The Growing Problem Of Wildfire Betting: A Los Angeles Case Study

Table of Contents
The Mechanics of Wildfire Betting in Los Angeles
Wildfire betting operates through various channels, exploiting the vulnerabilities of both the internet and social media. It's a dark underbelly of the tragedy, profiting from the suffering of others. The mechanics are surprisingly simple, making it accessible to a wide range of individuals.
-
Use of social media to spread rumors and influence bets: Social media platforms, particularly Twitter and Telegram, are being used to spread unsubstantiated rumors about fire spread, potentially influencing betting markets and manipulating outcomes. These platforms often lack robust fact-checking mechanisms, leading to rapid dissemination of misinformation. For instance, a false report of a rapidly spreading fire could trigger a surge in bets on increased acreage burned.
-
The role of unregulated online gambling platforms: Many unregulated online gambling platforms offer wildfire betting markets, often operating outside the jurisdiction of California's gambling laws. The anonymity offered by these platforms makes it difficult to track and prosecute those involved. These websites may offer bets on various aspects of the wildfire, from the total acreage burned to the estimated property damage.
-
Examples of specific betting markets: Betting markets can range from simple over/under bets on the acreage burned to more complex options, such as predicting which neighborhoods will be most affected or the total estimated cost of property damage. The specificity of these markets highlights the callous disregard for human suffering inherent in this practice.
-
Discussion on the ease of access to these platforms: The ease of access to these platforms via readily available search engines and social media links contributes significantly to the growing problem. This accessibility makes it increasingly challenging to combat the spread of wildfire betting.
The Ethical and Legal Ramifications
Wildfire betting raises profound ethical questions about profiting from human suffering and natural disasters. The practice is morally reprehensible and potentially illegal.
-
The impact on victims and their families: The emotional distress caused to wildfire victims is exacerbated by the knowledge that individuals are profiting from their misfortune. The thought that someone is placing bets on the extent of their loss adds another layer of trauma and injustice.
-
The potential for manipulation and misinformation to influence bets: The spread of false information can artificially inflate or deflate betting markets, creating an environment ripe for exploitation. Deliberate misinformation could potentially even influence the course of a fire through misdirection of resources or delayed responses.
-
Legal ambiguity surrounding wildfire betting and gambling laws in California: The legal status of wildfire betting in California is currently unclear. While existing gambling laws may cover some aspects, specific legislation targeting this emerging form of gambling is needed. This ambiguity allows illegal operations to flourish.
-
Potential criminal charges for individuals involved in organizing or promoting such bets: Depending on the circumstances, individuals involved in organizing or promoting wildfire betting could face criminal charges, including fraud, conspiracy, and potentially even reckless endangerment.
The Role of Social Media and Misinformation
Social media acts as a primary vector for the spread of wildfire betting and related misinformation. The immediacy and reach of social media platforms are being exploited to facilitate this harmful activity.
-
Examples of social media posts promoting or facilitating wildfire betting: Screenshots of online betting platforms and calls to place bets on wildfire outcomes are increasingly common on social media. These posts normalize and encourage the practice.
-
The amplification of rumors and speculation on fire spread: Social media’s algorithm often prioritizes sensational content, amplifying rumors and speculation about fire spread and exacerbating anxiety and fear. This creates an environment ripe for the exploitation of vulnerable individuals.
-
The difficulty in controlling misinformation on social media platforms: The sheer volume of information shared on social media makes it incredibly difficult to track and remove misinformation related to wildfire betting. The platforms’ existing fact-checking mechanisms often prove inadequate.
-
The responsibility of social media companies in tackling this issue: Social media companies bear a significant responsibility in combating the spread of wildfire betting. They must strengthen their efforts to identify and remove content promoting this practice. Proactive measures and improved algorithms are crucial.
The Impact on Emergency Response and Insurance
Wildfire betting also poses a serious threat to effective emergency response and the insurance industry. The consequences can be far-reaching and detrimental to the community as a whole.
-
Increased strain on emergency services due to increased calls or speculation: False reports and increased speculation generated by wildfire betting can overwhelm emergency services with unnecessary calls and divert resources from genuine emergencies. This places an additional burden on already stretched resources.
-
The potential for fraudulent insurance claims related to wildfire betting: Wildfire betting could create opportunities for fraudulent insurance claims. Individuals might exaggerate losses or even intentionally cause damage to profit from their bets.
-
The impact on insurance premiums in high-risk areas: The increased risk of fraudulent claims linked to wildfire betting could lead to higher insurance premiums for residents in high-risk areas, further burdening those already affected by wildfires.
-
The need for stricter regulations to prevent such manipulation: Stricter regulations are needed to prevent the manipulation of emergency responses and insurance claims related to wildfire betting. This includes enhanced monitoring of social media and improved coordination between emergency services and insurance companies.
Conclusion
Wildfire betting in Los Angeles represents a growing and deeply troubling phenomenon with significant ethical and legal implications. The ease of access through unregulated online platforms and the spread of misinformation on social media amplify the problem. This dangerous trend not only disrespects victims but also poses serious risks to emergency response and insurance systems. The casual cruelty of profiting from tragedy cannot be tolerated.
We must actively address the issue of wildfire betting to protect vulnerable communities and prevent further exploitation. Increased regulation, stronger enforcement of existing gambling laws, and greater social media responsibility are crucial steps toward eliminating this morally reprehensible practice. Let's work together to combat the growing problem of wildfire betting, its associated misinformation, and its devastating consequences. We need to prevent this unethical practice from gaining further traction and causing more harm.

Featured Posts
-
 Pley Off Vegas Golden Nayts Obygrali Minnesotu V Overtayme
May 10, 2025
Pley Off Vegas Golden Nayts Obygrali Minnesotu V Overtayme
May 10, 2025 -
 2025 Nhl Trade Deadline Predicting The Playoff Picture
May 10, 2025
2025 Nhl Trade Deadline Predicting The Playoff Picture
May 10, 2025 -
 Renaissance Et Modem Vers Une Fusion Sous L Impulsion D Elisabeth Borne
May 10, 2025
Renaissance Et Modem Vers Une Fusion Sous L Impulsion D Elisabeth Borne
May 10, 2025 -
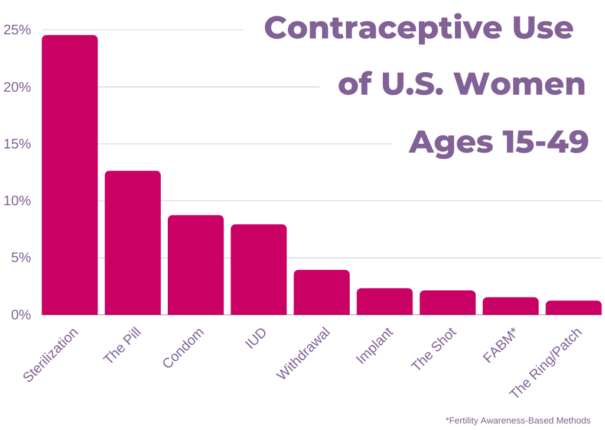 Access To Birth Control The Impact Of Over The Counter Options Post Roe
May 10, 2025
Access To Birth Control The Impact Of Over The Counter Options Post Roe
May 10, 2025 -
 King Povernuvsya Gostri Komentari Pro Trampa Y Maska
May 10, 2025
King Povernuvsya Gostri Komentari Pro Trampa Y Maska
May 10, 2025
