025 -
 2024 25 Nhl Season What Storylines Will Dominate The Remaining Games
May 09, 2025
2024 25 Nhl Season What Storylines Will Dominate The Remaining Games
May 09, 2025
