The Semiconductor Market Surge: Understanding The Preceding ETF Sell-Off
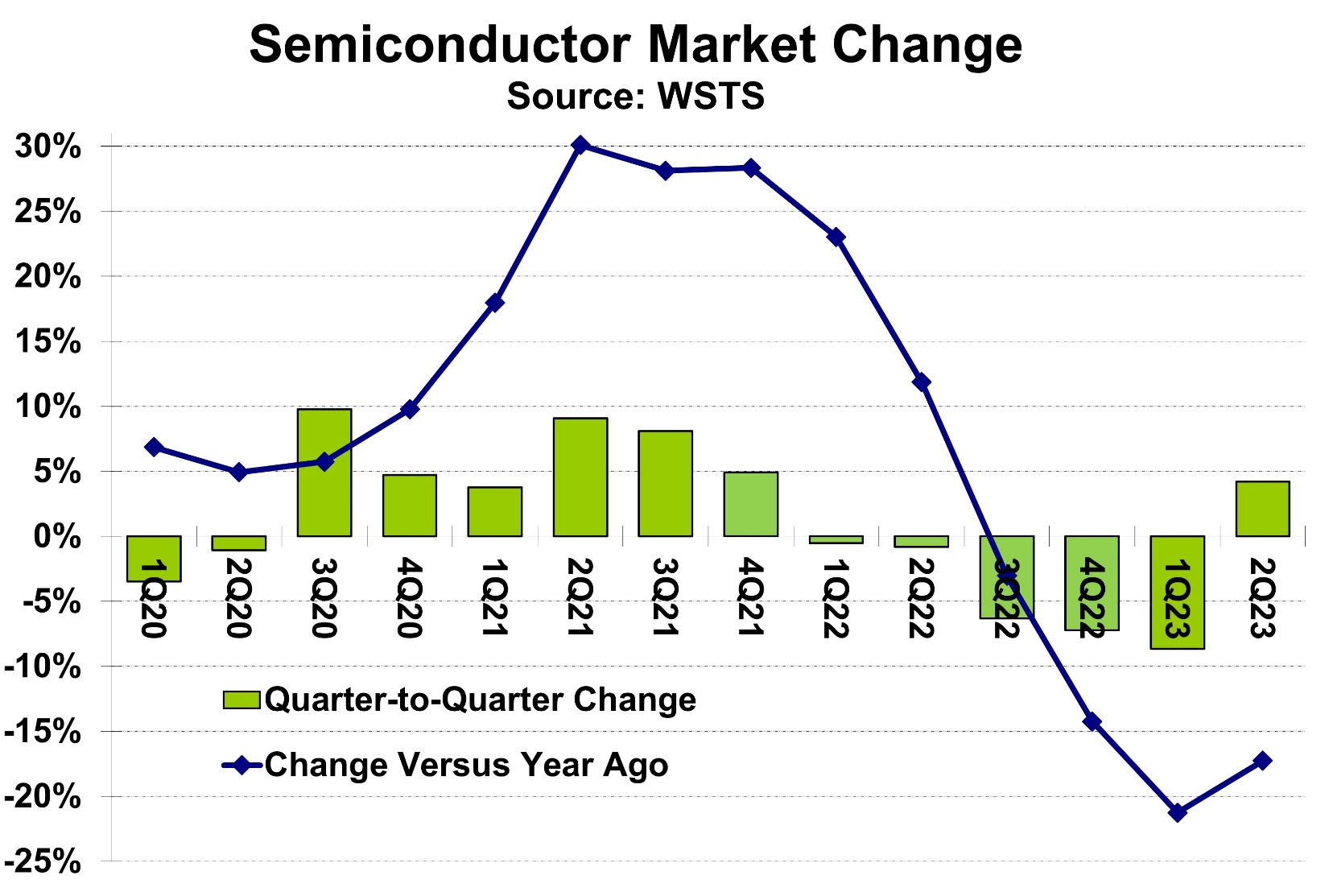
Table of Contents
Understanding the Semiconductor ETF Sell-Off
The decline in semiconductor ETFs wasn't a singular event but a confluence of factors impacting investor confidence and market sentiment.
Market Timing and Investor Sentiment
Short-term market fluctuations significantly influence ETF trading. Investor anxieties, often amplified by media coverage, can lead to rapid sell-offs.
- Increased uncertainty: Geopolitical instability, inflation concerns, and aggressive interest rate hikes by central banks all contributed to a climate of uncertainty, impacting investor confidence in the semiconductor market and prompting many to divest from semiconductor stocks and related tech ETFs.
- Profit-taking: The fear of missing out (FOMO) often drives rapid buying, but equally, the fear of losing out can cause equally rapid selling, leading to quick profit-taking as investors secure gains before a perceived downturn.
- Technical indicators: Technical analysis signals, such as bearish crossovers or declining trading volume, can trigger automated sell orders, exacerbating downward pressure on semiconductor ETF prices.
Sector-Specific Concerns within the Semiconductor Industry
Negative news or forecasts about specific semiconductor companies or market segments can significantly influence ETF prices.
- Supply chain disruptions: Ongoing supply chain bottlenecks, particularly concerning raw materials and specialized equipment, created uncertainty about the ability of chipmakers to meet demand, impacting investor sentiment toward semiconductor stocks.
- Overvaluation concerns: Some analysts voiced concerns about the potential overvaluation of certain high-growth chipmakers, leading some investors to reduce their exposure to semiconductor ETFs before a potential correction.
- Slowing demand: Concerns arose about slowing demand in specific markets, such as smartphones, creating apprehension about the future growth prospects for certain semiconductor companies and impacting the overall semiconductor industry outlook. This, in turn, led to a decline in semiconductor ETF values.
- Increased competition: The emergence of strong competitors, particularly from China and other Asian markets, added another layer of uncertainty for investors, affecting their confidence in some semiconductor stocks and related ETFs.
ETF Structure and Liquidity
The structure and liquidity of semiconductor ETFs themselves can contribute to volatility and sell-offs.
- Institutional selling: Large institutional investors, holding significant positions in semiconductor ETFs, may need to liquidate assets to meet other obligations, leading to substantial selling pressure.
- ETF mechanics: The creation and redemption mechanisms of ETFs can amplify price movements, especially during periods of high volatility.
- Leveraged/inverse ETFs: Investors using leveraged or inverse semiconductor ETFs to bet on market direction can magnify both gains and losses, contributing to amplified price swings.
The Semiconductor Market Surge: Factors Driving the Rebound
Despite the preceding sell-off, the semiconductor market has experienced a significant surge, driven by several key factors.
Increased Demand from Multiple Sectors
Demand for semiconductors is booming across various sectors.
- Data centers: The explosive growth of cloud computing and data centers fuels the relentless demand for high-performance computing chips, driving a significant portion of the semiconductor market surge.
- AI and machine learning: The advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning require increasingly powerful and specialized chips, resulting in a substantial increase in demand.
- Automotive sector recovery: The automotive industry is recovering from chip shortages, leading to a significant surge in orders for automotive-grade semiconductors.
- 5G infrastructure deployment: The rollout of 5G networks worldwide requires massive quantities of advanced semiconductors, propelling growth in the semiconductor market.
- High-performance computing (HPC): The increasing need for high-performance computing in scientific research, financial modeling, and other areas continues to drive demand for sophisticated semiconductor solutions.
Supply Chain Improvements and Capacity Expansion
Improvements in the semiconductor supply chain and increased manufacturing capacity are contributing to the market rebound.
- Government initiatives: Governments worldwide are investing heavily in domestic semiconductor production, aiming to reduce reliance on foreign manufacturers and strengthen their own semiconductor industries.
- Increased investments: Major chipmakers are investing heavily in expanding their manufacturing facilities and upgrading their production capabilities.
- Technological advancements: Advances in chip manufacturing technologies, such as EUV lithography, are enabling the production of more advanced and powerful chips, improving efficiency and capacity.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Continuous technological innovation fuels demand for advanced semiconductors.
- AI advancements: Breakthroughs in AI continue to push the boundaries of computing power, driving demand for more sophisticated and energy-efficient chips.
- The Metaverse: The development of the metaverse requires massive computing power and advanced semiconductors to support virtual and augmented reality experiences.
- IoT devices: The proliferation of internet-connected devices is creating a huge demand for low-power, high-efficiency semiconductors.
Conclusion
The recent semiconductor market surge, following a period of ETF sell-off, highlights the cyclical nature of this vital industry. While investor anxieties and market corrections are inevitable, understanding the underlying factors—ranging from macroeconomic trends to technological innovation and supply chain dynamics—is crucial for navigating the semiconductor investment landscape. By recognizing the interplay between these forces and staying informed about the industry's evolution, investors can develop a robust investment strategy in the semiconductor sector. Continue researching and monitoring the semiconductor market to make informed decisions about your semiconductor ETF investments and capitalize on future opportunities in this dynamic field. Remember to consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Tucows Board Of Directors New Nominations And Departures Announced
May 13, 2025
Tucows Board Of Directors New Nominations And Departures Announced
May 13, 2025 -
 Persipura Jayapura Vs Rans Fc Kemenangan Spektakuler 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2
May 13, 2025
Persipura Jayapura Vs Rans Fc Kemenangan Spektakuler 8 0 Di Playoff Liga 2
May 13, 2025 -
 5 Key Actions To Secure A Role In The Private Credit Boom
May 13, 2025
5 Key Actions To Secure A Role In The Private Credit Boom
May 13, 2025 -
 L Allemagne Investit Dans Sa Protection Civile Une Reponse A Des Annees De Sous Estimation
May 13, 2025
L Allemagne Investit Dans Sa Protection Civile Une Reponse A Des Annees De Sous Estimation
May 13, 2025 -
 50 Years Of Rescue Pieterburen Seal Center Releases Final Seals
May 13, 2025
50 Years Of Rescue Pieterburen Seal Center Releases Final Seals
May 13, 2025
