Ueda Warns Of Ripple Effects From Rising Long-Term Yields
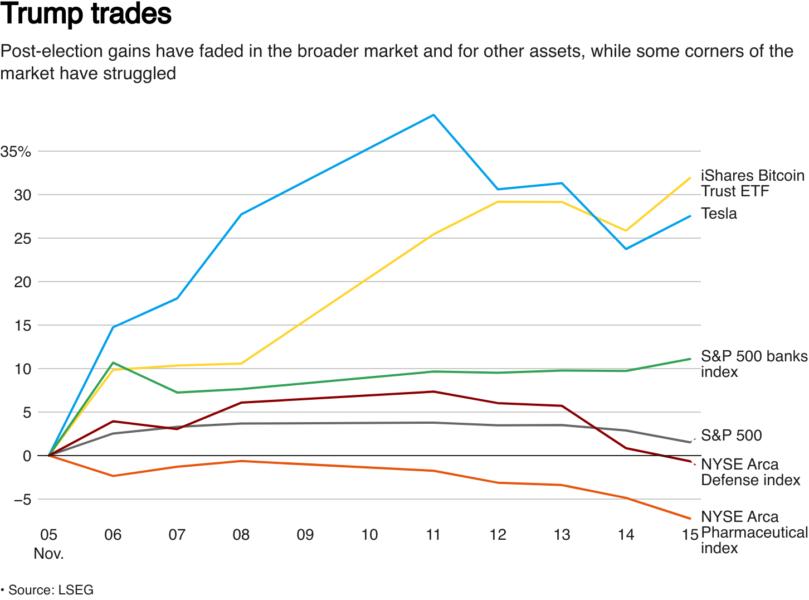
Table of Contents
Understanding the Rise in Long-Term Yields
The increase in Japanese long-term yields is a complex phenomenon with multiple contributing factors.
The Role of Inflation
The connection between rising inflation and increased long-term yields is fundamental. Higher inflation erodes the purchasing power of future interest payments on bonds, leading investors to demand higher yields as compensation for this risk.
- Impact of Inflation Expectations: Market participants closely watch inflation expectations. If they anticipate sustained inflation, they will demand higher yields on government bonds to protect their investments from purchasing power loss. The Bank of Japan's (BOJ) inflation target of 2% plays a crucial role here; exceeding this target fuels concerns about persistent inflation.
- Current Inflation Rate and Trajectory: Japan's current inflation rate, while showing signs of moderation, remains above the BOJ's target. The trajectory of inflation in the coming months will be critical in determining the future direction of long-term yields. [Insert relevant data points on current inflation rate and projections here, citing sources.]
BOJ's Monetary Policy and Yield Curve Control (YCC)
The BOJ's monetary policy, particularly its Yield Curve Control (YCC), significantly influences long-term yields. YCC aims to manage the yield curve by setting a target for 10-year government bond yields.
- Mechanics of YCC: The BOJ implements YCC by buying or selling government bonds to keep 10-year yields within its target range. This intervention aims to maintain low borrowing costs and stimulate economic activity.
- Challenges in Maintaining YCC: Rising inflation presents a significant challenge to the BOJ's ability to maintain YCC. The divergence between the BOJ's target and market forces creates pressure on the policy and potentially leads to adjustments.
- Potential for Policy Adjustments: The BOJ might be forced to adjust its YCC policy, potentially allowing long-term yields to rise further. This could have significant consequences for the Japanese economy.
Global Economic Factors
Global economic trends significantly influence Japanese long-term yields.
- Impact of Rising US Interest Rates: The increase in US interest rates makes US Treasury bonds more attractive to global investors, potentially drawing capital away from Japanese bonds and pushing up Japanese yields.
- Effect of Global Capital Flows: Global capital flows play a crucial role. Changes in investor sentiment and risk appetite can trigger shifts in capital allocation, impacting Japanese bond markets.
- Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical events and uncertainties can also influence investor behavior and contribute to fluctuations in long-term yields.
Potential Ripple Effects on the Japanese Economy
The rise in long-term yields carries significant implications for various sectors of the Japanese economy.
Impact on Investment and Business Spending
Higher long-term yields translate into increased borrowing costs for businesses.
- Increased Cost of Borrowing: Companies face higher interest expenses on loans, reducing their profitability and potentially dampening investment plans.
- Reduced Capital Expenditure: Businesses might postpone or scale back capital expenditures due to increased financing costs, hindering economic growth.
- Impact on Corporate Profits and Economic Expansion: Reduced investment and lower corporate profits can lead to slower economic expansion.
Effects on the Housing Market
Rising long-term yields directly affect mortgage rates, impacting the housing market.
- Effect on Housing Affordability: Higher mortgage rates reduce housing affordability, potentially slowing down demand and house price appreciation.
- Potential Slowdown in the Real Estate Market: The combination of higher borrowing costs and reduced affordability could lead to a slowdown in the real estate market.
- Impact on Construction and Related Industries: A decline in the housing market can negatively impact construction and related industries.
Fiscal Implications for the Government
Increased long-term yields lead to higher borrowing costs for the Japanese government.
- Increased Cost of Financing Government Debt: The government will have to pay more to service its national debt, straining public finances.
- Potential for Fiscal Strain and Policy Adjustments: This could necessitate fiscal policy adjustments, potentially impacting social welfare programs or other government initiatives.
- Implications for Social Welfare Programs: Fiscal strain might force difficult choices regarding the allocation of resources for social welfare programs.
International Implications and Global Market Response
The rise in Japanese long-term yields has implications beyond Japan's borders.
Impact on the Yen
Changes in interest rates significantly influence currency exchange rates.
- Relationship Between Interest Rates and Currency Exchange Rates: Higher yields in Japan can attract foreign investment, potentially strengthening the Yen. However, other factors can also play a role.
- Potential Capital Flight and Its Consequences: Conversely, a rapid rise in yields could lead to capital flight if investors seek higher returns elsewhere, weakening the Yen.
- Effects on Japanese Exports and Imports: Yen fluctuations can affect the competitiveness of Japanese exports and imports.
Global Market Volatility
The situation in Japan can impact global financial markets.
- Potential for Contagion Effects in Other Asian Economies: The rise in long-term yields in Japan could trigger contagion effects in other Asian economies with similar economic structures.
- Impact on Global Investor Sentiment: The situation can influence global investor sentiment and risk appetite, potentially impacting other markets.
- Potential for Increased Market Volatility: Uncertainty surrounding the BOJ's response and the future trajectory of long-term yields can increase market volatility globally.
Conclusion
Governor Ueda's warning about the ripple effects from rising long-term yields underscores a significant challenge for the Japanese economy. The interplay of inflation, the BOJ's monetary policy, and global economic conditions has created a complex situation with potentially far-reaching consequences. Understanding the potential impacts on investment, the housing market, government finances, and the Yen is crucial for both investors and policymakers. Continued monitoring of long-term yields and the BOJ's response to this evolving situation is vital to navigating the economic landscape. Staying informed about future developments regarding Ueda's warnings on rising long-term yields is essential for making sound financial decisions. Understanding the implications of rising long-term yields is paramount for navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Cuaca Jawa Tengah 23 April Waspada Hujan Deras
May 29, 2025
Cuaca Jawa Tengah 23 April Waspada Hujan Deras
May 29, 2025 -
 Stranger Things Season 5 Characters We Likely Wont See Again
May 29, 2025
Stranger Things Season 5 Characters We Likely Wont See Again
May 29, 2025 -
 Trumps Gront Lys Stalgigant Skifter Haender
May 29, 2025
Trumps Gront Lys Stalgigant Skifter Haender
May 29, 2025 -
 Live Nations Venue Dominance Doj Alleges Anti Competitive Practices
May 29, 2025
Live Nations Venue Dominance Doj Alleges Anti Competitive Practices
May 29, 2025 -
 The Coco 2 Announcement Concerns And Considerations For Pixars Future
May 29, 2025
The Coco 2 Announcement Concerns And Considerations For Pixars Future
May 29, 2025
