Understanding Stock Market Valuations: BofA's Perspective For Investors
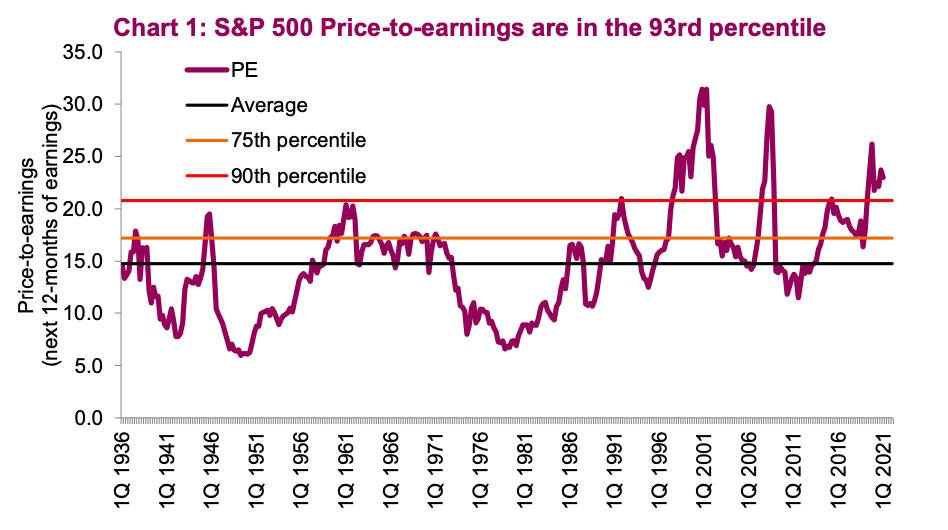
Table of Contents
Key Valuation Metrics Explained
Understanding how to value a stock is crucial for successful investing. Several key metrics provide insights into a company's worth relative to its earnings, assets, and sales. Let's delve into some of the most important ones:
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio)
The P/E ratio is perhaps the most widely used valuation metric. It represents the price an investor pays for each dollar of a company's earnings. It's calculated by dividing the market price per share by the earnings per share (EPS). For example, if a company's stock trades at $50 and its EPS is $5, its P/E ratio is 10.
- Interpreting High vs. Low P/E Ratios: A high P/E ratio suggests investors expect higher future earnings growth, while a low P/E ratio might indicate lower growth potential or undervaluation. However, comparing P/E ratios across different industries is crucial, as some sectors naturally have higher P/E ratios than others.
- Industry Comparisons: It's essential to compare a company's P/E ratio to its competitors within the same industry to get a more meaningful comparison.
- Considering Earnings Growth: The P/E ratio alone is not sufficient. Analyzing the company's earnings growth rate provides a more complete picture. A high P/E ratio can be justified if earnings are growing rapidly.
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B Ratio)
The P/B ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its book value of equity. Book value represents the net asset value of a company's assets minus its liabilities. It's particularly useful for valuing companies with significant tangible assets, such as those in the manufacturing or real estate sectors.
- Interpreting High vs. Low P/B Ratios: A high P/B ratio might suggest the market values the company's intangible assets (brand, intellectual property) highly, while a low P/B ratio could signal undervaluation or potential financial distress.
- Identifying Undervalued Companies: Investors often use the P/B ratio to screen for potentially undervalued companies, particularly in value investing strategies.
- Sector-Specific Considerations: The significance of the P/B ratio varies across sectors. It's more relevant for companies with substantial tangible assets.
Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S Ratio)
The P/S ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its revenue. It's particularly useful for valuing companies with negative earnings or those in early stages of growth, where traditional P/E ratios may not be applicable.
- Interpreting High vs. Low P/S Ratios: A high P/S ratio can indicate high growth expectations, while a low ratio might suggest undervaluation or slower growth prospects.
- Industry Comparisons: Like the P/E ratio, comparing P/S ratios across companies within the same industry provides a more effective benchmark.
- Limitations of the Metric: The P/S ratio doesn't consider profitability or expenses, so it shouldn't be used in isolation.
Dividend Yield
Dividend yield represents the annual dividend per share relative to the stock's market price. It's a crucial metric for income-focused investors.
- Factors Affecting Dividend Yield: Factors influencing dividend yield include a company's profitability, dividend payout policy, and stock price.
- Relationship Between Dividend Yield and Stock Price: Generally, a higher dividend yield implies a lower stock price (or vice versa), but this is not always the case.
- Risks Associated with High Dividend Yields: While attractive, high dividend yields can sometimes signal underlying financial difficulties or unsustainable dividend policies.
BofA's Current Market Outlook and Valuation Strategies
[This section requires referencing current BofA reports and analysis. Insert a summary of BofA's current assessment of the stock market and its valuation levels, including their recommended investment strategies based on their valuation analysis. Mention specific sectors or asset classes BofA favors or advises against, and explain why based on valuation. Include bullet points summarizing key takeaways from BofA's reports, specific examples of undervalued or overvalued sectors according to BofA, and risk factors to consider.] For example, BofA might currently favor technology stocks due to their growth potential, while being cautious on certain energy sectors due to valuation concerns. Remember to cite the source of your information.
Practical Applications for Investors: How to Use Valuation Data
Understanding valuation metrics is only half the battle. Knowing how to apply this knowledge to your investment decisions is crucial.
- Step-by-Step Guide on Analyzing a Company's Valuation: Begin by gathering financial data (income statement, balance sheet). Calculate the key metrics (P/E, P/B, P/S, dividend yield). Compare these metrics to industry averages and historical trends.
- Resources for Finding Valuation Data: Utilize reputable financial websites (e.g., Yahoo Finance, Google Finance) and company filings (10-K reports).
- Warning Signs to Watch Out For: Be wary of companies with exceptionally high P/E ratios without strong earnings growth, or extremely low P/B ratios that might indicate financial problems. Always conduct thorough due diligence before investing.
- Combining Valuation Analysis with Other Approaches: Don't rely solely on valuation metrics. Combine this analysis with fundamental (company performance, industry trends) and technical (chart patterns, trading volume) analysis for a more holistic investment approach.
- Diversification and Risk Management: Diversify your portfolio across different asset classes and sectors to reduce risk. Never invest more than you can afford to lose.
Conclusion: Mastering Stock Market Valuations with BofA's Guidance
Mastering stock market valuations is a continuous learning process. Understanding key metrics like the P/E ratio, P/B ratio, P/S ratio, and dividend yield provides a crucial foundation for informed investment decisions. By incorporating BofA's insights into your investment strategy, and by carefully considering their perspective on current market valuations and recommended strategies, you can enhance your ability to identify potential opportunities and mitigate risks. Remember to continuously learn, stay informed about market trends, and adapt your approach as needed. Further research into BofA's market analysis and the application of these valuation tools will significantly enhance your stock market valuation strategies, allowing you to make better-informed investment decisions. Leverage BofA's resources to enhance your understanding of stock market valuations, and continue your education on stock valuation analysis to become a more successful investor.

Featured Posts
-
 Peppa Pigs Real Name A Surprise For Longtime Fans
May 22, 2025
Peppa Pigs Real Name A Surprise For Longtime Fans
May 22, 2025 -
 The Allure Of Cassis Blackcurrant Flavor Profile Uses And Growing Guide
May 22, 2025
The Allure Of Cassis Blackcurrant Flavor Profile Uses And Growing Guide
May 22, 2025 -
 Understanding The Love Monster Navigating Difficult Emotions In Relationships
May 22, 2025
Understanding The Love Monster Navigating Difficult Emotions In Relationships
May 22, 2025 -
 Southern French Alps Weather Update Late Season Snow And Storms
May 22, 2025
Southern French Alps Weather Update Late Season Snow And Storms
May 22, 2025 -
 First Images Released For Echo Valley Thriller Starring Sydney Sweeney And Julianne Moore
May 22, 2025
First Images Released For Echo Valley Thriller Starring Sydney Sweeney And Julianne Moore
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Blake Lively And The Hadid Swift Feud Family Support In The Spotlight
May 22, 2025
Blake Lively And The Hadid Swift Feud Family Support In The Spotlight
May 22, 2025 -
 Blake Lively Alleged Controversies And Speculations
May 22, 2025
Blake Lively Alleged Controversies And Speculations
May 22, 2025 -
 The Blake Lively Alleged Incident A Comprehensive Overview Bored Panda
May 22, 2025
The Blake Lively Alleged Incident A Comprehensive Overview Bored Panda
May 22, 2025 -
 Blake Lively Iced Out Sisters Rally Around Amidst A List Falling Out
May 22, 2025
Blake Lively Iced Out Sisters Rally Around Amidst A List Falling Out
May 22, 2025 -
 Recent Allegations About Blake Lively What We Know Bored Panda
May 22, 2025
Recent Allegations About Blake Lively What We Know Bored Panda
May 22, 2025
