Why Excessive Heat Warnings Are Often Missing From Forecasts
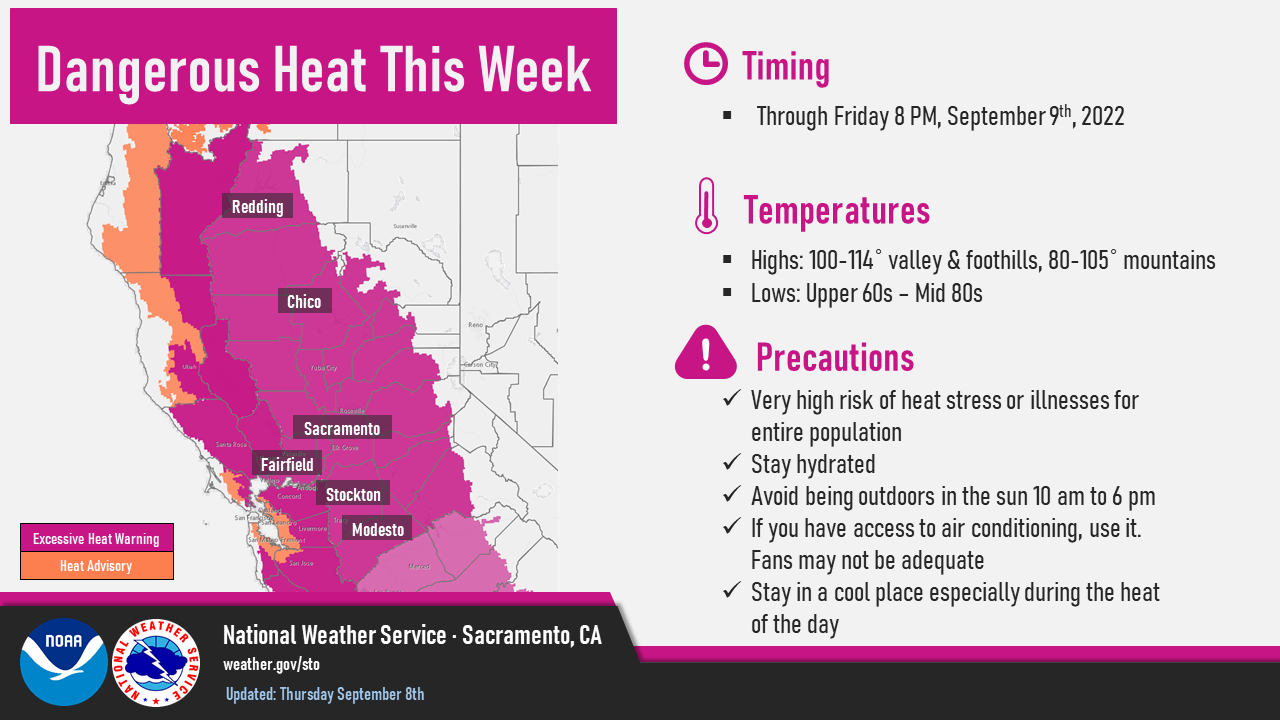
Table of Contents
Limitations of Current Weather Forecasting Models
Predicting extreme weather events, especially localized heat spikes, remains a significant challenge for meteorological agencies. Accurately forecasting Excessive Heat Warnings requires sophisticated models capable of capturing the nuances of heat distribution.
Difficulty in Predicting Localized Extreme Heat
One major hurdle is the difficulty in pinpointing hyperlocal heat spikes. Current models often lack the resolution to capture the fine-grained details necessary for accurate predictions at a neighborhood or even city block level.
- Resolution limitations: Current weather models operate on a grid system, meaning they provide average temperatures over relatively large areas. This struggles to capture the variations within those areas.
- Urban heat island effect: Urban areas, with their abundance of concrete and asphalt, absorb and retain significantly more heat than surrounding rural regions, creating "heat islands" that are difficult to model precisely. This leads to discrepancies between forecasted temperatures and the reality experienced by residents in these dense areas.
- Topographical influences: Topography plays a crucial role in heat distribution. Valleys, for instance, often trap heat, exacerbating extreme conditions and creating microclimates that are not always captured by large-scale models. This means a valley might experience significantly higher temperatures than the surrounding hills, requiring a higher level of localized prediction accuracy for effective Excessive Heat Warnings.
Uncertainties in Predicting Heat Index
The heat index, a crucial factor in assessing the true impact of heat on human health, combines temperature and humidity readings. Its complexity introduces further challenges in forecasting accuracy.
- Complex calculation: The heat index is not a simple sum; it's a complex formula requiring precise measurements of both air temperature and relative humidity. Even slight inaccuracies in either measurement can significantly affect the calculated heat index.
- Humidity prediction challenges: Variations in humidity are notoriously difficult to predict accurately, adding another layer of uncertainty to heat index forecasts. Changes in humidity can drastically impact the perceived temperature and the risk of heatstroke, making precise prediction critical for accurate Excessive Heat Warnings.
- Model limitations: Weather models often struggle to accurately predict localized humidity variations. The result is that calculated heat indexes can vary significantly from reality, potentially leading to under- or over-estimation of heat risks.
Data Gaps and Infrastructure Challenges
The lack of sufficient data and robust infrastructure further hinders the accurate prediction and timely issuance of Excessive Heat Warnings.
Sparse Weather Stations in Underserved Areas
Many areas, particularly rural and low-income communities, lack adequate weather monitoring infrastructure. This data scarcity leads to less accurate models and predictions in these vulnerable regions.
- Data scarcity: Fewer weather stations mean fewer data points for weather models to utilize, resulting in coarser resolution and less accurate predictions, particularly concerning localized heat extremes.
- Infrastructure disparity: This disparity in weather monitoring infrastructure disproportionately affects vulnerable populations who are often more susceptible to heat-related illnesses. Improved access to accurate Excessive Heat Warnings is crucial to protecting these communities.
- Investment needs: Increased investment in weather stations, particularly in underserved areas, is essential for improving the accuracy and coverage of heatwave forecasts. This includes deploying more sensors, utilizing newer technologies like remote sensing, and ensuring proper data transmission capabilities.
Insufficient Integration of Real-Time Data Sources
Leveraging real-time data from alternative sources can greatly enhance forecast accuracy. However, the integration of these sources remains inadequate.
- Crowdsourced data: Social media posts, citizen science initiatives, and mobile sensor data can provide valuable real-time insights into localized heat conditions. These supplemental data streams can fill gaps in traditional monitoring networks.
- Data integration challenges: Integrating these diverse data sources requires sophisticated algorithms and data processing techniques that are not yet widely implemented. This technology gap slows the improvement of real-time Excessive Heat Warning systems.
- Technological advancements: New technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced data analytics, offer exciting opportunities to combine traditional weather models with real-time data streams to provide more accurate and timely heatwave forecasts.
Communication and Dissemination Challenges
Even when accurate predictions are available, effective communication remains a critical challenge in ensuring that the public is adequately warned.
Effective Communication of Heat Risk
Clear and accessible communication strategies are essential for disseminating Excessive Heat Warnings effectively.
- Simple language: Using simple, understandable language is paramount to ensure that warnings reach diverse communities, including those with limited literacy or language skills.
- Multi-channel approach: Employing multiple communication channels, including social media, mobile alerts, traditional media, and community outreach programs, is essential to maximize reach and impact.
- Public awareness campaigns: Effective communication requires ongoing public awareness campaigns to educate the public about the risks of heatwaves, the signs of heatstroke, and how to stay safe during periods of extreme heat.
Thresholds and Warning Criteria
The lack of consistent thresholds for issuing heat warnings across different regions and organizations can create confusion and undermine public trust.
- Inconsistent thresholds: Variations in the temperature thresholds used to trigger heat warnings can lead to inconsistencies in public messaging and create confusion among the public.
- Establishing consistent criteria: Establishing clear, consistent, and evidence-based warning criteria is essential for public trust and effective risk communication. These criteria should be regularly reviewed and updated as climate change continues to alter extreme weather patterns.
- Standardization: Greater standardization in warning criteria across geographical areas would significantly enhance the effectiveness of Excessive Heat Warnings and improve public understanding of heat risks.
Conclusion
The absence of Excessive Heat Warnings in many forecasts is a complex issue stemming from limitations in weather modeling, data gaps, and challenges in communication. Addressing these issues requires a multi-pronged approach. This includes investing in weather infrastructure, improving data integration techniques, and developing more effective communication strategies. Understanding why these warnings are sometimes missing is critical for improving public safety and preparedness. We need to advocate for better funding and technology to improve the accuracy and accessibility of excessive heat warnings and ultimately save lives. By demanding improved weather forecasting, we can mitigate the risk and impact of future heat waves and protect vulnerable populations from the devastating effects of extreme heat.

Featured Posts
-
 Taylor Swift Ticket Sales Ticketmaster Updates Queue System
May 30, 2025
Taylor Swift Ticket Sales Ticketmaster Updates Queue System
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Ofrece Mayor Transparencia Sobre El Precio De Los Boletos
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Ofrece Mayor Transparencia Sobre El Precio De Los Boletos
May 30, 2025 -
 Amorim Garante Bruno Fernandes Continua No Manchester United
May 30, 2025
Amorim Garante Bruno Fernandes Continua No Manchester United
May 30, 2025 -
 Ndal Alastqlal Sfhat Mn Btwlat Alamt
May 30, 2025
Ndal Alastqlal Sfhat Mn Btwlat Alamt
May 30, 2025 -
 Capturing Baths Beauty A Somerset Photo Essay
May 30, 2025
Capturing Baths Beauty A Somerset Photo Essay
May 30, 2025
