Seagrass Planting Projects: Restoring Scotland's Coastline
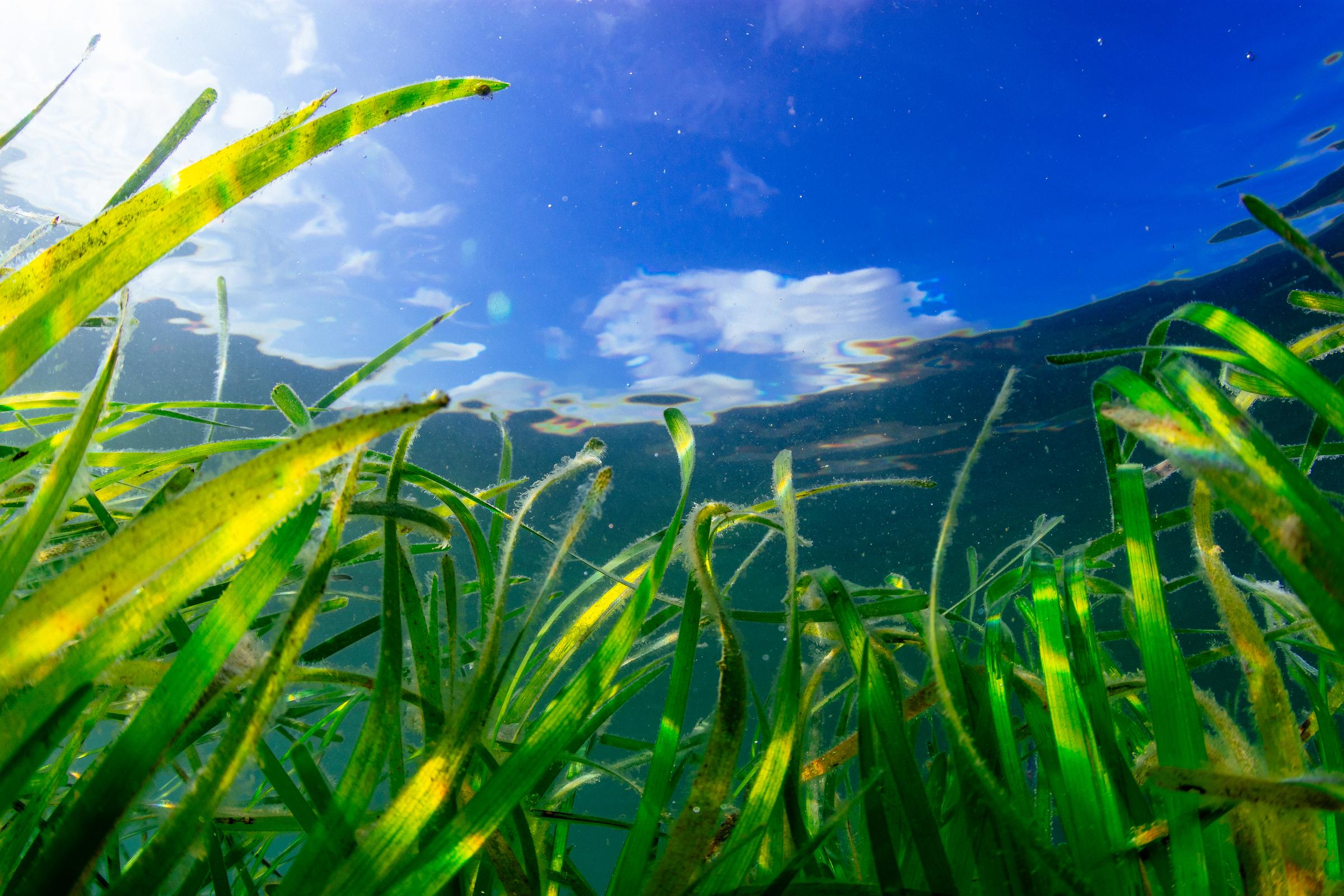

Table of Contents
The Ecological Importance of Seagrass Meadows
Seagrass meadows, often overlooked, are incredibly valuable ecosystems supporting a wealth of marine life and playing a crucial role in climate change mitigation. Their restoration is paramount for the health of Scotland's coastline.
Biodiversity Hotspots
Seagrass meadows are incredibly biodiverse, acting as nurseries and havens for countless species.
- Fish nurseries: Many commercially important fish species, such as cod, plaice, and sea bass, rely on seagrass for breeding grounds and juvenile development. The dense leaves provide protection from predators, and the rich invertebrate life provides a plentiful food source.
- Invertebrate havens: Seagrass supports a vast array of invertebrates, including shrimp, crabs, worms, and shellfish. These invertebrates form the base of the food web, supporting larger animals further up the chain.
- Shelter and protection: The dense, tangled structure of seagrass provides vital refuge for many marine animals, offering protection from strong currents, storms, and predators. This shelter is especially important for smaller, more vulnerable species.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change Mitigation
Seagrass is exceptionally effective at absorbing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, making it a vital player in the fight against climate change.
- Blue carbon sinks: Seagrass meadows are considered "blue carbon" ecosystems due to their high carbon storage capacity. They sequester carbon at a rate much faster than terrestrial forests, locking it away in the sediment for centuries.
- Coastal protection: The dense root systems of seagrass stabilize sediments, reducing coastal erosion and protecting shorelines from the impacts of storms and rising sea levels. This natural coastal defense is invaluable, particularly in the face of climate change.
Water Quality Improvement
Seagrass plays a vital role in improving water quality by acting as a natural filter.
- Nutrient cycling: Seagrass meadows actively cycle nutrients within the marine environment, reducing the risk of nutrient pollution that can lead to harmful algal blooms.
- Reduced algal blooms: By absorbing excess nutrients, healthy seagrass meadows can help prevent harmful algal blooms, which can deplete oxygen in the water and harm marine life. This contributes to a healthier and more balanced ecosystem.
Seagrass Planting Projects in Scotland: Challenges and Successes
Successfully restoring Scotland's seagrass meadows requires careful planning, appropriate techniques, and ongoing monitoring.
Site Selection and Preparation
Choosing the right location is critical for the success of any seagrass planting project.
- Water quality assessment: Thorough testing of water parameters, including salinity, temperature, and nutrient levels, is crucial to ensure the selected site is suitable for seagrass growth.
- Substrate analysis: Examining the seabed composition is essential to determine its suitability for planting. The substrate must be stable and provide adequate anchorage for seagrass roots.
Planting Techniques and Methods
Various methods are employed for seagrass planting, each suited to different conditions and circumstances.
- Seed dispersal: Scattering seeds directly onto the seabed is a cost-effective method suitable for larger areas, though success rates can vary depending on environmental conditions.
- Plug planting: Transplanting small sections of established seagrass is a more labor-intensive but often more successful approach, offering higher survival rates.
- Restoration of existing patches: Rehabilitating degraded seagrass areas through targeted interventions, such as removing pollutants or addressing sedimentation issues, is crucial for preserving existing meadows.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Long-term monitoring is vital to assess the success of seagrass planting initiatives and guide future projects.
- Seagrass growth assessment: Regular measurements of seagrass density and coverage provide essential data to track progress and identify any challenges.
- Biodiversity monitoring: Tracking changes in associated species populations allows researchers to assess the overall impact of seagrass restoration on the wider ecosystem.
Community Involvement and Future Prospects for Seagrass Restoration in Scotland
The success of seagrass restoration relies heavily on community engagement, sustained funding, and the adoption of innovative technologies.
Engaging Local Communities
Involving local communities is crucial for the long-term success of seagrass restoration projects.
- Volunteer programs: Engaging local residents in planting and monitoring activities fosters a sense of ownership and strengthens community ties.
- Educational initiatives: Raising public awareness about the importance of seagrass meadows through educational programs and outreach events is essential for securing lasting support.
Funding and Support
Securing adequate funding and ongoing support is vital for the expansion of seagrass restoration efforts in Scotland.
- Government grants and initiatives: Government funding programs supporting environmental conservation play a critical role in supporting these projects.
- Private sector partnerships: Collaborations with businesses committed to sustainability can provide crucial funding and resources.
Technological Advancements
New technologies are enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of seagrass planting projects.
- Drone technology: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras allow for improved monitoring and mapping of seagrass beds, enabling more efficient assessments of project success.
- Advanced planting techniques: Ongoing research and development are leading to the development of more efficient and effective methods for seagrass transplantation.
Conclusion
Seagrass planting projects are indispensable for the restoration of Scotland's coastline and the health of its marine environment. These initiatives not only enhance biodiversity and protect vital coastal habitats but also contribute significantly to climate change mitigation. By fostering community involvement, securing robust funding, and embracing technological advancements, Scotland can significantly expand its seagrass restoration efforts, ensuring a thriving and resilient coastal ecosystem for generations to come. Get involved and support seagrass planting projects in Scotland – help us restore our vital coastal ecosystems! Learn more about how you can participate in seagrass planting and contribute to the restoration of Scotland’s coastline.

Featured Posts
-
 Fleetwood Macs New Album Familiar Sounds Chart Topping Potential
May 04, 2025
Fleetwood Macs New Album Familiar Sounds Chart Topping Potential
May 04, 2025 -
 Britains Got Talent Addresses Fan Inquiries Regarding Teddy Magic Act
May 04, 2025
Britains Got Talent Addresses Fan Inquiries Regarding Teddy Magic Act
May 04, 2025 -
 Ambleside Couples Garden Centre Theft 300 Worth Of Goods Stolen
May 04, 2025
Ambleside Couples Garden Centre Theft 300 Worth Of Goods Stolen
May 04, 2025 -
 Le Elezioni Francesi E L Avanzata Dell Estrema Destra Il Ruolo Di Bayrou
May 04, 2025
Le Elezioni Francesi E L Avanzata Dell Estrema Destra Il Ruolo Di Bayrou
May 04, 2025 -
 Joseph Parker Vs Martin Bakole A Heavyweight Clash For The Ages
May 04, 2025
Joseph Parker Vs Martin Bakole A Heavyweight Clash For The Ages
May 04, 2025
