Toxic Chemicals From Ohio Train Derailment: Lingering Contamination In Buildings
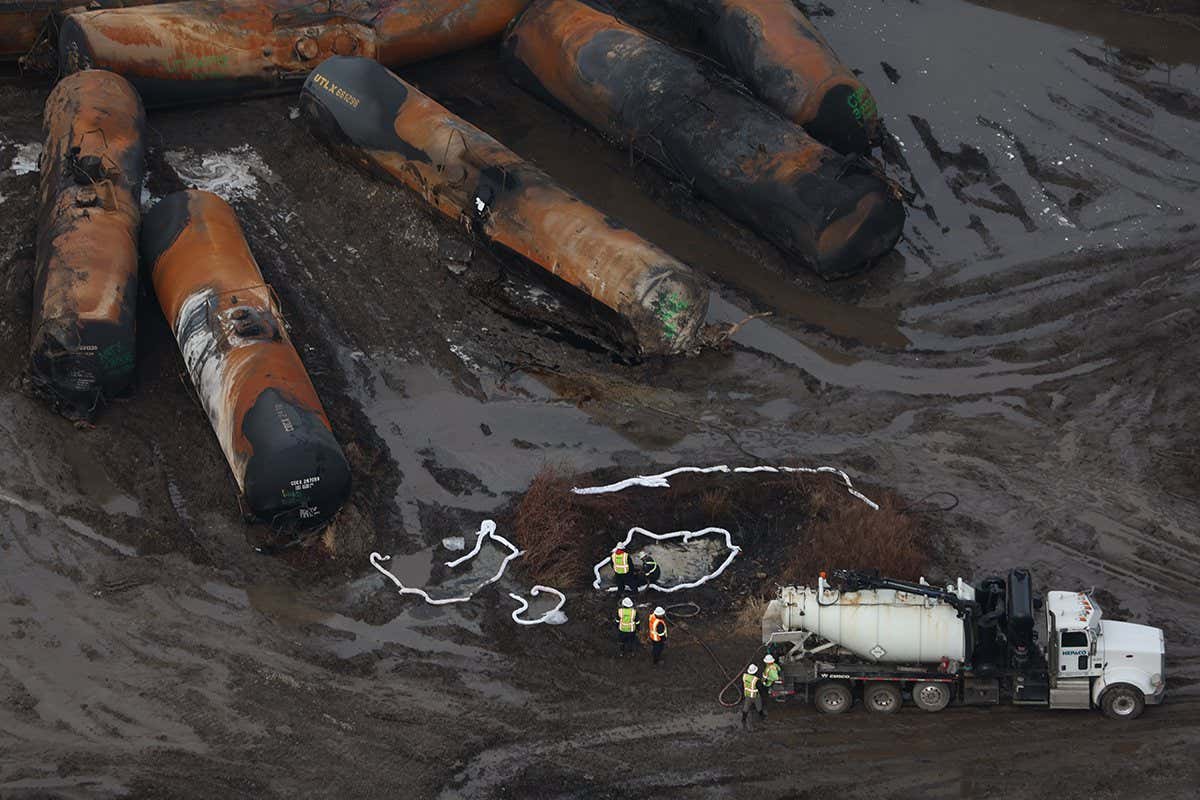

Table of Contents
Pathways of Contamination into Buildings
The toxic chemicals released from the derailment found their way into buildings through various pathways, leading to persistent contamination and potential long-term exposure.
Airborne Dispersion
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), like vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate, readily evaporate and disperse through the air. These chemicals easily infiltrated buildings via:
- Ventilation systems: HVAC systems can inadvertently draw contaminated air directly into buildings.
- Open windows and doors: Even briefly opened windows provided pathways for contaminated air to enter.
- Porous building materials: Chemicals can permeate through less-dense materials like wood, drywall, and certain types of insulation.
Wind direction and weather patterns significantly impacted the spread of contamination. Strong winds carried the plume further, while prevailing weather conditions influenced the deposition of chemicals onto building surfaces.
Surface Contamination
Chemicals also settled on both interior and exterior building surfaces, resulting in persistent contamination. This poses a risk through:
- Direct contact: Touching contaminated surfaces can transfer chemicals to the skin.
- Dust inhalation: Chemicals adhering to surfaces can become airborne as dust particles, leading to inhalation exposure.
Surfaces likely to retain contaminants include:
- Exterior siding
- Carpets and rugs
- Porous flooring materials
- Window sills
The persistence of different chemicals varies greatly. Some VOCs may evaporate relatively quickly, while others, such as heavier compounds, may remain on surfaces for extended periods.
Groundwater Contamination
The derailment also presents a risk of groundwater contamination. Leaking chemicals can infiltrate the soil and reach the water table, potentially contaminating wells and seeping into building foundations and basements.
- Leaching: Rainwater can wash chemicals from the soil into the groundwater.
- Long-term pollution: Groundwater contamination can persist for many years, posing a continuous threat.
- Spread beyond the immediate vicinity: Groundwater flows can carry contaminants considerable distances from the derailment site.
Health Risks Associated with Lingering Contamination
Exposure to the lingering toxic chemicals from the Ohio train derailment presents various health risks, with potential long-term consequences.
Respiratory Issues
Inhaling contaminated air can cause a range of respiratory problems:
- Acute bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes.
- Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs.
- Asthma exacerbations: Increased severity and frequency of asthma attacks.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Long-term damage to the lungs.
Long-term exposure can lead to irreversible lung damage and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections.
Neurological Impacts
Certain chemicals released in the derailment, such as vinyl chloride, are known neurotoxins:
- Headaches and dizziness: Common short-term effects.
- Cognitive impairment: Difficulty concentrating, memory loss.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Damage to nerves in the extremities.
- Central nervous system disorders: Severe neurological conditions in cases of high exposure.
Long-term cognitive effects can significantly impair quality of life.
Other Health Concerns
Beyond respiratory and neurological effects, other health risks include:
- Skin irritation: Direct contact can cause rashes, burns, and other skin problems.
- Reproductive issues: Exposure to certain chemicals can impact fertility and fetal development.
- Increased cancer risk: Some of the released chemicals are known carcinogens.
The cumulative effect of exposure to multiple chemicals can exacerbate health problems, potentially leading to more severe outcomes.
Remediation and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the lingering contamination in buildings requires a comprehensive approach.
Professional Assessment and Testing
Professional assessment and testing are crucial for determining the extent and nature of contamination. This includes:
- Air quality testing: Measuring the concentration of VOCs and other harmful substances in the air.
- Surface sampling: Analyzing surfaces for the presence of contaminants.
- Groundwater testing (if applicable): Assessing the level of contamination in the groundwater.
The type of testing required depends on the specific chemicals involved and the suspected pathways of contamination.
Remediation Techniques
Various remediation techniques can be employed, depending on the type and level of contamination:
- Air filtration: Using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to remove contaminants from the air.
- Surface cleaning: Specialized cleaning methods to remove contaminants from surfaces.
- Decontamination and removal of materials: In severe cases, removal and replacement of heavily contaminated materials may be necessary.
The safety of remediation workers is paramount, and specialized equipment and protocols must be followed.
Long-Term Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring is essential to ensure the effectiveness of remediation efforts and to protect the health of building occupants. This may involve:
- Regular air quality testing: Periodic checks to ensure contaminant levels remain below safe thresholds.
- Surface testing: Monitoring for re-contamination.
- Long-term health surveillance: Tracking the health status of individuals exposed to the contamination.
Conclusion
The lingering effects of toxic chemicals from the Ohio train derailment pose a serious threat to building occupants. The pathways of contamination, including airborne dispersion, surface contamination, and potential groundwater contamination, necessitate comprehensive assessment and remediation. The significant health risks associated with exposure, encompassing respiratory problems, neurological impacts, and other health concerns, highlight the urgent need for action. Don't ignore the potential threat of toxic chemicals from the Ohio train derailment. Contact a qualified environmental professional for assessment and remediation of your building today. Protect your health and the health of your family by addressing lingering contamination.

Featured Posts
-
 Indias Record 19 Paddlers At Wtt Star Contender Chennai
May 22, 2025
Indias Record 19 Paddlers At Wtt Star Contender Chennai
May 22, 2025 -
 Second Reintroduced Colorado Gray Wolf Found Dead In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
Second Reintroduced Colorado Gray Wolf Found Dead In Wyoming
May 22, 2025 -
 Severe Weather Alert Thunderstorm Watch Issued For South Central Pa
May 22, 2025
Severe Weather Alert Thunderstorm Watch Issued For South Central Pa
May 22, 2025 -
 Otter Conservation In Wyoming Challenges And Solutions
May 22, 2025
Otter Conservation In Wyoming Challenges And Solutions
May 22, 2025 -
 The Costco Campaign And Saskatchewan Politics A Panel Discussion
May 22, 2025
The Costco Campaign And Saskatchewan Politics A Panel Discussion
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Fuel Prices Fall In Toledo Good News For Drivers
May 22, 2025
Fuel Prices Fall In Toledo Good News For Drivers
May 22, 2025 -
 Lower Gas Prices Reported In Toledo
May 22, 2025
Lower Gas Prices Reported In Toledo
May 22, 2025 -
 Gas Prices In Toledo Recent Decrease In Fuel Costs
May 22, 2025
Gas Prices In Toledo Recent Decrease In Fuel Costs
May 22, 2025 -
 Toledo Gas Prices Drop Lower Costs Per Gallon
May 22, 2025
Toledo Gas Prices Drop Lower Costs Per Gallon
May 22, 2025 -
 Gas Buddy Virginia Sees Week Over Week Gas Price Decrease
May 22, 2025
Gas Buddy Virginia Sees Week Over Week Gas Price Decrease
May 22, 2025
