Understanding The Link Between Federal Debt And Mortgage Costs
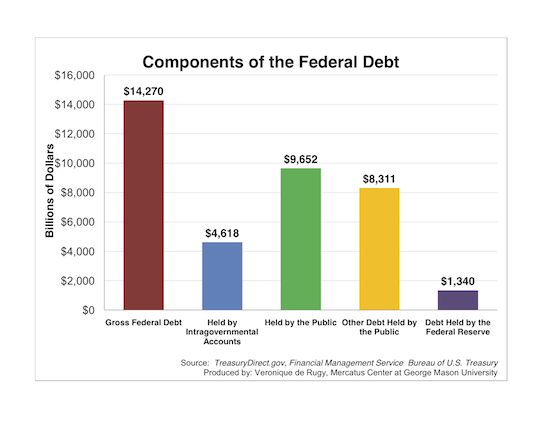
Table of Contents
How Government Borrowing Influences Interest Rates
The U.S. government frequently borrows money to fund its operations. When the federal government needs to borrow, it issues Treasury bonds. This increased borrowing directly impacts the overall supply and demand of loanable funds. Think of it like this: the more the government borrows, the more competition there is for available money.
- Increased federal debt leads to increased Treasury bond issuance: To finance its deficits, the government sells more bonds.
- Increased bond issuance competes with private sector borrowing: This increased demand for funds pushes up interest rates across the board, not just for government borrowing.
- Higher demand for funds increases interest rates across the board: Banks and other lenders, facing higher competition for capital, charge higher interest rates on all types of loans, including mortgages. This is because the cost of borrowing for them increases.
The Direct Impact on Mortgage Rates
The connection between government borrowing and your mortgage rate is quite direct. Mortgage rates are often benchmarked against Treasury yields – the return on government bonds. When Treasury yields rise due to increased government borrowing, mortgage rates typically follow suit.
- Mortgage rates are often benchmarked against Treasury yields: Lenders use these yields as a base for setting their mortgage rates.
- Higher Treasury yields translate to higher mortgage rates: This means that when the government borrows more, and bond yields increase, your mortgage rate will likely increase as well.
- Changes in Fed policy aimed at controlling inflation can impact both Treasury yields and mortgage rates: The Federal Reserve's actions to manage inflation, often through interest rate adjustments, also play a significant role. For instance, if the Fed raises rates to combat inflation, both Treasury yields and mortgage rates tend to rise.
Inflation's Role in Connecting Federal Debt and Mortgage Costs
Sustained high inflation creates a vicious cycle that impacts both federal debt and mortgage costs. High inflation necessitates increased government spending (often on social programs or to offset inflation's impact on the economy), leading to a larger national debt. To control inflation, the Federal Reserve often raises interest rates.
- High inflation necessitates increased government spending: This is due to increased demand for government support and programs.
- Increased government spending contributes to a larger national debt: This adds to the total amount the government needs to borrow.
- The Fed's efforts to control inflation through rate hikes affect mortgage rates: This tightening of monetary policy increases borrowing costs for everyone, including homeowners.
Other Factors Affecting Mortgage Rates Beyond Federal Debt
While federal debt is a significant factor, it's not the only one influencing mortgage rates. Several other crucial elements come into play:
- Credit scores: A higher credit score generally qualifies you for lower interest rates.
- Loan type: Different types of mortgages (e.g., fixed-rate, adjustable-rate, FHA, VA) carry varying interest rates.
- Down payment amount: A larger down payment often translates to a lower interest rate.
- Housing market conditions: Supply and demand in the housing market also affect mortgage rates.
Understanding these factors is crucial for a holistic view of your mortgage costs. It's important to consider the entire financial picture when evaluating how much you'll pay.
Conclusion: Understanding the Interplay of Federal Debt and Your Mortgage
The relationship between federal debt and mortgage costs is intricate, involving government borrowing, Treasury yields, the Federal Reserve's actions, and inflation. Increased federal debt generally leads to higher interest rates, directly impacting mortgage rates. However, it’s essential to remember that multiple factors influence your mortgage rate. Staying informed about economic indicators like inflation and interest rates is crucial for managing your personal finances effectively. Research current interest rates, understand your credit score, and proactively plan for potential increases in mortgage costs related to federal debt. For further learning, explore resources from the Federal Reserve and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). Understanding the dynamics of federal debt and mortgage costs empowers you to make informed decisions about your homeownership journey.

 Haalands Injury Expected Recovery Time For Man City
Haalands Injury Expected Recovery Time For Man City
 Ny Mets Schedule A Look At Mays Toughest Tests
Ny Mets Schedule A Look At Mays Toughest Tests
 Funding Opportunity Olive Branch Pickleball Court Construction
Funding Opportunity Olive Branch Pickleball Court Construction
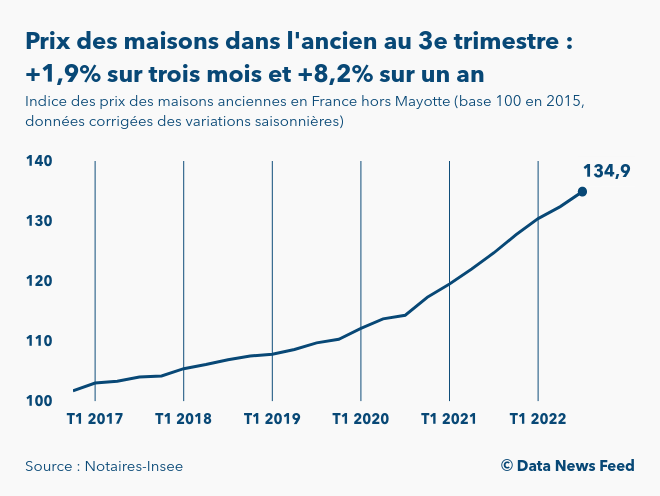 Carte Immobiliere Visualisez Les Variations Des Prix Des Maisons En France
Carte Immobiliere Visualisez Les Variations Des Prix Des Maisons En France
 Grupo Finlandes Representara A Suecia En Eurovision 2024 Cantando En Sueco
Grupo Finlandes Representara A Suecia En Eurovision 2024 Cantando En Sueco
