Rosenberg's Analysis: Canadian Labour Data And Interest Rate Expectations
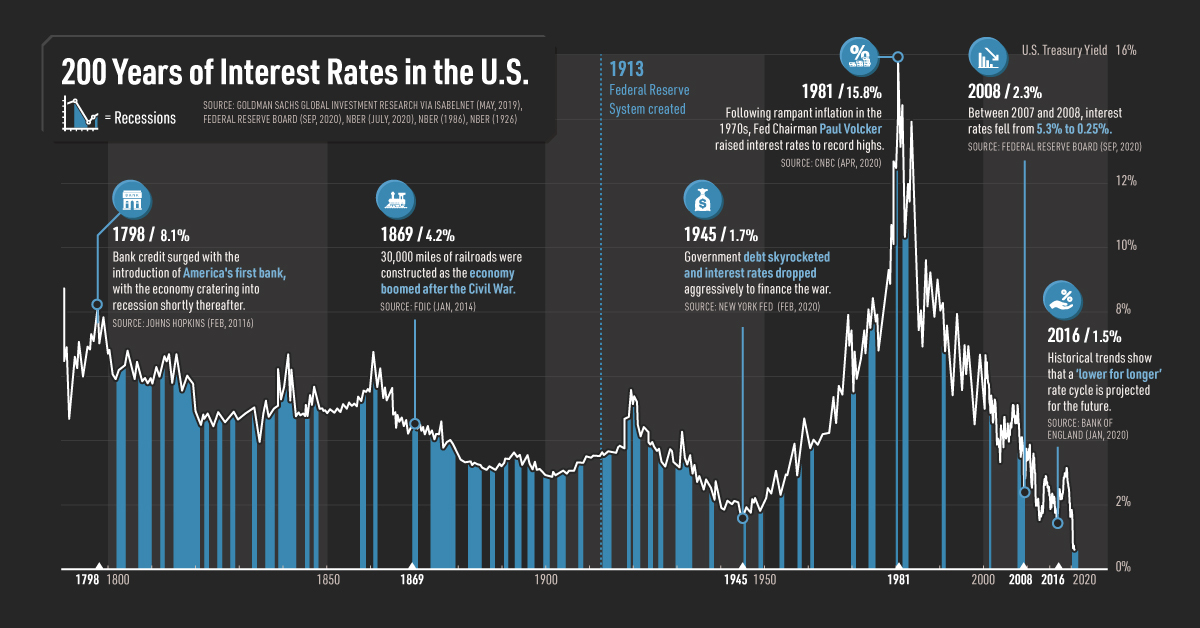
Table of Contents
Recent Trends in Canadian Employment Data
The Canadian employment landscape has shown mixed signals recently. While job creation has been positive in certain sectors, concerns remain about unemployment rates, particularly in specific provinces. Analyzing the latest employment figures reveals a nuanced picture. We must look beyond the headline numbers to understand the underlying trends.
- Unemployment Rate: The national unemployment rate has fluctuated, and understanding provincial variations is critical. For instance, provinces heavily reliant on specific industries might experience higher or lower unemployment than the national average.
- Sectoral Variations: Job growth has been uneven across sectors. While the technology sector has experienced robust growth, other sectors like manufacturing have shown more moderate gains or even declines. This sectoral disparity highlights the need for a granular analysis of the Canadian employment market.
- Wage Growth: Average hourly earnings have been increasing, but the pace of growth and its impact on inflation need careful consideration. Is wage growth outpacing productivity, potentially contributing to inflationary pressure?
- Labour Force Participation: Changes in the labour force participation rate – the percentage of the working-age population actively seeking employment – offer another key indicator of the overall health of the labour market. A declining participation rate could mask underlying weakness.
- Seasonal Adjustments: It is essential to consider the impact of seasonal adjustments on the data to gain a clearer understanding of underlying trends, as seasonal fluctuations can significantly impact short-term figures.
Inflationary Pressures and their Influence on Interest Rate Decisions
The relationship between employment data and inflation is intrinsically linked. High employment often leads to increased consumer spending and demand-pull inflation. Analyzing current inflation rates and their drivers is crucial for predicting the Bank of Canada's response.
- Current Inflation Rate: The current inflation rate in Canada, and its components (energy, food, etc.), significantly influence the Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions. Persistent inflation above the target range necessitates intervention.
- Supply Chain Issues: Global supply chain disruptions have played a role in inflationary pressures. These challenges impact the availability and cost of goods, contributing to rising prices.
- Wage-Price Spiral: The interaction between wage growth and inflation is a key concern. If wage increases lead to further price hikes, a wage-price spiral can emerge, making inflation more persistent and challenging to control.
- Bank of Canada's Inflation Target: The Bank of Canada has a specific inflation target, typically around 2%. Deviations from this target prompt adjustments to monetary policy, including interest rate changes.
Rosenberg's Perspective on the Canadian Economy
David Rosenberg's economic analysis offers a contrarian viewpoint on the Canadian economy, often diverging from mainstream forecasts. Understanding his perspective is vital for a comprehensive assessment.
- Rosenberg's Outlook: Rosenberg's forecasts often highlight potential risks and vulnerabilities in the economy that are not always reflected in mainstream analyses.
- Inflation Predictions: His predictions regarding inflation trends often differ from consensus forecasts, sometimes suggesting a more pessimistic outlook.
- Interest Rate Expectations: He may anticipate interest rate adjustments by the Bank of Canada that differ from market expectations.
- Underlying Factors: His analysis usually focuses on key factors like debt levels, productivity growth, and global economic conditions, influencing his economic predictions.
Implications for Investors and Businesses
Rosenberg's analysis has significant implications for investors and businesses. Understanding his perspective can inform investment strategies and business planning.
- Investment Implications: Investors can use Rosenberg's insights to adjust their portfolio allocations, considering potential risks and opportunities in different asset classes.
- Impact on Borrowing Costs: Businesses need to anticipate potential changes in borrowing costs as interest rates fluctuate. This impacts investment decisions and profitability.
- Consumer Spending: Changes in interest rates affect consumer spending and overall economic growth. Higher rates can curb spending, impacting businesses relying on consumer demand.
- Hedging Strategies: Businesses can use hedging strategies to mitigate the risks associated with interest rate fluctuations and protect their bottom line.
Conclusion: Applying Rosenberg's Analysis to Navigate Canadian Labour Data and Interest Rate Expectations
This analysis demonstrates the complex relationship between Canadian labour data and interest rate expectations, viewed through the lens of Rosenberg's often-contrarian economic framework. Understanding these dynamics is critical for investors, businesses, and policymakers to navigate the Canadian economic landscape effectively. To gain a deeper understanding, continue your analysis of Rosenberg's insights into Canadian labour data and interest rate expectations. Stay updated on the latest Rosenberg analysis concerning Canadian employment and interest rate forecasts, paying close attention to upcoming economic data releases. This will allow you to make more informed decisions in the ever-evolving Canadian economic environment.

Featured Posts
-
 Analyzing The Psg Vs Inter Milan Champions League Final Matchup
May 31, 2025
Analyzing The Psg Vs Inter Milan Champions League Final Matchup
May 31, 2025 -
 Hudbay Minerals Staff Evacuated From Flin Flon Manitoba Due To Wildfires
May 31, 2025
Hudbay Minerals Staff Evacuated From Flin Flon Manitoba Due To Wildfires
May 31, 2025 -
 Houstons Rat Problem A Drug Addiction Crisis
May 31, 2025
Houstons Rat Problem A Drug Addiction Crisis
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguia Denies Doping Claims After Positive Test Result
May 31, 2025
Munguia Denies Doping Claims After Positive Test Result
May 31, 2025 -
 Ouistreham Lancement De La Saison Estivale Avec Son Carnaval
May 31, 2025
Ouistreham Lancement De La Saison Estivale Avec Son Carnaval
May 31, 2025
