US Measles Cases Reach 1,046 Amidst Indiana Outbreak End
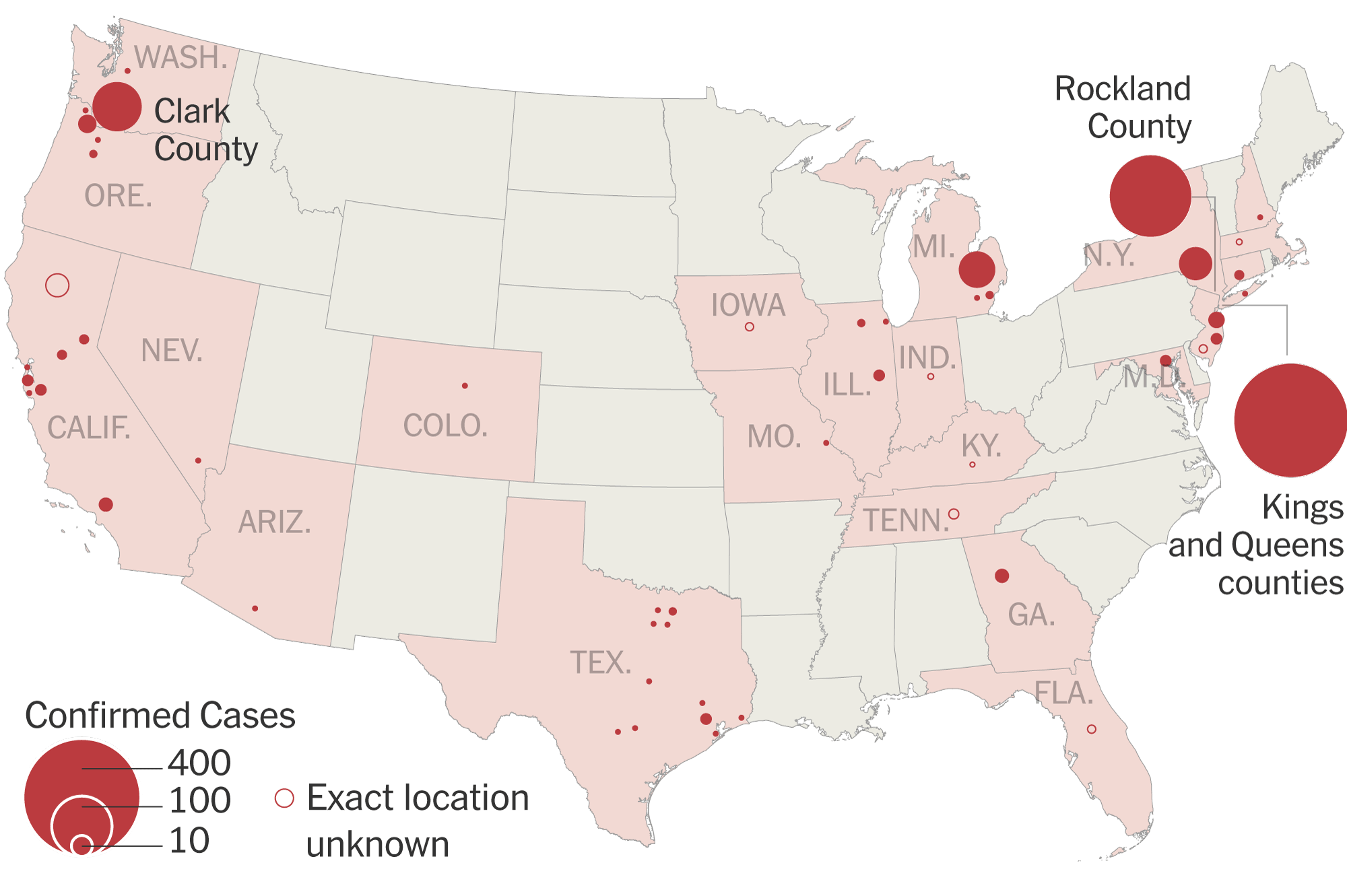
Table of Contents
The Indiana Measles Outbreak: A Case Study
The Indiana measles outbreak served as a stark reminder of the contagious nature of this preventable disease. The outbreak, spanning several months, resulted in a substantial number of confirmed cases, impacting various communities and straining the local healthcare system. Several factors contributed to its severity.
-
Specifics of the Indiana Outbreak: While the exact figures may vary slightly depending on the reporting agency, the Indiana outbreak involved a significant number of confirmed measles cases. The affected areas primarily encompassed regions with lower vaccination rates, facilitating rapid community spread. The timeline of the outbreak showed a rapid escalation followed by a gradual decline thanks to focused public health interventions.
-
Contributing Factors: Low vaccination rates within specific communities played a significant role in the outbreak's spread. This allowed the virus to easily circulate among unvaccinated individuals. Delayed or inadequate medical care for affected individuals further complicated the situation.
-
Key Data Points:
- Confirmed cases in Indiana: [Insert precise number from reliable source]
- Age demographics most affected: [Specify age groups – e.g., young children, unvaccinated adults].
- Healthcare system strain: [Describe the impact on hospitals and clinics - e.g., increased ER visits, bed shortages].
- Public health response: [Detail measures taken – e.g., contact tracing, isolation protocols, public health announcements].
National Measles Case Numbers and Trends
The 1,046 confirmed US measles cases represent a concerning increase compared to previous years. This rise is not solely attributed to the Indiana outbreak, indicating a broader trend of declining vaccination rates and increasing susceptibility to measles nationwide.
-
National Trends: [Insert data comparing the current number of US measles cases to the previous 5 years, using a graph or chart if possible]. Highlight any significant spikes or decreases.
-
Geographical Distribution: While Indiana experienced a significant outbreak, measles cases have been reported across multiple states. [List states with higher incidence rates, citing reliable sources].
-
Key Data Points:
- National measles case count (past 5 years): [Include data in a table or graph]
- States with the highest number of cases: [List states with the highest reported cases and numbers]
- Impact on different age groups: [Mention age groups most affected nationwide]
- Potential contributing factors: [Discuss factors like vaccine hesitancy, international travel, and community spread].
The Importance of Measles Vaccination
The MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles. Vaccination is not only crucial for individual protection but also for achieving herd immunity, which shields vulnerable populations who cannot be vaccinated.
-
Vaccine Efficacy: The MMR vaccine boasts a high efficacy rate, significantly reducing the risk of measles infection. [Include specific percentage from reliable source].
-
Measles Risks: Measles is a highly contagious viral illness. Severe complications can include pneumonia, encephalitis (brain inflammation), and even death. [Include statistics on complication rates if available].
-
Herd Immunity: Achieving herd immunity requires a high percentage of the population to be vaccinated. This protects those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. [Explain the herd immunity threshold and its importance].
-
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy: Addressing vaccine hesitancy requires a multifaceted approach. Providing evidence-based information, dispelling myths, and fostering open dialogue with healthcare providers are crucial. [Provide counterarguments to common vaccine myths].
-
Key Data Points:
- MMR vaccine efficacy rate: [Include precise percentage from a reputable source].
- Potential complications of measles: [List potential severe complications and their associated risks].
- Herd immunity threshold: [Specify the percentage needed for effective herd immunity].
- Common vaccine myths and their refutations: [Address and debunk common misconceptions].
Public Health Response and Prevention Strategies
Effective public health measures are essential in controlling the spread of measles and preventing future outbreaks. These strategies involve a multi-pronged approach including swift action, community involvement, and public awareness.
-
Public Health Measures: Contact tracing, isolation of infected individuals, and timely public health announcements are critical in limiting the spread. [Elaborate on the effectiveness of these measures].
-
Improving Vaccination Rates: Targeted outreach programs focused on underserved communities, educational initiatives, and collaborative efforts with community leaders are vital in increasing vaccination rates.
-
Healthcare Provider Role: Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in promoting vaccination and educating patients about its importance. [Discuss the importance of provider recommendations and patient education].
-
Key Data Points:
- Effectiveness of contact tracing: [Provide data or examples showcasing its effectiveness]
- Strategies for improving vaccination rates: [Detail various strategies and their potential impact]
- Role of healthcare providers: [Describe their role in education, vaccination, and outbreak response]
- Public health campaign effectiveness: [Analyze past campaigns and suggest improvements]
Conclusion: Understanding and Preventing Future US Measles Cases
The recent surge in US measles cases, reaching 1,046, highlights the urgent need for enhanced measles prevention efforts. The Indiana outbreak served as a stark reminder of the rapid spread of measles in communities with low vaccination rates. Effective measles vaccination is paramount for protecting individuals and achieving herd immunity. Public health strategies, including robust contact tracing, targeted outreach programs, and strong healthcare provider engagement, are crucial in controlling outbreaks and preventing future surges in US measles cases.
To safeguard your health and the health of your community, get vaccinated against measles. Talk to your healthcare provider about the MMR vaccine and ensure you are up-to-date on your vaccinations. Stay informed about public health recommendations regarding measles prevention and help us combat this preventable disease. Protecting yourself and your community against measles is a shared responsibility, and proactive measles prevention is essential to a healthier future.

Featured Posts
-
 Sagging Housing Market Home Sales At Crisis Levels Report Shows
May 30, 2025
Sagging Housing Market Home Sales At Crisis Levels Report Shows
May 30, 2025 -
 Otay Mountains Border Patrols Successful Rescue Of Two Women
May 30, 2025
Otay Mountains Border Patrols Successful Rescue Of Two Women
May 30, 2025 -
 Bruno Fernandes To Real Madrid Examining The Transfer Rumours
May 30, 2025
Bruno Fernandes To Real Madrid Examining The Transfer Rumours
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm La Guia Definitiva Para La Preparacion De Conciertos
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm La Guia Definitiva Para La Preparacion De Conciertos
May 30, 2025 -
 World Class Jazz Education At The Herbie Hancock Institute In Des Moines
May 30, 2025
World Class Jazz Education At The Herbie Hancock Institute In Des Moines
May 30, 2025
