Understanding The 31% Decrease In BP's CEO Pay Package
Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the 31% Pay Cut
Several factors contributed to the 31% reduction in Bernard Looney's compensation. This wasn't a spontaneous decision but rather the culmination of several interconnected issues impacting BP's performance and reputation.
-
BP's Financial Performance in the Preceding Year: The company's financial results fell short of expectations, leading to pressure on executive compensation. Lower profits compared to previous years and projections directly influenced the board's decision regarding CEO pay. This underscores the link between executive remuneration and company profitability, a key element in modern corporate governance.
-
The Impact of Safety Incidents: Safety incidents, while not directly linked to Looney's performance, inevitably impact BP's overall profitability and reputation. The associated costs, including investigations, remediation, and potential legal liabilities, significantly influence the company's financial health and, consequently, executive compensation decisions. These costs represent a direct deduction from the pool available for executive bonuses and salaries.
-
The Company's Ongoing Transition to Renewable Energy Sources: BP's significant investments in renewable energy, while crucial for long-term sustainability, also come at a cost. These substantial capital expenditures impact short-term profits, affecting the overall financial picture considered when determining executive compensation. The long-term vision necessitates adjustments to short-term reward structures.
-
Pressure from Activist Investors: Activist investors played a crucial role. They voiced concerns about executive compensation levels, particularly in light of the company's financial performance and the transition to renewable energy. This shareholder pressure exerted significant influence on the board's decision-making process regarding executive pay, highlighting the power of shareholder activism in driving corporate governance reforms.
-
Formal Review of BP's Executive Compensation Structure: The board conducted a formal review of BP's executive compensation structure, taking into account all these factors. This comprehensive review led to the decision to adjust the CEO's pay package, ensuring greater alignment with company performance and shareholder expectations. Transparency in this process further enhances investor confidence and trust.
Impact on Shareholder Sentiment and Corporate Governance
The pay cut has significant implications for shareholder sentiment and corporate governance.
-
Positive Responses from Shareholders: Many shareholders concerned about executive pay disparities responded positively to the reduction. This reflects a growing demand for greater fairness and alignment between executive compensation and company performance. This positive reaction strengthens the perception of BP's commitment to responsible corporate governance.
-
Improved Perception of BP's Commitment to Corporate Governance Best Practices: The move is seen as a step towards improving BP's corporate governance profile. This action demonstrates a commitment to transparency and accountability in executive compensation practices, attracting investors prioritizing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors.
-
Alignment of Executive Compensation with the Company's Long-Term Strategic Objectives: The adjustment demonstrates an alignment of executive incentives with the company's long-term sustainability goals. This signifies a move away from short-term profit maximization and towards a more holistic approach encompassing long-term value creation and environmental responsibility.
-
Increased Engagement from ESG Investors: The pay cut could lead to increased engagement from ESG investors. These investors are increasingly focused on corporate social responsibility and ethical practices, and BP's decision is likely to be viewed favorably within this investor segment. This could lead to a renewed investor base prioritizing long-term sustainability and corporate social responsibility over short-term gains.
Wider Implications for the Energy Sector
This pay cut may set a precedent for other energy companies.
-
Comparison of BP's CEO Pay to That of Other Major Energy Companies: Analyzing BP's CEO pay in relation to its competitors reveals trends and disparities in executive compensation within the energy sector. This comparison sheds light on industry benchmarks and the influence of various factors on executive pay structures.
-
Analysis of the Broader Trend in Executive Compensation Within the Oil and Gas Industry: This single event is part of a larger movement towards greater scrutiny of executive compensation within the oil and gas industry, highlighting the impact of increased shareholder activism and evolving societal expectations.
-
The Potential Influence on Future Executive Pay Negotiations and Corporate Governance Policies Across the Sector: The BP case could significantly influence future executive pay negotiations and corporate governance policies across the broader energy sector, promoting greater transparency and accountability in executive remuneration. This sets a new standard for linking executive pay directly to company performance and long-term strategic goals.
-
The Role of Regulatory Pressure and Societal Expectations in Influencing Executive Compensation Decisions: Increasing regulatory pressure and shifting societal expectations are playing a crucial role in shaping executive compensation decisions. These external forces influence corporate governance practices and drive changes in executive pay structures, mirroring broader societal concerns regarding corporate responsibility and ethical business conduct.
Conclusion
The 31% decrease in BP's CEO pay package is a significant event with far-reaching implications. It reflects a confluence of factors – including financial performance, safety concerns, the transition to renewable energy, and shareholder pressure – highlighting the evolving dynamics of executive compensation in the energy sector. The impact on shareholder sentiment, corporate governance, and the broader industry is substantial, setting a potential precedent for greater transparency, accountability, and alignment between executive pay and long-term strategic objectives. This demonstrates the increasing influence of shareholder activism and ESG investing in shaping corporate governance practices. Understanding these complexities is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of executive compensation and its influence on company performance and investor confidence. Stay informed about the evolving landscape of BP CEO pay and its broader impact on the energy industry.

Featured Posts
-
 Sound Perimeter How Music Connects Us
May 21, 2025
Sound Perimeter How Music Connects Us
May 21, 2025 -
 Sold Out Shows Prove Vybz Kartels Continued Popularity In Brooklyn
May 21, 2025
Sold Out Shows Prove Vybz Kartels Continued Popularity In Brooklyn
May 21, 2025 -
 Irish Actor Barry Ward A Candid Interview On His Career
May 21, 2025
Irish Actor Barry Ward A Candid Interview On His Career
May 21, 2025 -
 The Impact Of The Love Monster On Childrens Literature
May 21, 2025
The Impact Of The Love Monster On Childrens Literature
May 21, 2025 -
 Love Monster Exploring The Nuances Of Unconditional Love
May 21, 2025
Love Monster Exploring The Nuances Of Unconditional Love
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
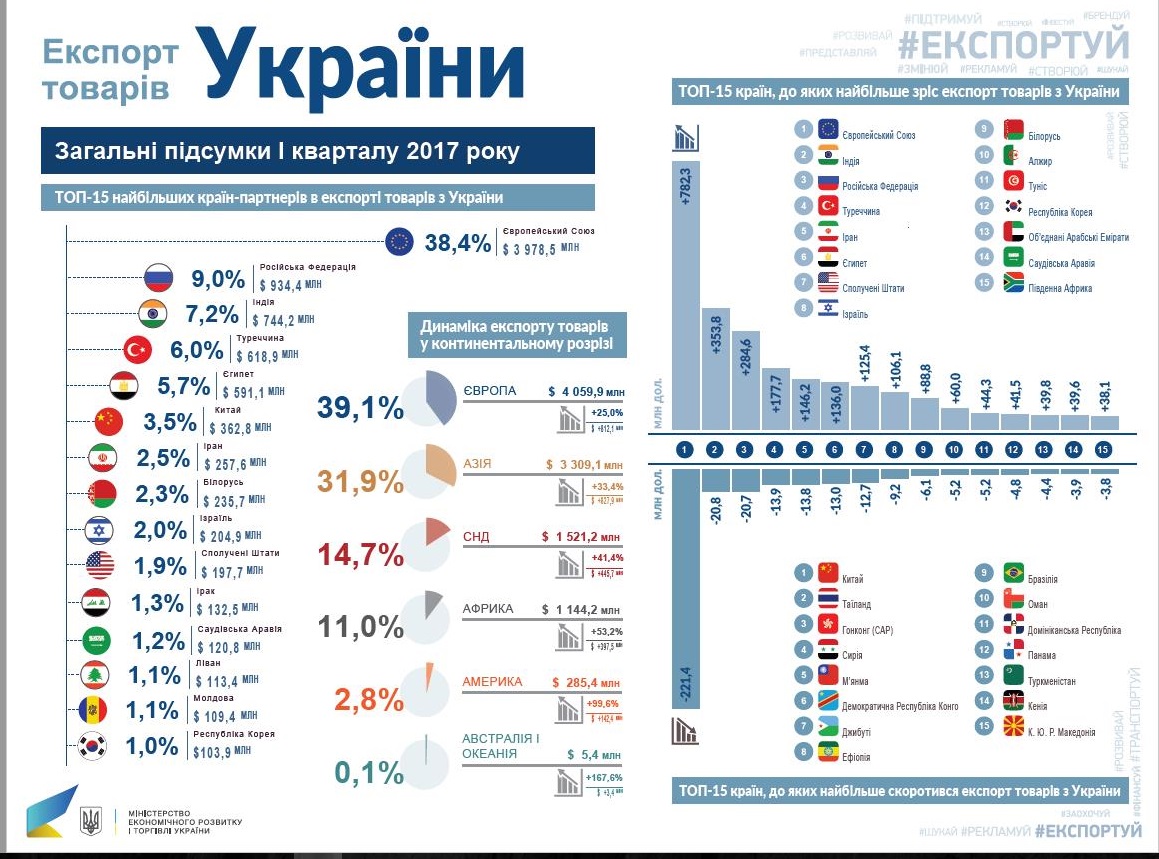 Analiz Rinku Finansovikh Poslug Ukrayini Credit Kasa Finako Ukrfinzhitlo Atlana Ta Credit Plus U 2024 Rotsi
May 21, 2025
Analiz Rinku Finansovikh Poslug Ukrayini Credit Kasa Finako Ukrfinzhitlo Atlana Ta Credit Plus U 2024 Rotsi
May 21, 2025 -
 Finansoviy Reyting Ukrayini 2024 Lideri Rinku Finansovikh Poslug
May 21, 2025
Finansoviy Reyting Ukrayini 2024 Lideri Rinku Finansovikh Poslug
May 21, 2025 -
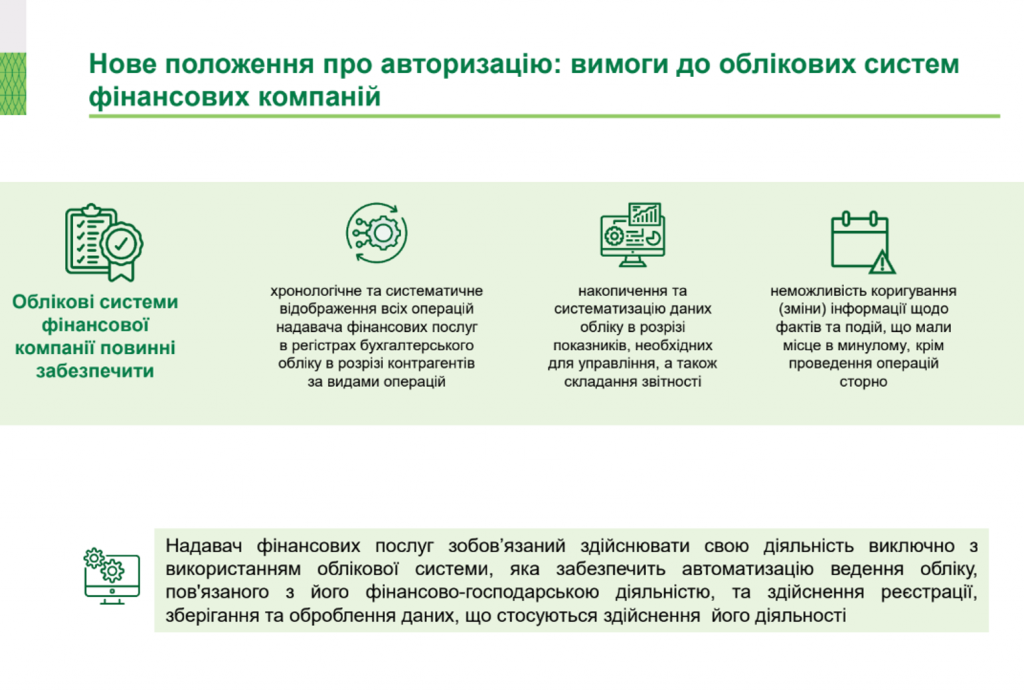 Top 5 Finansovikh Kompaniy Ukrayini Za Dokhodami U 2024 Rotsi Analiz Rinku
May 21, 2025
Top 5 Finansovikh Kompaniy Ukrayini Za Dokhodami U 2024 Rotsi Analiz Rinku
May 21, 2025 -
 Reyting Providnikh Finansovikh Kompaniy Ukrayini Za 2024 Rik Credit Kasa Finako Ukrfinzhitlo Atlana Ta Credit Plus
May 21, 2025
Reyting Providnikh Finansovikh Kompaniy Ukrayini Za 2024 Rik Credit Kasa Finako Ukrfinzhitlo Atlana Ta Credit Plus
May 21, 2025 -
 Understanding Ing Groups 2024 Performance A Look At The Form 20 F
May 21, 2025
Understanding Ing Groups 2024 Performance A Look At The Form 20 F
May 21, 2025
