The End Of An Era: Analysis Of The Rescinded School Desegregation Order
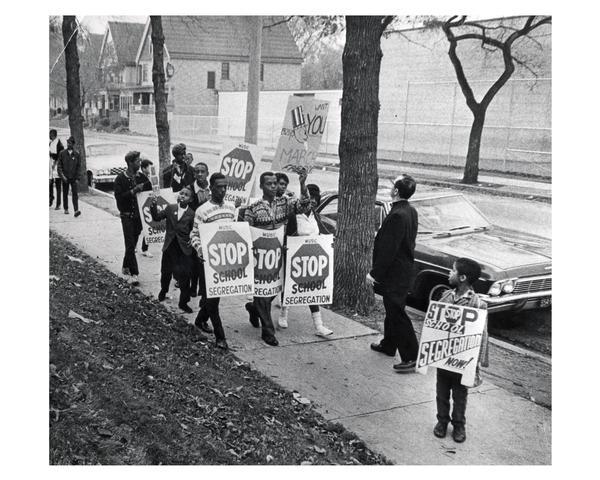

Table of Contents
Historical Context of the Original School Desegregation Order
Understanding the implications of the School Desegregation Order Rescission requires examining its historical context. The struggle for integrated schools is deeply rooted in the history of racial segregation in the United States. The landmark Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court case in 1954 declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. This pivotal decision laid the groundwork for desegregation efforts across the nation. However, implementation proved incredibly challenging, met with resistance in many communities.
-
Timeline of key events leading to the order's implementation: The years following Brown v. Board saw a slow and uneven process of desegregation, marked by legal battles, protests, and federal intervention. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 further strengthened the push for desegregation, but significant resistance continued for decades. The specific school desegregation order in question likely followed years of litigation and court-mandated integration plans.
-
Initial successes and challenges in desegregating schools: While some schools successfully integrated, many faced significant hurdles, including resistance from local authorities, white flight to suburban schools, and insufficient funding for resources in historically underserved communities.
-
Long-term effects of the original order on education and society: The original order, despite its challenges, fostered increased opportunities for minority students and contributed to broader societal changes. However, the legacy of segregation continues to manifest in persistent achievement gaps and socioeconomic disparities. Understanding this legacy is crucial for interpreting the impact of its rescission.
Legal Arguments Surrounding the Rescission of the School Desegregation Order
The legal basis for the School Desegregation Order Rescission is a crucial aspect of this analysis. Proponents likely argued for the rescission based on claims of changed circumstances, suggesting that the original order's objectives have been achieved or that its continued enforcement is no longer legally justified. They might point to improved demographic shifts or argue that the order is an undue infringement on local control of schools.
-
Summary of arguments presented by proponents of the rescission: These arguments often center around state's rights, the belief that the original order is outdated, and assertions that its enforcement is no longer necessary.
-
Counterarguments and legal challenges to the rescission: Opponents of the rescission will likely argue that it violates the principle of equal educational opportunity enshrined in the Constitution. They may point to continuing racial and socioeconomic disparities in education as evidence of the ongoing need for court oversight. Legal challenges would focus on whether the rescission meets the standards of judicial review and constitutional law.
-
Potential legal precedents set by this action: The rescission of this order could set a significant legal precedent, impacting future efforts to address school segregation and potentially emboldening similar challenges to desegregation orders nationwide. The Supreme Court’s response will be crucial in shaping the future legal landscape surrounding educational equity.
Societal Impact of the Rescinded School Desegregation Order
The societal impact of the School Desegregation Order Rescission is far-reaching and complex. The potential consequences extend beyond the immediate effects on student populations, influencing social integration, economic opportunities, and future generations.
-
Predicted impact on academic achievement for minority students: The rescission could lead to a widening of the achievement gap, negatively impacting minority students’ educational outcomes, particularly in areas where resegregation is likely to occur.
-
Potential increase in school segregation and resegregation: The removal of the desegregation order creates a risk of increased school segregation and a return to racially homogenous schools, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities. This resegregation could lead to a decline in educational quality and resources in historically underserved communities.
-
Long-term consequences for social cohesion and economic inequality: Increased segregation can have profound consequences for social cohesion, fostering greater social division and potentially widening the gap in economic opportunities between different racial groups.
The Role of Funding and Resources in Maintaining Integrated Schools
Equitable funding plays a critical role in maintaining integrated schools. Funding disparities between districts, often correlating with racial demographics, perpetuate inequalities.
-
How funding affects the ability to maintain integrated schools: Sufficient funding is essential for providing quality education and resources in all schools, regardless of their racial makeup. Lack of funding can create disparities in teacher quality, facilities, and programs, impacting the ability to effectively integrate student populations.
-
The role of equitable resource allocation in promoting desegregation: Equitable resource allocation is paramount in creating a level playing field for all students, promoting desegregation, and fostering a sense of inclusion. Strategies like weighted student funding formulas can help to address historical inequities.
-
Potential solutions to address funding disparities: Solutions include increased federal funding for education, school finance reform at the state level, and strategies to redistribute resources more equitably.
Conclusion
The rescission of the school desegregation order is a complex issue with significant historical context and potential long-term consequences. While proponents argue for local control and changed circumstances, opponents emphasize the ongoing need for measures to address systemic inequalities and ensure equal access to education. The potential for increased school segregation, widening achievement gaps, and exacerbated social and economic disparities underscores the seriousness of this decision. The continuing fight for educational equity demands attention and action.
The rescission of the school desegregation order is not the end of the conversation; it is a call to renewed action. We must continue to advocate for policies and initiatives that promote educational equity and dismantle the systemic barriers to integrated schools. Let's work together to ensure that every child has access to a quality education, regardless of race or socioeconomic background. Learn more about the ongoing fight against school segregation and how you can get involved in promoting a more equitable educational system. Continue the conversation about the implications of the School Desegregation Order Rescission and help us build a better future for all students.

Featured Posts
-
 Graeme Souness Premier League Favourite Player Revealed
May 03, 2025
Graeme Souness Premier League Favourite Player Revealed
May 03, 2025 -
 End Of School Desegregation Order Implications For Other Districts
May 03, 2025
End Of School Desegregation Order Implications For Other Districts
May 03, 2025 -
 Chinese Naval Activity Near Sydney Implications For Australias Security
May 03, 2025
Chinese Naval Activity Near Sydney Implications For Australias Security
May 03, 2025 -
 Abu Jinapor Npps Unexpected 2024 Election Defeat
May 03, 2025
Abu Jinapor Npps Unexpected 2024 Election Defeat
May 03, 2025 -
 Orta Afrika Cumhuriyeti Nin Bae Ile Yeni Ticaret Anlasmasi Gelecege Bakis
May 03, 2025
Orta Afrika Cumhuriyeti Nin Bae Ile Yeni Ticaret Anlasmasi Gelecege Bakis
May 03, 2025
