Slight Increase In US Measles Cases: Total Reaches 1,046
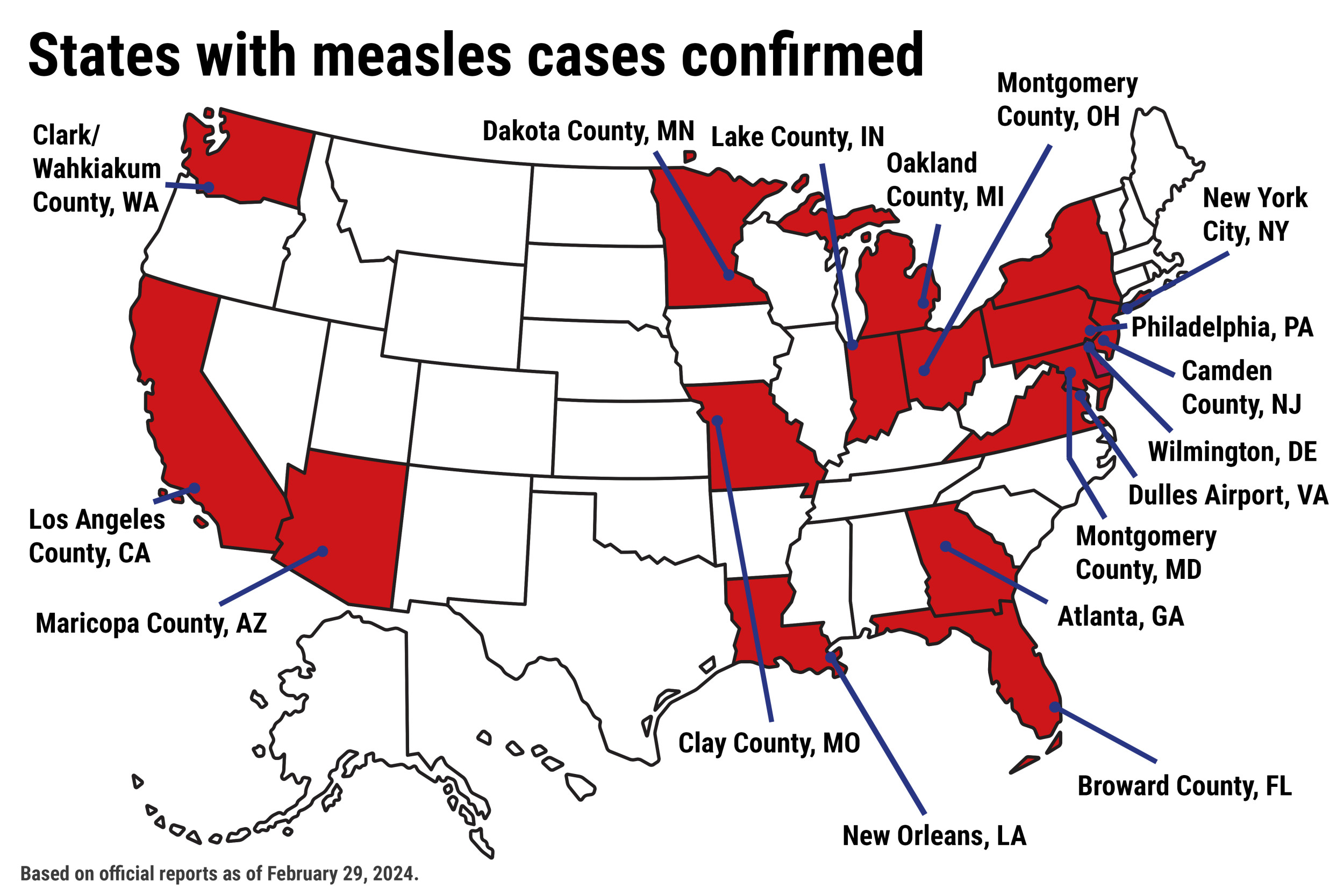
Table of Contents
Geographic Distribution of US Measles Cases
The recent increase in US measles cases isn't evenly distributed across the country. Several states have reported a disproportionate number of infections, necessitating targeted public health interventions. Understanding the geographic spread is crucial for effective resource allocation and preventing further transmission.
- Measles outbreak California: California has experienced a significant number of cases, particularly in certain counties with lower vaccination rates.
- Measles cases New York: New York has also seen a notable increase in measles cases, often linked to specific communities with lower vaccination coverage.
- Other affected states: [Insert data on other states with significant measles cases, e.g., Texas, Ohio etc.]. Use long-tail keywords like "measles cases Texas 2024" to improve SEO.
A map visualizing the distribution of measles cases across the US would be beneficial here (if available). The regional variations in case numbers are likely linked to factors such as vaccination rates, population density, and the extent of international travel within those communities. Areas with lower vaccination rates and higher population density tend to be more vulnerable to outbreaks.
Underlying Causes of the Measles Case Increase
The resurgence of measles in the US is largely attributed to decreased vaccination rates. The rise of the anti-vaccine movement and the spread of misinformation about vaccine safety have contributed significantly to this decline.
- Measles vaccine hesitancy: Hesitancy towards the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is a major contributing factor.
- Anti-vaccine movement: The influence of anti-vaccine groups and their dissemination of misleading information online and offline has eroded public trust in vaccines.
- Access to healthcare: Limited access to healthcare, particularly in underserved communities, can impede vaccination efforts.
- International travel: Outbreaks linked to international travel have also played a role, with individuals returning to the US carrying the measles virus.
Ongoing investigations into specific outbreaks are crucial for identifying the exact sources of infection and implementing targeted prevention strategies. Understanding these underlying causes is vital for designing effective public health campaigns to counter vaccine hesitancy and promote vaccination.
Public Health Response and Prevention Strategies
Public health agencies have implemented several measures to control the spread of measles and prevent further outbreaks. These strategies are critical in containing the virus and protecting vulnerable populations.
- Measles prevention: The cornerstone of measles prevention is vaccination. Public health initiatives focus on increasing vaccination rates through targeted campaigns and outreach programs.
- Measles control measures: Contact tracing, isolation of infected individuals, and quarantine measures are employed to limit the spread of the virus.
- Public health response: Rapid response teams are deployed to investigate outbreaks, identify contacts, and implement control measures.
Recommended Vaccination Schedules and MMR Vaccine Benefits:
- The CDC recommends two doses of the MMR vaccine for children, typically given at 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age.
- The MMR vaccine is highly effective, offering protection against measles, mumps, and rubella.
Resources are available to help individuals access vaccination information and assistance, including the CDC website and local health departments.
The Importance of MMR Vaccination
The MMR vaccine is the most effective way to prevent measles outbreaks and protect individuals from this highly contagious disease. It's crucial to address any misconceptions and concerns surrounding its safety and efficacy.
- MMR vaccine safety: The MMR vaccine is safe and effective, with minimal side effects. Extensive research has demonstrated its safety and efficacy.
- Long-term consequences of measles: Measles can lead to serious complications, including pneumonia, encephalitis (brain swelling), and even death.
Credible sources such as the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) and WHO (World Health Organization) provide comprehensive information about the MMR vaccine and measles prevention. These resources can help address concerns and promote informed decision-making.
Conclusion: Addressing the Rise in US Measles Cases – The Need for Continued Vigilance
The slight increase in US measles cases, reaching 1,046, highlights the ongoing need for robust public health interventions. The geographic distribution of cases, coupled with the underlying causes such as decreased vaccination rates and misinformation, underscores the urgency of action. Effective public health responses, including contact tracing and vaccination campaigns, are crucial in controlling the spread of the virus. The MMR vaccine remains the most effective tool in preventing measles outbreaks and protecting individuals from its potentially devastating consequences. To prevent measles outbreaks and boost measles immunity, we must maintain high vaccination rates and continue to address vaccine hesitancy through education and outreach. Consult your healthcare provider for vaccination information and stay informed about measles outbreaks in your area. The continued vigilance of public health officials and the community is essential in preventing future US measles cases.

Featured Posts
-
 Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm La Guia Definitiva Para La Experiencia Del Concierto Perfecto
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm La Guia Definitiva Para La Experiencia Del Concierto Perfecto
May 30, 2025 -
 New Us Solar Duties How Hanwha And Oci Plan To Expand Market Share
May 30, 2025
New Us Solar Duties How Hanwha And Oci Plan To Expand Market Share
May 30, 2025 -
 Dmps Implements New District Wide Cell Phone Policy For Next School Year
May 30, 2025
Dmps Implements New District Wide Cell Phone Policy For Next School Year
May 30, 2025 -
 Kolaborasi Rm Bts Dan Tablo Gebrakan Baru Raih Nominasi Amas 2025
May 30, 2025
Kolaborasi Rm Bts Dan Tablo Gebrakan Baru Raih Nominasi Amas 2025
May 30, 2025 -
 Emergency Red Tide Warning Cape Cod Beaches Closed
May 30, 2025
Emergency Red Tide Warning Cape Cod Beaches Closed
May 30, 2025
