The GOP Tax Plan And The Deficit: A Fact-Based Assessment

Table of Contents
The GOP Tax Plan's Key Provisions and Their Projected Revenue Impact
The 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) significantly altered the US tax code. Let's examine its key provisions and their projected revenue impact.
Individual Income Tax Cuts
The TCJA reduced individual income tax rates across the board. It also altered several deductions and credits.
- Standard Deduction Increase: The standard deduction was significantly increased, benefiting many lower and middle-income taxpayers. However, this also reduced the number of taxpayers itemizing deductions.
- Child Tax Credit Expansion: The Child Tax Credit was expanded, providing greater relief to families with children.
- Elimination of Personal and Dependent Exemptions: The elimination of personal and dependent exemptions offset some of the benefits of the increased standard deduction.
The Tax Policy Center estimated that these individual income tax cuts would reduce federal revenue by trillions of dollars over ten years. [cite source: Tax Policy Center report]. The impact varied significantly across income groups, with higher-income taxpayers receiving a disproportionately larger share of the tax cuts.
Corporate Tax Rate Reduction
The TCJA dramatically reduced the top corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%. Proponents argued this would boost business investment, leading to increased economic activity and ultimately offsetting the revenue loss.
- Increased Investment Argument: Supporters claimed the lower rate would incentivize companies to invest more, creating jobs and boosting economic growth. [cite source: Supporting economic study]
- Repatriation of Overseas Profits: The TCJA also included provisions designed to encourage repatriation of profits held overseas by US corporations.
- Projected Revenue Loss: The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) projected significant revenue losses from the corporate tax rate reduction. [cite source: CBO report]. However, the actual impact remains a subject of ongoing debate.
Revenue Projections and Shortfalls
Initial revenue projections for the TCJA proved overly optimistic.
- Discrepancies: Actual revenue collected fell short of the initial projections, contributing to a widening budget deficit. [cite source: Treasury Department data]
- Reasons for Shortfalls: Several factors contributed to these shortfalls, including slower-than-anticipated economic growth and potential loopholes in the tax code.
- (Insert Chart/Graph Here with appropriate alt text showing projected vs. actual revenue)
Economic Growth Arguments and Their Validity
The GOP tax plan was largely justified on the basis of supply-side economics.
Supply-Side Economics and the Laffer Curve
Supply-side economics posits that tax cuts incentivize increased investment and production, ultimately leading to higher tax revenue. The Laffer Curve is often cited to support this theory.
- Laffer Curve Critique: Critics argue that the Laffer Curve is simplistic and doesn't accurately reflect the complexities of the real-world economy. The optimal tax rate where revenue is maximized is highly debated and depends on many factors. [cite source: Critical economic analysis]
- Alternative Economic Models: Keynesian economics, for example, suggests that government spending, rather than tax cuts, is more effective in stimulating demand during economic downturns.
Empirical Evidence of Economic Growth Following Tax Cuts
Following the TCJA's enactment, there was some economic growth.
- GDP Growth and Job Creation: Data shows modest increases in GDP growth and job creation in the years following the tax cuts. [cite source: Bureau of Economic Analysis data]
- Correlation vs. Causation: It's crucial to differentiate between correlation and causation. While there was economic growth, it's difficult to definitively attribute it solely to the tax cuts. Other factors, such as monetary policy and global economic conditions, likely played a role. [cite source: Peer-reviewed study on economic growth factors]
The Impact on the National Deficit and Debt
The GOP tax plan had a significant impact on the national deficit and debt.
Increased Federal Debt
The tax cuts led to a substantial increase in the federal debt.
- Debt Before and After: [Insert chart/graph comparing national debt levels before and after the TCJA with appropriate alt text]. The increase reflects the reduced tax revenue combined with increased government spending. [cite source: Federal Reserve data]
Long-Term Fiscal Sustainability
The rising national debt raises concerns about long-term fiscal sustainability.
- Increased Interest Payments: A higher national debt necessitates increased interest payments, crowding out spending on other vital government programs.
- Credit Rating Downgrades: Persistently high levels of debt could lead to credit rating downgrades, increasing borrowing costs for the US government.
Alternative Policy Proposals to Address the Deficit
Alternative approaches to addressing the deficit could have been pursued.
- Spending Cuts: Targeted spending cuts could have reduced the deficit without relying solely on tax cuts.
- Increased Taxes on Higher Earners: Increasing taxes on higher-income earners could have generated additional revenue. [cite source: Proposals for alternative fiscal policy]
Conclusion: A Critical Look at the GOP Tax Plan and the Deficit
The 2017 GOP tax plan significantly impacted the US national deficit. While proponents argued that the tax cuts would stimulate economic growth, offsetting revenue losses, the actual results show a substantial increase in the national debt. The analysis presented here demonstrates the complexities of assessing the plan's true economic consequences. This assessment highlights the need for careful consideration of both short-term and long-term effects when implementing major tax policy changes. Understanding the complexities of the GOP tax plan and its effect on the deficit requires careful consideration of the evidence. Continue your research and become an informed participant in the conversation surrounding the GOP tax plan and deficit spending.

Featured Posts
-
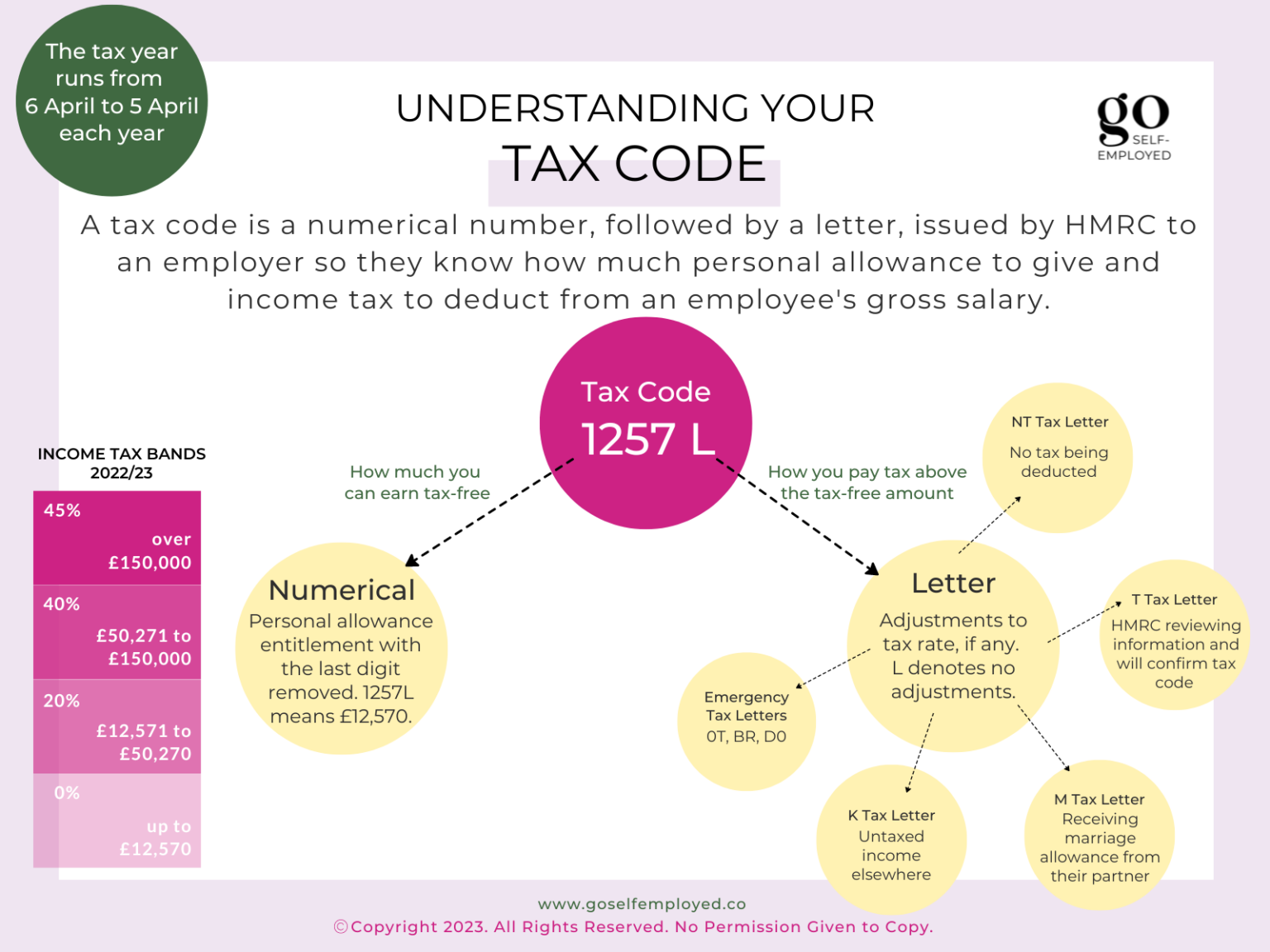 Hmrc Tax Codes Understanding Your New Code For Savings
May 20, 2025
Hmrc Tax Codes Understanding Your New Code For Savings
May 20, 2025 -
 Ajax Fenerbahce Yildizini Kadrosuna Katiyor Transfer Detaylari
May 20, 2025
Ajax Fenerbahce Yildizini Kadrosuna Katiyor Transfer Detaylari
May 20, 2025 -
 Public Works Ministrys 6 Billion Investment In Coastal Protection
May 20, 2025
Public Works Ministrys 6 Billion Investment In Coastal Protection
May 20, 2025 -
 Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword March 13 Answers And Helpful Hints
May 20, 2025
Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword March 13 Answers And Helpful Hints
May 20, 2025 -
 Delving Into The Psychology Of Agatha Christies Poirot
May 20, 2025
Delving Into The Psychology Of Agatha Christies Poirot
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Gretzky Loyalty Debate Trumps Tariffs And Statehood Comments Spark Controversy In Canada
May 20, 2025
The Gretzky Loyalty Debate Trumps Tariffs And Statehood Comments Spark Controversy In Canada
May 20, 2025 -
 Wayne Gretzkys Canadian Patriotism Questioned Amidst Trump Tariff And Statehood Controversy
May 20, 2025
Wayne Gretzkys Canadian Patriotism Questioned Amidst Trump Tariff And Statehood Controversy
May 20, 2025 -
 Trump Tariffs Gretzky Loyalty And Canadas Statehood Debate A Complex Issue
May 20, 2025
Trump Tariffs Gretzky Loyalty And Canadas Statehood Debate A Complex Issue
May 20, 2025 -
 Quick Facts About Wayne Gretzky A Concise Biography
May 20, 2025
Quick Facts About Wayne Gretzky A Concise Biography
May 20, 2025 -
 Wayne Gretzky Fast Facts Key Moments And Milestones In His Career
May 20, 2025
Wayne Gretzky Fast Facts Key Moments And Milestones In His Career
May 20, 2025
