The End Of A Desegregation Order: A Turning Point In School Integration?
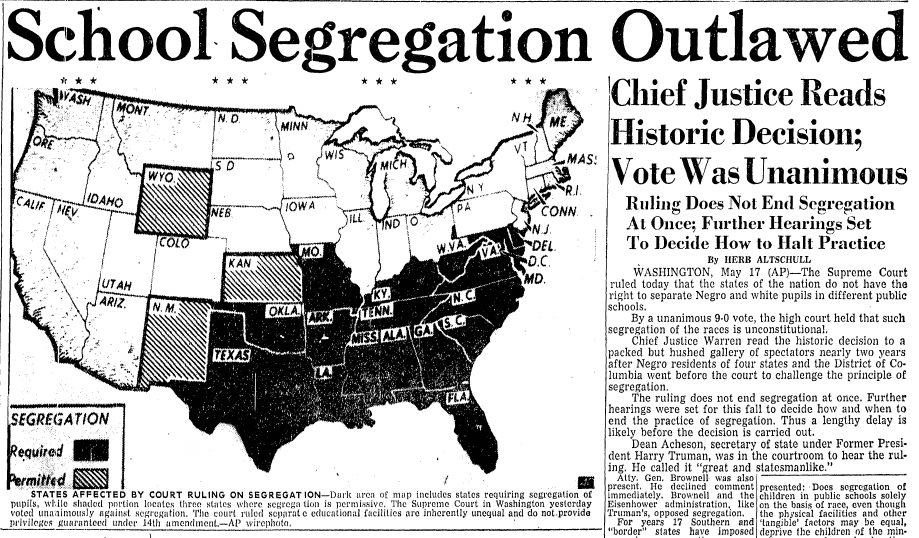
Table of Contents
H2: The History and Context of the Specific Desegregation Order:
The [Insert specific desegregation order] was implemented in [Year] in response to decades of legally mandated racial segregation in the [School district name] school system. The order, stemming from [Mention the legal basis, e.g., a federal court ruling, a consent decree], mandated [Explain the specifics of the order, e.g., busing programs, school closures, redrawing of school district boundaries]. The initial years following the order saw [Describe initial successes, e.g., increased racial diversity in some schools, improvements in educational resources in previously underserved schools]. However, these gains were frequently challenged by:
- Key players involved: [List key figures involved in the legal battles and implementation, e.g., school officials, community activists, lawyers].
- Significant milestones: [Mention important events like court hearings, appeals, community protests].
- Initial impact: [Quantify the changes in student demographics in affected schools]. For example: "Following the order, the percentage of Black students at Central High School rose from 2% to 25% within five years."
H2: The Factors Leading to the End of the Desegregation Order:
The eventual end or significant weakening of the [Insert specific desegregation order] was a culmination of several intertwined factors. These included:
- Supreme Court rulings: [Discuss relevant Supreme Court cases that shifted legal interpretations of desegregation, e.g., Milliken v. Bradley].
- Shifting public opinion: [Analyze changes in public attitudes toward school integration and busing].
- Political pressures: [Describe the role of local, state, and federal politics in the decision to end or weaken the order]. For example: "The election of a new school board, openly opposed to busing, significantly contributed to the dismantling of the desegregation plan."
- Increased resistance: [Discuss opposition from white families and communities who resisted desegregation measures].
H2: The Immediate and Long-Term Effects of the Order's End on School Integration:
The termination of the [Insert specific desegregation order] had immediate and lasting repercussions.
- Immediate consequences: [Describe the immediate impact, e.g., re-segregation of schools, changes in school demographics, increased racial tensions].
- Long-term impact: [Analyze data on student achievement, graduation rates, and educational equity across racial groups following the order's end].
- Evidence of re-segregation: [Present data indicating a return to racial segregation in schools, citing specific examples].
H3: Case Studies:
[Insert one or two relevant case studies, e.g., a specific high school that experienced dramatic shifts in its demographics after the desegregation order ended, or a school district that saw persistent achievement gaps widen after the end of the order. Provide data on student demographics, achievement levels, and any observable trends. This could include charts or graphs to visually illustrate the data.]
3. Conclusion:
The end of the [Insert specific desegregation order] serves as a powerful illustration of the complexities inherent in achieving school integration and the enduring legacy of racial segregation in American education. While initially hailed as a success by some, the order’s eventual termination ultimately led to a measurable decline in school integration and widened the achievement gap in many cases. The key takeaway is that the fight for educational equity is an ongoing process, demanding constant vigilance and proactive strategies. Understanding the end of this desegregation order is crucial to informing future strategies for achieving true school integration. Learn more about current efforts to promote educational equity and how you can get involved in promoting the impact of desegregation orders and the legacy of school desegregation through advocacy, community engagement, or further research on school integration.

Featured Posts
-
 Kivinin Kabugu Yenir Mi Besin Degeri Ve Tueketim Sekilleri
May 03, 2025
Kivinin Kabugu Yenir Mi Besin Degeri Ve Tueketim Sekilleri
May 03, 2025 -
 Belgiums Merchant Energy Market Financing A 270 M Wh Bess Project
May 03, 2025
Belgiums Merchant Energy Market Financing A 270 M Wh Bess Project
May 03, 2025 -
 Court Case Tests Limits Of Presidential Power On Tariffs
May 03, 2025
Court Case Tests Limits Of Presidential Power On Tariffs
May 03, 2025 -
 Daily Lotto Results Wednesday April 16 2025
May 03, 2025
Daily Lotto Results Wednesday April 16 2025
May 03, 2025 -
 The Truth Behind The Radio 4 Nick Robinson And Emma Barnett Hosting Split
May 03, 2025
The Truth Behind The Radio 4 Nick Robinson And Emma Barnett Hosting Split
May 03, 2025
