The Persistence Of Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Following The Ohio Train Derailment
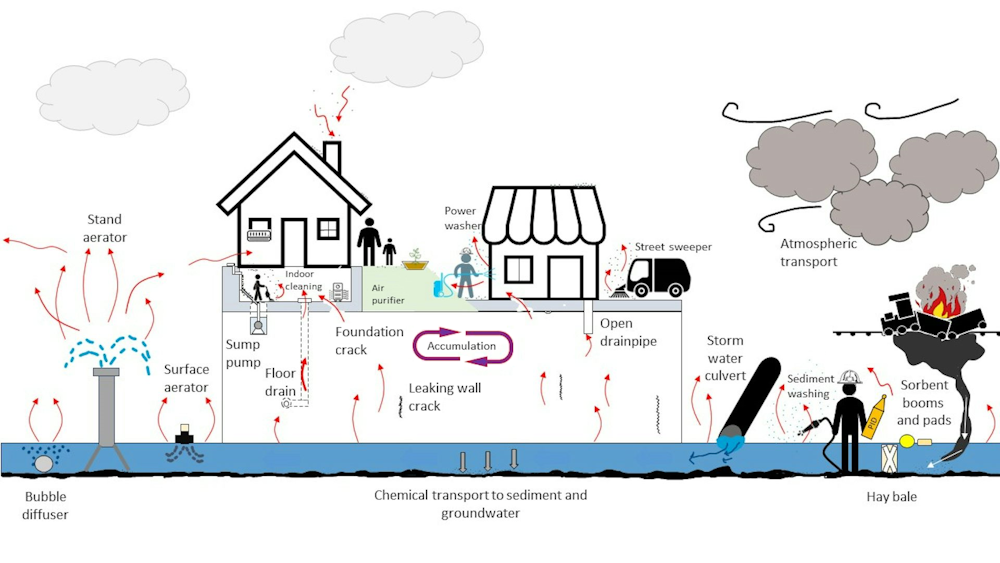
Table of Contents
Types of Toxic Chemicals and Their Persistence
The Ohio train derailment involved the release of several hazardous chemicals, notably vinyl chloride, butyl acrylate, and ethylhexyl acrylate. These chemicals present significant health risks and varying degrees of persistence in the environment.
-
Vinyl chloride: Known to be a human carcinogen, vinyl chloride is a volatile organic compound (VOC) that can easily evaporate. However, it can also adsorb onto surfaces within buildings, lingering in porous materials like drywall, carpets, and insulation. Its persistence depends heavily on temperature and ventilation.
-
Butyl acrylate and Ethylhexyl acrylate: These acrylates are also VOCs, known to cause respiratory irritation and other health problems. While they are less persistent than some other chemicals, they can still accumulate in building materials, particularly those with a large surface area.
-
Chemical Breakdown and Half-Life: The breakdown rate of these chemicals varies significantly depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, sunlight exposure, and the presence of other chemicals. Determining the precise half-life in building materials requires specific testing, but their volatile nature suggests a potential for lingering contamination. The interaction of these chemicals with building materials also needs further investigation.
Pathways of Chemical Contamination in Buildings
The released chemicals found their way into buildings through various pathways:
-
Airborne Contamination: The initial release created a plume of airborne chemicals that infiltrated buildings through HVAC systems, open windows, and cracks in walls and foundations. Poorly sealed buildings are particularly vulnerable.
-
Surface Contamination: Airborne particles settled on surfaces, leading to direct contamination of building materials. This is particularly concerning in porous materials that readily absorb chemicals. Direct contact with contaminated soil or water can also lead to surface contamination.
-
Water Contamination: The derailment contaminated local water sources, posing a risk of contamination through plumbing systems. This is of particular concern for buildings drawing water from affected wells or municipal water sources.
-
Soil Contamination: Contaminated soil can leach chemicals into building foundations and basements, contributing to indoor air and water contamination.
Health Risks Associated with Long-Term Exposure
Exposure to the released chemicals poses significant health risks, both short-term and long-term.
-
Respiratory Problems: All three chemicals can cause respiratory irritation, coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Long-term exposure can lead to chronic respiratory illnesses.
-
Cancer Risk: Vinyl chloride is a known human carcinogen, significantly increasing the risk of various cancers.
-
Neurological Damage: Exposure to these chemicals may lead to neurological effects, including headaches, dizziness, and cognitive impairment.
-
Reproductive Effects: Some studies suggest that exposure to acrylates may have adverse reproductive effects.
-
Vulnerable Populations: Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory or other health conditions are particularly vulnerable to the adverse health effects of these chemicals. Ongoing health monitoring and medical surveillance are crucial for these populations.
Challenges in Detecting and Remediating Chemical Contamination
Addressing the contamination presents significant challenges:
-
Contamination Assessment: Accurately assessing the extent of contamination requires sophisticated testing methods and specialized expertise. The sheer scale of the affected area makes comprehensive testing a complex and resource-intensive undertaking.
-
Remediation Strategies: Remediation strategies vary depending on the type and extent of contamination. Options include air scrubbing, surface cleaning, and, in severe cases, demolition. Each approach has its own cost and logistical implications.
-
Cost of Cleanup: The cost of a large-scale cleanup effort is substantial, and responsibility for funding remains a significant point of contention.
-
Regulatory Challenges: Navigating the regulatory landscape and obtaining necessary permits for cleanup and remediation adds complexity to the process.
The Need for Comprehensive Building Assessments and Remediation
To protect public health, comprehensive action is required:
-
Building Inspection: Thorough inspections of all potentially affected buildings are necessary to assess the level of contamination.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Ongoing environmental monitoring is crucial to track the effectiveness of remediation efforts and ensure long-term safety.
-
Safety Protocols: Strict safety protocols must be implemented during cleanup and remediation processes to protect workers and residents.
-
Preventative Measures: Investing in preventative measures, such as improved infrastructure and stricter regulations for hazardous materials transportation, is essential to reduce the risk of future incidents.
Conclusion
The persistence of toxic chemicals in buildings following the Ohio train derailment presents a significant and ongoing public health concern. Understanding the pathways of contamination, the associated health risks, and the challenges of remediation is crucial for effective response and long-term mitigation. Comprehensive assessments, robust remediation strategies, and ongoing monitoring are essential to protect residents and workers from the lingering effects of this environmental disaster. The long-term implications of this event necessitate continued vigilance and proactive measures.
Call to Action: Demand accountability for the responsible parties and advocate for stricter regulations to prevent future incidents. Learn more about the long-term effects of toxic chemical exposure following the Ohio train derailment and how to protect yourself and your community. Stay informed about building contamination and the latest updates on the ongoing cleanup efforts. #OhioTrainDerailment #ToxicChemicals #BuildingSafety #EnvironmentalPollution #PublicHealth
 Corinthians X Guarani Onde Assistir Ao Vivo O Jogo Do Paulistao 2025
Corinthians X Guarani Onde Assistir Ao Vivo O Jogo Do Paulistao 2025
 Anger Over Bgt Semi Final Winner Was It Rigged
Anger Over Bgt Semi Final Winner Was It Rigged
 Nigel Farage And Rupert Lowe Explosive Texts Reveal Bitter Feud
Nigel Farage And Rupert Lowe Explosive Texts Reveal Bitter Feud
 Sandhagen Vs Figueiredo Ufc Fight Night Expert Predictions And Betting Picks
Sandhagen Vs Figueiredo Ufc Fight Night Expert Predictions And Betting Picks
 2025 Streaming Landscape Fox And Espn Enter The Fray With Standalone Services
2025 Streaming Landscape Fox And Espn Enter The Fray With Standalone Services
