The US-China Trade War: Who Compromised And How?
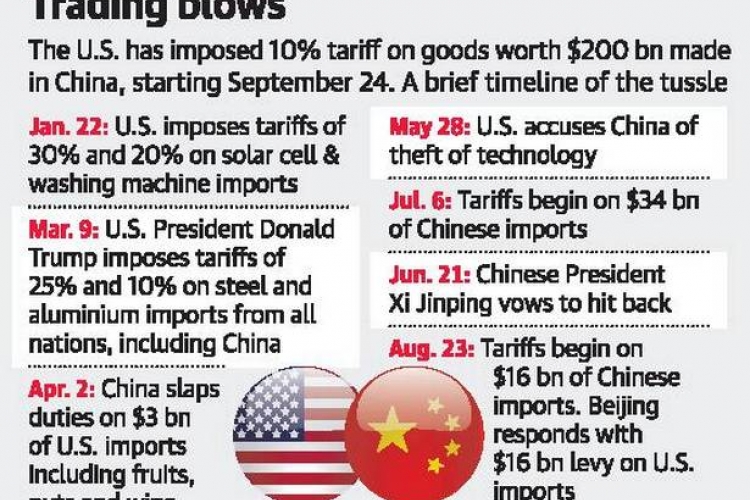
Table of Contents
The US Approach: Aggressive Tariffs and Pressure Tactics
The United States employed a strategy of aggressive tariffs and pressure tactics to try and force concessions from China. This approach aimed to address long-standing concerns about unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and the massive trade deficit with China.
Initial US Tariffs and their Impact
The initial imposition of tariffs by the US targeted a wide range of Chinese goods. These tariffs, ranging from 10% to 25%, significantly impacted various sectors. The economic impact was felt globally, with ripple effects throughout supply chains.
- Quantifiable Impact: Estimates vary, but the tariffs led to billions of dollars in increased costs for American consumers and businesses. China also experienced economic slowdown and disruptions to its export-oriented industries.
- Industries Affected: The agricultural sector (soybeans, pork), technology (semiconductors, electronics), and manufacturing were among the most heavily impacted industries in both countries.
- Examples of Tariffs:
- 25% tariff on $200 billion worth of Chinese goods.
- 10% tariff on another $200 billion worth of goods (later increased to 25%).
- Tariffs on specific products like steel and aluminum.
The "Phase One" Trade Deal and US Concessions
The "Phase One" trade deal, signed in January 2020, marked a temporary de-escalation. While touted as a victory by the Trump administration, it involved certain concessions from the US side.
- Key Elements: China committed to purchasing a significantly larger amount of US agricultural products and other goods. The deal also addressed some intellectual property concerns.
- US Concessions: The US agreed to reduce some existing tariffs on Chinese goods. This reduction, though partial, represented a concession in the ongoing trade battle.
- Strategic Reasoning: The US likely aimed to secure some immediate gains and create a foundation for further negotiations, while also signaling a willingness to compromise.
- Specific Commitments: The US pledged to reduce tariffs on certain categories of Chinese goods in exchange for China's commitments to increased purchases of US goods and services.
Continued Pressure and Shifting Negotiating Strategies
Despite the "Phase One" deal, the pressure on China continued. The US administration maintained a focus on addressing structural issues within the Chinese economy.
- Ongoing Pressure Tactics: The US continued to investigate and impose tariffs on Chinese goods suspected of violating trade regulations. It also continued its efforts to restrict Chinese technology companies.
- Effectiveness: The effectiveness of these strategies remains a topic of debate. While some argue that they forced China to make concessions, others point to the limited success in achieving long-term structural changes in the Chinese economy.
- Examples: Further tariffs were imposed on certain Chinese goods, and restrictions were placed on Chinese companies operating in the United States.
China's Response: Retaliatory Tariffs and Domestic Policy Adjustments
China responded to US tariffs with its own retaliatory measures and significant internal adjustments. Its response was multifaceted, combining trade-based countermeasures with domestic policy reforms.
China's Retaliatory Measures
China's response to the US tariffs was swift and substantial, targeting various US goods to mitigate the impact on its economy.
- Retaliatory Tariffs: China imposed tariffs on a wide range of US goods, impacting sectors like agriculture, automobiles, and energy.
- Economic Impact on the US: These tariffs increased the cost of US goods in China and reduced US exports, contributing to economic uncertainty in certain sectors.
- Diversification of Trade Partners: China actively sought to diversify its trade partners, reducing its reliance on the US market.
- Examples of Retaliatory Tariffs: Tariffs were imposed on soybeans, cars, and other US products.
Internal Economic Adjustments and Structural Reforms
Facing economic pressure, China made significant internal economic adjustments and pursued certain structural reforms.
- Internal Adjustments: China implemented measures to support domestic industries and reduce its reliance on exports.
- Structural Reforms: While not directly addressing US demands, China continued its efforts to reform its state-owned enterprises and improve its domestic market.
- Impact on Chinese Economy: These adjustments and reforms helped to stabilize the Chinese economy, although the overall impact of the trade war remains a subject of ongoing research and debate.
- Examples of Internal Reforms: Emphasis on technological self-reliance, development of domestic supply chains, and investments in innovation.
China's Negotiating Strategy and Compromises
China's negotiation strategy was characterized by a combination of resistance, counter-offers, and eventual concessions.
- Negotiating Approach: China's approach involved a careful balance of defending its interests while also seeking to de-escalate tensions.
- Areas of Concession: While not publicly admitting to significant compromises, China made some adjustments to its trade practices in areas like intellectual property protection and agricultural purchases.
- Implications for China's Long-Term Goals: The trade war pushed China to accelerate its efforts to become technologically self-reliant and reduce its dependence on foreign markets.
- Specific Commitments: China made specific commitments related to intellectual property protection and agricultural purchases as part of the Phase One agreement.
Assessing the Overall Impact and Long-Term Implications
The US-China trade war had a profound and multifaceted impact on both countries and the global economy.
Winners and Losers
The trade war produced winners and losers across various sectors in both countries. Some industries benefited from increased domestic demand or protectionist measures, while others suffered from reduced exports or increased costs.
- Impact on Industries: The agricultural sector in both countries experienced significant impacts, as did manufacturing and technology companies. Winners and losers were determined by factors such as supply chain diversification, domestic market strength, and the specific products subject to tariffs.
The Future of US-China Trade Relations
The long-term implications of the trade war are still unfolding. The future of US-China trade relations remains uncertain, with potential for both further escalation and eventual cooperation.
- Potential for Escalation: The underlying tensions between the two countries remain, creating the potential for further trade disputes.
- Potential for Cooperation: There is also a potential for increased cooperation on issues of mutual interest, though this will likely depend on the overall geopolitical landscape.
- Global Implications: The trade war highlighted the interconnectedness of the global economy and the potential for major trade disputes to disrupt global supply chains and economic growth.
Conclusion
The US-China trade war involved significant compromises from both sides, driven by strategic considerations and economic pressures. The US employed aggressive tariffs and pressure tactics, while China responded with retaliatory measures and internal adjustments. The "Phase One" trade deal provided temporary relief, but the underlying tensions remain. Understanding the complexities of the US-China trade war requires a thorough analysis of the compromises made by both sides and their significant economic consequences. Further research into specific industries affected by the trade war and the long-term implications for global trade is encouraged to gain a complete picture of this critical economic event. Continue your exploration of the US-China trade war by researching specific policy changes and their effects on global trade negotiations.

Featured Posts
-
 The Future Of Block Mirrors Innovation In Censorship Circumvention
May 16, 2025
The Future Of Block Mirrors Innovation In Censorship Circumvention
May 16, 2025 -
 Is Trump Right Us Dependence On Canadian Goods An Expert Assessment
May 16, 2025
Is Trump Right Us Dependence On Canadian Goods An Expert Assessment
May 16, 2025 -
 Tam Krwz Awr Mdah Ka Ghyr Mtwqe Waqeh Jwte Pr Pawn
May 16, 2025
Tam Krwz Awr Mdah Ka Ghyr Mtwqe Waqeh Jwte Pr Pawn
May 16, 2025 -
 Significant Job Cuts At Microsoft 6 000 Employees Impacted
May 16, 2025
Significant Job Cuts At Microsoft 6 000 Employees Impacted
May 16, 2025 -
 Can The Padres Beat The Yankees And Extend Their Winning Streak To 7
May 16, 2025
Can The Padres Beat The Yankees And Extend Their Winning Streak To 7
May 16, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Pyatiy Shataut Bobrovskogo V Pley Off Vratar Floridy Blistaet
May 16, 2025
Pyatiy Shataut Bobrovskogo V Pley Off Vratar Floridy Blistaet
May 16, 2025 -
 Bobrovskiy Snova Na Vysote Pyatiy Shataut V Pley Off
May 16, 2025
Bobrovskiy Snova Na Vysote Pyatiy Shataut V Pley Off
May 16, 2025 -
 Rekord Ovechkina Bolshe Golov V Pley Off N Kh L Chem U Leme
May 16, 2025
Rekord Ovechkina Bolshe Golov V Pley Off N Kh L Chem U Leme
May 16, 2025 -
 Sergey Bobrovskiy 5 Y Shataut V Pley Off N Kh L
May 16, 2025
Sergey Bobrovskiy 5 Y Shataut V Pley Off N Kh L
May 16, 2025 -
 How Apple Watches Are Transforming Nhl Officiating
May 16, 2025
How Apple Watches Are Transforming Nhl Officiating
May 16, 2025
