US Army's Right-to-Repair Policy: A Deeper Dive Into Its Impact

Table of Contents
Understanding the US Army's Right-to-Repair Policy
The US Army's Right-to-Repair policy is a comprehensive strategy designed to improve the maintenance and repair of military equipment. Its primary objectives are to reduce costs, improve equipment availability, enhance operational readiness, and foster innovation within the military's maintenance infrastructure. This proactive approach shifts from a primarily replacement-focused model to one that emphasizes repair and refurbishment, maximizing the lifespan of existing assets. Key aspects of the policy include:
- Enhanced Access to Repair Manuals and Parts: The policy facilitates access to technical manuals, schematics, and parts, empowering authorized personnel to conduct repairs more effectively. This includes both internal and, in certain cases, third-party access.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: The Army invests in extensive training programs for mechanics and technicians, ensuring they possess the necessary skills to repair complex military equipment. This covers both traditional methods and emerging technologies.
- Third-Party Repair Authorization: In some instances, the policy allows for authorized third-party repair services, leveraging external expertise and capacity to address specific repair needs. This expands the pool of available resources and potentially reduces repair times.
- Standardization of Parts and Equipment: The policy promotes standardization across different equipment platforms, simplifying maintenance procedures and reducing the need for specialized parts. This also improves supply chain efficiency.
- Data Sharing and Collaboration: The policy encourages data sharing and collaboration between different units and organizations, enabling the collective learning and improvement of repair techniques and strategies. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement within the Army's maintenance ecosystem.
Benefits of the US Army's Right-to-Repair Policy
The implementation of the US Army's Right-to-Repair policy yields numerous benefits across various aspects of military operations and resource management.
- Significant Cost Savings: Repairing equipment is significantly cheaper than purchasing replacements. For example, repairing a damaged engine component can cost a fraction of the price of a complete engine replacement, resulting in substantial budget savings over time.
- Improved Equipment Availability: Faster repairs translate to reduced equipment downtime, leading to enhanced operational readiness and increased mission success rates. Units can maintain a higher state of preparedness with fewer delays caused by equipment malfunctions.
- Enhanced Logistical Efficiency: Easier access to repair information and parts streamlines the entire maintenance process, improving logistical efficiency and reducing the burden on supply chains. This reduces logistical bottlenecks and improves responsiveness to operational demands.
- Increased Sustainability: Extending the lifespan of equipment through repair significantly reduces waste and promotes environmental sustainability. This aligns with broader military efforts to minimize its environmental impact.
The overall economic and operational advantages are substantial: reduced expenditure, increased operational readiness, streamlined logistics, and a more sustainable approach to equipment management.
Challenges and Obstacles in Implementing the US Army's Right-to-Repair Policy
Despite its numerous advantages, the implementation of the US Army's Right-to-Repair policy faces several challenges:
- Technical Complexities: Repairing sophisticated military equipment requires highly specialized skills and knowledge. The technological complexity of modern systems presents a significant hurdle.
- Supply Chain Issues: Maintaining a consistent supply of parts and ensuring their timely availability can be challenging, particularly for older or obsolete equipment. Supply chain disruptions can significantly impact repair efforts.
- Training and Skill Gaps: Adequately training personnel to effectively utilize the policy's resources is crucial. Addressing skill gaps through comprehensive training programs is essential for success.
- Security Concerns: Open access to repair information raises security concerns regarding sensitive technological data and the potential for unauthorized access or modification. Robust security protocols are vital to mitigate these risks.
- Budgetary Constraints: Implementing the policy requires investment in training, tools, and infrastructure. Securing adequate funding can be a significant challenge.
These hurdles necessitate careful planning, resource allocation, and a proactive approach to overcome them.
The Future of the US Army's Right-to-Repair Policy
The US Army's Right-to-Repair policy is an evolving initiative. Future developments include:
- Policy Refinements and Expansions: Continuous evaluation and improvement of the policy will ensure its effectiveness in addressing emerging challenges.
- Technological Advancements: Integrating advanced technologies such as AI-powered diagnostics and 3D printing for parts fabrication will further enhance repair capabilities.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations with private sector companies can leverage their expertise and resources to improve repair efficiency and innovation.
- Emphasis on Predictive Maintenance: Using data analytics to predict potential equipment failures and proactively schedule maintenance will further reduce downtime and costs.
The future of the policy hinges on adapting to technological advancements, strengthening partnerships, and proactively addressing the identified challenges.
Conclusion
The US Army's Right-to-Repair policy presents a significant opportunity to enhance military readiness and optimize resource management. While challenges remain, the potential cost savings, improved equipment availability, and enhanced sustainability make it a crucial initiative. The policy's success hinges on addressing the technical complexities, supply chain issues, and security concerns involved. By investing in training, leveraging technological advancements, and fostering collaboration, the Army can fully realize the benefits of this critical policy. To learn more about the specifics of the US Army’s Right-to-Repair initiatives, visit the official Army website and stay informed about the evolution of the US Army's Right-to-Repair policy and its impact on military operations by following relevant defense news outlets.

Featured Posts
-
 New Kanye West Song Drops Daughter North West And Diddy Collaborate Despite Kim Kardashians Opposition
May 18, 2025
New Kanye West Song Drops Daughter North West And Diddy Collaborate Despite Kim Kardashians Opposition
May 18, 2025 -
 Skandalas Kanye Westas Paviesino Biancos Censori Nuotrauka
May 18, 2025
Skandalas Kanye Westas Paviesino Biancos Censori Nuotrauka
May 18, 2025 -
 Red Carpet Etiquette Why Guests Ignore The Rules
May 18, 2025
Red Carpet Etiquette Why Guests Ignore The Rules
May 18, 2025 -
 The Stunning Wardrobe Of Taylor Swifts Eras Tour Pictures And Insights
May 18, 2025
The Stunning Wardrobe Of Taylor Swifts Eras Tour Pictures And Insights
May 18, 2025 -
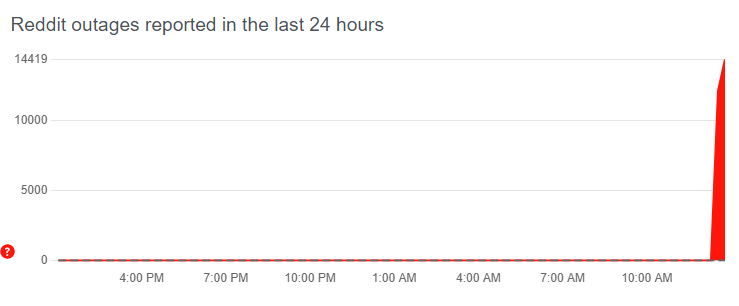 Global Reddit Outage Leaves Users Offline
May 18, 2025
Global Reddit Outage Leaves Users Offline
May 18, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analyzing Mlb Home Run Prop Bets For May 8th Featuring Kyle Schwarber
May 18, 2025
Analyzing Mlb Home Run Prop Bets For May 8th Featuring Kyle Schwarber
May 18, 2025 -
 Best Mlb Home Run Prop Bets Today May 8th Schwarber Spotlight
May 18, 2025
Best Mlb Home Run Prop Bets Today May 8th Schwarber Spotlight
May 18, 2025 -
 May 8th Mlb Home Run Prop Bets Analysis And Predictions
May 18, 2025
May 8th Mlb Home Run Prop Bets Analysis And Predictions
May 18, 2025 -
 Schwarber Home Run Prop Mlb Betting Odds And Analysis For May 8th
May 18, 2025
Schwarber Home Run Prop Mlb Betting Odds And Analysis For May 8th
May 18, 2025 -
 Tigers Riley Greenes Unprecedented Two Ninth Inning Home Runs
May 18, 2025
Tigers Riley Greenes Unprecedented Two Ninth Inning Home Runs
May 18, 2025
