School Desegregation Order Terminated: A Turning Point?
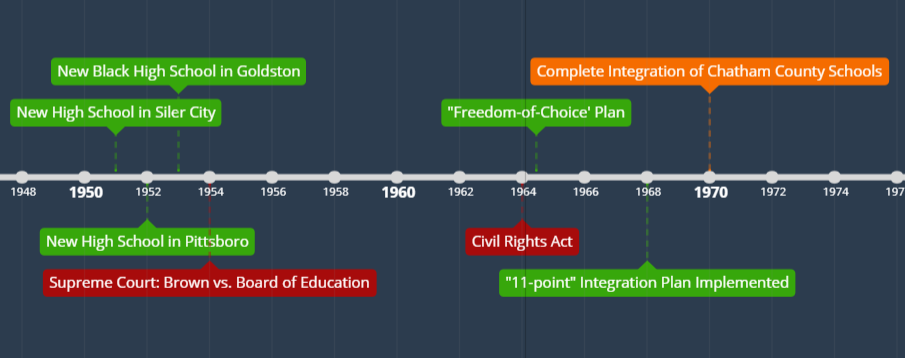
Table of Contents
The History of the Terminated Order
The termination of the desegregation order in the [Specific City/County, State] school district, implemented in [Year], represents the culmination of a decades-long legal battle. The original order, stemming from a lawsuit alleging [brief description of the legal argument, e.g., de jure segregation], mandated [specific actions taken to desegregate the schools, e.g., busing, redrawing school district boundaries]. This decision, while seemingly ending a chapter, highlights the enduring legacy of racial inequality in American education.
- Original legal challenges and court rulings: The initial lawsuit, [Name of Lawsuit if known], challenged the [State's/District's] school board's policies, arguing they violated the [Relevant Constitutional Amendment, e.g., Fourteenth Amendment's Equal Protection Clause]. Subsequent court rulings led to the implementation of the desegregation order.
- Key milestones in the implementation of the order: The order's implementation involved significant changes, including [Examples: mandatory busing programs, the redrawing of school district lines, the construction of new schools, and the implementation of specific diversity initiatives]. These actions aimed to achieve racial balance in the schools.
- Significant resistance or support encountered over the years: The order faced both considerable resistance and staunch support throughout its duration. [Describe examples of resistance, such as protests or legal challenges, and examples of support, such as community organizations working to ensure compliance]. This resistance underscores the deeply entrenched societal attitudes that continue to impede progress toward educational equity.
Immediate Impact and Consequences
The immediate aftermath of the order's termination has raised serious concerns. The potential for a swift return to racially segregated schools is a significant worry for many.
- Potential for re-segregation of schools: The lifting of the order could lead to a rapid increase in school segregation, mirroring patterns seen in other districts after similar rulings. This could result in schools with predominantly minority student populations facing significant disadvantages.
- Changes in student demographics and diversity: The demographic makeup of schools is expected to change significantly, potentially leading to a less diverse learning environment for many students. This lack of diversity can negatively impact educational outcomes and limit opportunities for cross-cultural understanding.
- Impact on educational resources and funding: Schools in predominantly minority neighborhoods often face inequities in funding and resource allocation. The termination of the order may exacerbate these existing disparities, impacting access to quality education.
- Immediate reactions from students, parents, and community leaders: Reactions to the termination have been varied, ranging from outrage and concern to cautious optimism. [Describe the range of reactions and the perspectives of different stakeholders]. This highlights the deep emotional and political stakes involved in this issue.
Long-Term Implications for Educational Equity
The termination of this order has far-reaching implications for educational equity across the nation.
- Potential for setting a precedent for other desegregation orders: This decision could embolden challenges to other desegregation orders nationwide, potentially unraveling decades of progress toward racial integration in schools.
- Impact on federal and state policies regarding school integration: The ruling may influence future legislation and policies related to school integration, potentially weakening federal oversight and enforcement.
- The role of continued legal challenges and activism: The fight for educational equality will likely continue through legal challenges and activism, highlighting the ongoing need for vigilance and advocacy.
- The ongoing relevance of the concept of school desegregation in modern society: The decision underscores the enduring relevance of the concept of school desegregation in ensuring equal educational opportunities in a society still grappling with systemic racism.
The Role of Socioeconomic Factors
Even without explicit legal mandates for segregation, socioeconomic factors significantly contribute to school segregation.
- Residential segregation and its impact on school districts: Residential segregation creates de facto segregation in schools, concentrating poverty and minority populations in certain districts.
- Differences in school funding based on property taxes and other factors: Funding disparities based on property taxes and other factors often disadvantage schools in low-income communities, perpetuating educational inequities.
- Access to quality education and resources in different communities: Unequal access to quality teachers, resources, and educational programs further exacerbates the educational disparities between different communities.
Looking Ahead: Strategies for Maintaining Educational Equality
Despite the challenges, strategies exist to maintain educational equality.
- Increased funding for under-resourced schools: Increased and equitable funding for under-resourced schools is crucial to address existing disparities and ensure equal opportunities for all students.
- Community-based initiatives to promote integration: Community-based initiatives focused on promoting integration and bridging divides can foster a more inclusive and equitable educational environment.
- The continued importance of equitable school assignment policies: Equitable school assignment policies are essential for promoting diversity and preventing the re-segregation of schools.
- The need for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of school diversity: Regular monitoring and evaluation of school diversity are necessary to identify and address any emerging trends towards segregation.
Conclusion
The termination of this school desegregation order serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing struggle for educational equality in the United States. While the immediate effects are felt locally, the implications are far-reaching and raise profound questions about the future of school integration and the pursuit of a truly equitable educational system. Understanding the history, impact, and potential long-term consequences of this decision is crucial to fostering meaningful dialogue and developing effective strategies to combat segregation and promote equal opportunity for all students. We must continue to advocate for policies and practices that actively support the dismantling of school segregation and ensure that all children have access to quality education, regardless of their race or socioeconomic status. The fight for educational equity, even after the termination of this school desegregation order, must continue.

Featured Posts
-
 The Mental Health Crisis In Ghana Insufficient Psychiatrists And Its Impact
May 03, 2025
The Mental Health Crisis In Ghana Insufficient Psychiatrists And Its Impact
May 03, 2025 -
 Daisy May Cooper And Anthony Huggins Engagement Confirmed
May 03, 2025
Daisy May Cooper And Anthony Huggins Engagement Confirmed
May 03, 2025 -
 Report Play Station Showcase Imminent After Two Year Hiatus
May 03, 2025
Report Play Station Showcase Imminent After Two Year Hiatus
May 03, 2025 -
 Solidarnosc I Republika Czy To Wyjatkowe Wyroznienie Zasluguje Na Uwage
May 03, 2025
Solidarnosc I Republika Czy To Wyjatkowe Wyroznienie Zasluguje Na Uwage
May 03, 2025 -
 The Missing Piece Souness On Arsenals Title Challenge
May 03, 2025
The Missing Piece Souness On Arsenals Title Challenge
May 03, 2025
