Spatial Concepts In Fine Arts: Requirements For A Professorship

Table of Contents
Mastery of Artistic Techniques and Media
A professor of fine arts specializing in spatial concepts needs demonstrable skill across various media, showcasing how spatial relationships are manipulated and experienced by the viewer. This practical mastery is crucial for both effective teaching and credible research in the field.
Painting & Drawing
Proficiency in representing three-dimensional space on a two-dimensional plane is fundamental. This requires a thorough understanding of perspective, chiaroscuro, and atmospheric perspective – techniques used to create the illusion of depth and volume.
- Demonstrated expertise in linear perspective: This includes a strong grasp of one-point, two-point, and three-point perspective, crucial for representing realistic space.
- Ability to create a sense of depth and volume: Mastering techniques like shading, modeling, and the use of light and shadow is critical for conveying three-dimensionality on a flat surface.
- Understanding of foreshortening and spatial illusion: The ability to accurately depict objects receding into space, manipulating size and proportion to achieve realistic depth, is essential. Understanding how to create illusions of space through artistic devices is equally important.
Sculpture & Installation Art
Skill in manipulating actual three-dimensional space is equally critical. This encompasses understanding volume, mass, negative space, and the complex spatial relationships within installations. Professors need to demonstrate not just technical skills but also an innovative approach to spatial design.
- Experience creating large-scale and site-specific works: This demonstrates an ability to work with and understand the constraints and opportunities of a given space.
- Understanding of spatial dynamics and viewer interaction: A successful professor will understand how viewers navigate and experience the work within its spatial context, actively considering the viewer’s perspective.
- Knowledge of different sculptural techniques and materials: Familiarity with a range of materials and techniques allows for a greater diversity of spatial exploration and creative problem-solving.
Digital Art & New Media
Proficiency in using digital tools to create and manipulate spatial illusions is increasingly important. This involves understanding virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and immersive environments, opening up new dimensions in spatial artistic expression.
- Familiarity with 3D modeling software: Software like Blender, Maya, or Cinema 4D is essential for creating and manipulating three-dimensional spaces digitally.
- Experience with interactive installations and virtual galleries: Understanding how to create engaging experiences in digital spaces demonstrates an understanding of the possibilities of this evolving field.
- Understanding of the unique spatial considerations of digital art: This involves grasping the differences between physical and virtual space and how spatial relationships are perceived and experienced differently in digital environments.
Theoretical Understanding of Spatial Concepts
A solid theoretical grounding is essential for effective teaching and research in the field of spatial concepts in fine arts. This involves a deep engagement with art history, spatial theory, and related disciplines.
History of Art and Spatial Theory
Knowledge of how spatial concepts have evolved across different art historical periods and movements is crucial. This understanding provides a framework for analyzing and understanding contemporary practices.
- Understanding of Renaissance perspective, Baroque theatricality, Cubist fragmentation, and other relevant movements: Tracing the historical evolution of spatial representation provides a rich theoretical backdrop.
- Familiarity with key theorists on space and art: Engaging with the writings of influential theorists such as Erwin Panofsky, Michel Foucault, and Henri Lefebvre provides a deeper theoretical understanding of space.
Semiotics and Spatial Meaning
The ability to analyze how spatial arrangements convey meaning and communicate ideas is a critical skill for a fine arts professor. Understanding semiotics allows for a deeper interpretation of artistic choices and their impact on the viewer.
- Understanding of semiotic systems and their application to spatial analysis: This involves interpreting how spatial elements function as signs and symbols, conveying meaning within a broader cultural context.
- Ability to interpret the symbolic and cultural significance of space in art: Recognizing the cultural and historical context within which spatial choices are made is crucial for a nuanced understanding of art.
Architectural and Design Influences on Spatial Concepts
Awareness of the interplay between art, architecture, and design in shaping spatial experience is essential. The relationship between these disciplines provides a broader context for understanding spatial concepts in art.
- Knowledge of architectural history and theory: Understanding the evolution of architectural design provides a crucial perspective on how space has been shaped and conceptualized across different historical periods.
- Understanding of the relationship between interior and exterior spaces: Recognizing the interplay between enclosed and open spaces informs a holistic understanding of spatial experience.
- Familiarity with the principles of environmental design: Understanding how spaces are designed to impact the behavior and experience of individuals is crucial for understanding the broader context of spatial concepts in art.
Pedagogical Skills and Research Experience
A successful professor needs to be a skilled teacher and a productive researcher. These two aspects are interconnected and mutually reinforcing.
Teaching Methodology
The ability to effectively communicate complex spatial concepts to students of varying skill levels is essential. This requires adapting teaching methods to meet diverse learning styles.
- Experience developing and delivering engaging lectures and studio critiques: Effectively presenting theoretical frameworks and providing constructive feedback on students’ work are crucial skills.
- Proficiency in mentoring and providing constructive feedback to students: Guiding and supporting student learning is a key part of a professor's role.
- Ability to adapt teaching methods to meet diverse learning styles: Catering to different learning preferences ensures inclusive and effective teaching.
Research and Publication
A strong publication record demonstrating expertise in spatial concepts in art is vital for a successful academic career. Active engagement with the scholarly community is crucial.
- Publications in peer-reviewed journals and presentations at academic conferences: This demonstrates engagement with the scholarly community and a contribution to the field.
- Active engagement with the current scholarship in the field: Staying up-to-date with current research ensures the teaching and research remain relevant and cutting-edge.
- Grants and research funding experience: Securing grants and funding demonstrates the ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the field.
Conclusion
Securing a professorship in fine arts, particularly one focused on spatial concepts, necessitates a comprehensive skill set. This includes a deep understanding and mastery of artistic techniques across various media, a robust theoretical foundation in art history and spatial theory, and proven abilities in teaching and research. By cultivating proficiency in these areas, aspiring professors can strengthen their candidacy and significantly enhance their prospects of success in this competitive field. Continue to expand your knowledge of spatial concepts in fine arts, exploring different artistic mediums and theoretical frameworks to build a compelling application and secure your future in academia. Develop your understanding of spatial design and its implications for artistic practice to stand out as a leading candidate.

Featured Posts
-
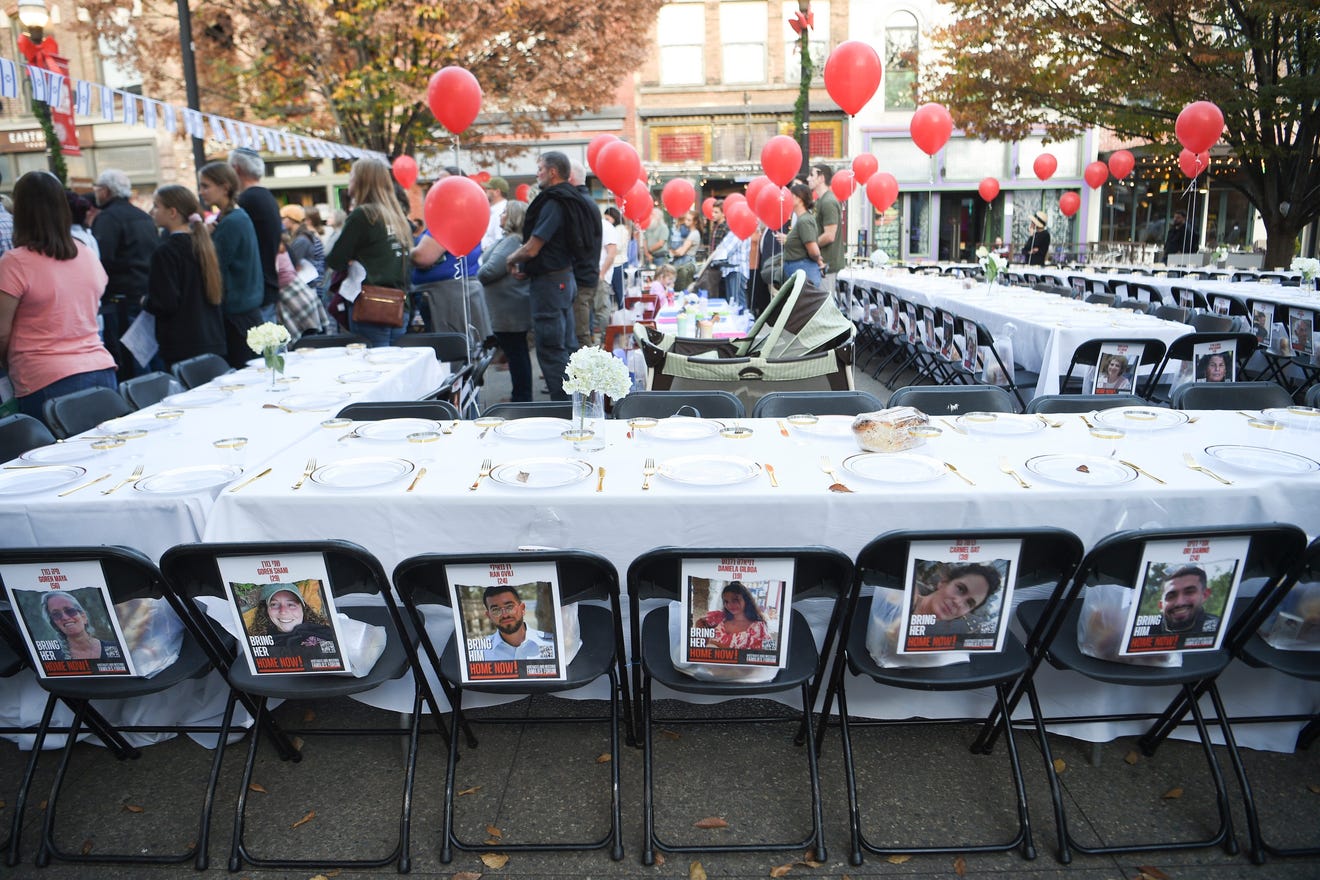 Gaza Hostage Edan Alexanders Father Holds Onto Hope Calls For Us Intervention
May 13, 2025
Gaza Hostage Edan Alexanders Father Holds Onto Hope Calls For Us Intervention
May 13, 2025 -
 Efficient Podcast Production Ais Role In Processing Repetitive Scatological Documents
May 13, 2025
Efficient Podcast Production Ais Role In Processing Repetitive Scatological Documents
May 13, 2025 -
 Is Byds 5 Minute Ev Charging Technology A Reality
May 13, 2025
Is Byds 5 Minute Ev Charging Technology A Reality
May 13, 2025 -
 La And Orange Counties Sizzle Under Record Breaking Heat Extreme Temperatures And Safety Precautions
May 13, 2025
La And Orange Counties Sizzle Under Record Breaking Heat Extreme Temperatures And Safety Precautions
May 13, 2025 -
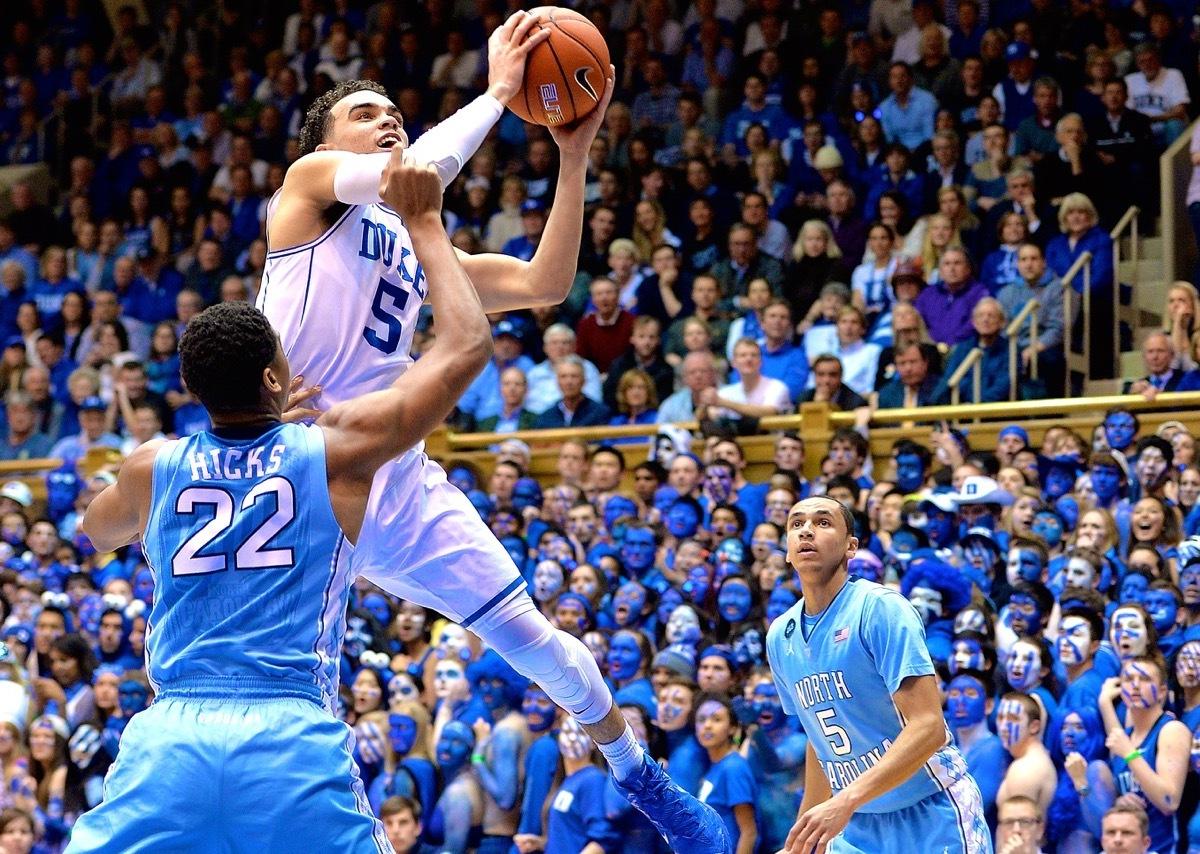 Ncaa Tournament Deja Blue Formerly Tar Heel Vs Duke
May 13, 2025
Ncaa Tournament Deja Blue Formerly Tar Heel Vs Duke
May 13, 2025
