Taiwan's Energy Shift: Reliance On LNG After Nuclear Shutdown
Table of Contents
The Phase-Out of Nuclear Power in Taiwan
The Political and Public Pressure Behind the Nuclear Shutdown:
The decision to phase out nuclear power in Taiwan was driven by a confluence of political and public factors. The 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in Japan profoundly impacted public opinion, reigniting fears about nuclear safety and prompting widespread anti-nuclear protests. Keywords: nuclear power phaseout Taiwan, Fukushima effect, anti-nuclear movement Taiwan.
- Public outcry: Following Fukushima, public support for nuclear power plummeted, with numerous protests demanding the closure of existing plants.
- Political shifts: Successive governments faced increasing pressure to address public concerns, leading to policy changes that accelerated the phase-out timeline.
- Timeline of closures: The closure schedule involved a gradual decommissioning of Taiwan's nuclear power plants, creating a significant energy gap in the process.
Immediate Impacts of Nuclear Plant Closures:
The abrupt reduction in nuclear power generation created a substantial energy gap, posing immediate challenges to Taiwan's energy supply. Keywords: energy gap Taiwan, energy crisis Taiwan, short-term energy solutions.
- Increased reliance on fossil fuels: To meet the shortfall, Taiwan initially increased its reliance on fossil fuel-based power generation, leading to higher emissions.
- Power shortages and blackouts: In the short term, the country experienced periods of power shortages and even occasional blackouts, highlighting the urgency of finding alternative energy sources.
- Short-term solutions: These included increased imports of coal and the acceleration of other power plant projects, many of which utilized natural gas.
The Growing Importance of LNG in Taiwan's Energy Mix
Increased LNG Imports and Infrastructure Development:
With the decline of nuclear power, LNG imports have dramatically increased to fill the energy void. This surge necessitated substantial investment in infrastructure. Keywords: LNG import Taiwan, LNG terminal expansion, LNG infrastructure development.
- New LNG terminals: Significant investments have been made in building and expanding LNG import terminals to handle the growing volume of LNG shipments.
- Storage capacity: The construction of new LNG storage facilities has been crucial to ensure a reliable supply and manage price fluctuations.
- Transportation networks: Upgrades to the transportation networks, including pipelines and trucking routes, have been implemented to distribute LNG efficiently across the island.
Economic Implications of LNG Reliance:
While LNG offers a cleaner alternative to coal, its price volatility presents economic challenges. Keywords: LNG price volatility, energy costs Taiwan, LNG industry Taiwan.
- Price fluctuations: The global price of LNG can fluctuate significantly, impacting Taiwan's energy costs and potentially affecting its trade balance.
- Energy costs for consumers: Fluctuations in LNG prices directly influence electricity prices, impacting consumers and businesses alike.
- Domestic opportunities: Despite the challenges, the increased reliance on LNG has created opportunities for domestic industries involved in LNG storage, transportation, and related services.
Environmental Considerations of the LNG Shift:
Although cleaner than coal, LNG combustion still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Keywords: LNG emissions, greenhouse gas emissions Taiwan, renewable energy transition Taiwan.
- Greenhouse gas emissions: While lower than coal, LNG combustion still releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change.
- Emission reduction efforts: Taiwan is actively pursuing measures to reduce emissions from LNG power plants, including upgrading technology and exploring carbon capture and storage options.
- Transition to renewables: The increased reliance on LNG is viewed as a transitional phase, with a long-term commitment to a greater share of renewable energy.
Diversification of Energy Sources and Future Outlook
Exploring Renewable Energy Options:
Taiwan is actively pursuing a diversified energy strategy that emphasizes renewable energy sources. Keywords: renewable energy Taiwan, solar energy Taiwan, wind energy Taiwan.
- Solar and wind power: Significant investments are being made in solar and wind power generation, leveraging Taiwan's geographical advantages.
- Renewable energy infrastructure: The development of offshore wind farms and large-scale solar power plants is underway, but faces challenges like land availability and grid integration.
- Government incentives: The government has implemented various policies and incentives to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
The Long-Term Energy Strategy of Taiwan:
Taiwan's long-term energy strategy aims for a balance between energy security and environmental sustainability. Keywords: Taiwan energy strategy, energy security Taiwan, sustainable energy Taiwan.
- Energy independence: Reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels is a key goal, enhancing energy independence and resilience.
- Renewable energy targets: Ambitious targets have been set for the share of renewable energy in Taiwan's energy mix within the coming decades.
- Challenges and uncertainties: Achieving these goals involves navigating technological, economic, and political challenges.
Conclusion: Securing Taiwan's Energy Future with a Balanced Approach
Taiwan's energy transition, marked by the phase-out of nuclear power and the increasing reliance on LNG, presents both opportunities and challenges. LNG plays a critical role in bridging the energy gap, but its long-term use must be part of a broader strategy that prioritizes renewable energy sources. A balanced approach, incorporating LNG as a transition fuel while aggressively developing renewable energy infrastructure and implementing sustainable energy policies, is essential to securing Taiwan's energy future. Keywords: Taiwan energy future, LNG role in Taiwan, renewable energy solutions Taiwan, sustainable energy Taiwan. Learn more about Taiwan's energy transition and how we can work together to create a sustainable energy future for Taiwan.

Featured Posts
-
 March 18 2025 Nyt Mini Crossword Answers And Clues
May 20, 2025
March 18 2025 Nyt Mini Crossword Answers And Clues
May 20, 2025 -
 Gaza Food Supply Israel Permits Entry After Months Of Restrictions
May 20, 2025
Gaza Food Supply Israel Permits Entry After Months Of Restrictions
May 20, 2025 -
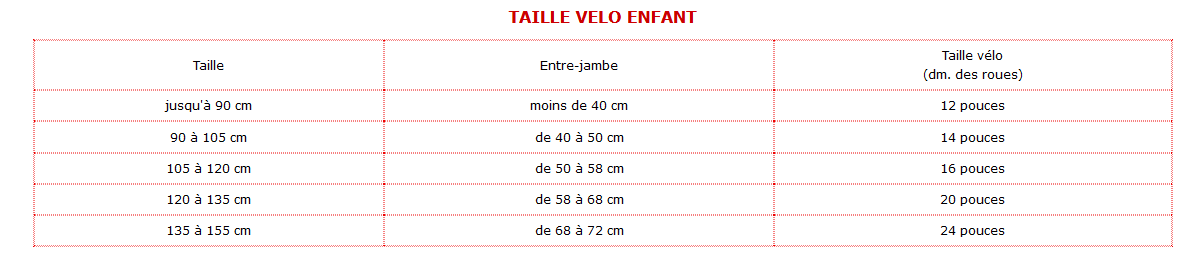 Boulevard Fhb Ex Vge Interdiction Des 2 Et 3 Roues A Partir Du 15 Avril
May 20, 2025
Boulevard Fhb Ex Vge Interdiction Des 2 Et 3 Roues A Partir Du 15 Avril
May 20, 2025 -
 Significant Increase Dubai Holdings 584 Million Reit Ipo
May 20, 2025
Significant Increase Dubai Holdings 584 Million Reit Ipo
May 20, 2025 -
 Dusan Tadic Fenerbahce Nin Unutulmaz Yildizlarindan
May 20, 2025
Dusan Tadic Fenerbahce Nin Unutulmaz Yildizlarindan
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Wayne Gretzkys Canadian Patriotism Questioned Amidst Trump Tariff And Statehood Controversy
May 20, 2025
Wayne Gretzkys Canadian Patriotism Questioned Amidst Trump Tariff And Statehood Controversy
May 20, 2025 -
 Trump Tariffs Gretzky Loyalty And Canadas Statehood Debate A Complex Issue
May 20, 2025
Trump Tariffs Gretzky Loyalty And Canadas Statehood Debate A Complex Issue
May 20, 2025 -
 Quick Facts About Wayne Gretzky A Concise Biography
May 20, 2025
Quick Facts About Wayne Gretzky A Concise Biography
May 20, 2025 -
 Wayne Gretzky Fast Facts Key Moments And Milestones In His Career
May 20, 2025
Wayne Gretzky Fast Facts Key Moments And Milestones In His Career
May 20, 2025 -
 Wayne Gretzkys Fast Facts A Quick Look At The Great Ones Life
May 20, 2025
Wayne Gretzkys Fast Facts A Quick Look At The Great Ones Life
May 20, 2025
