Retail Sales Growth Impacts Bank Of Canada's Monetary Policy
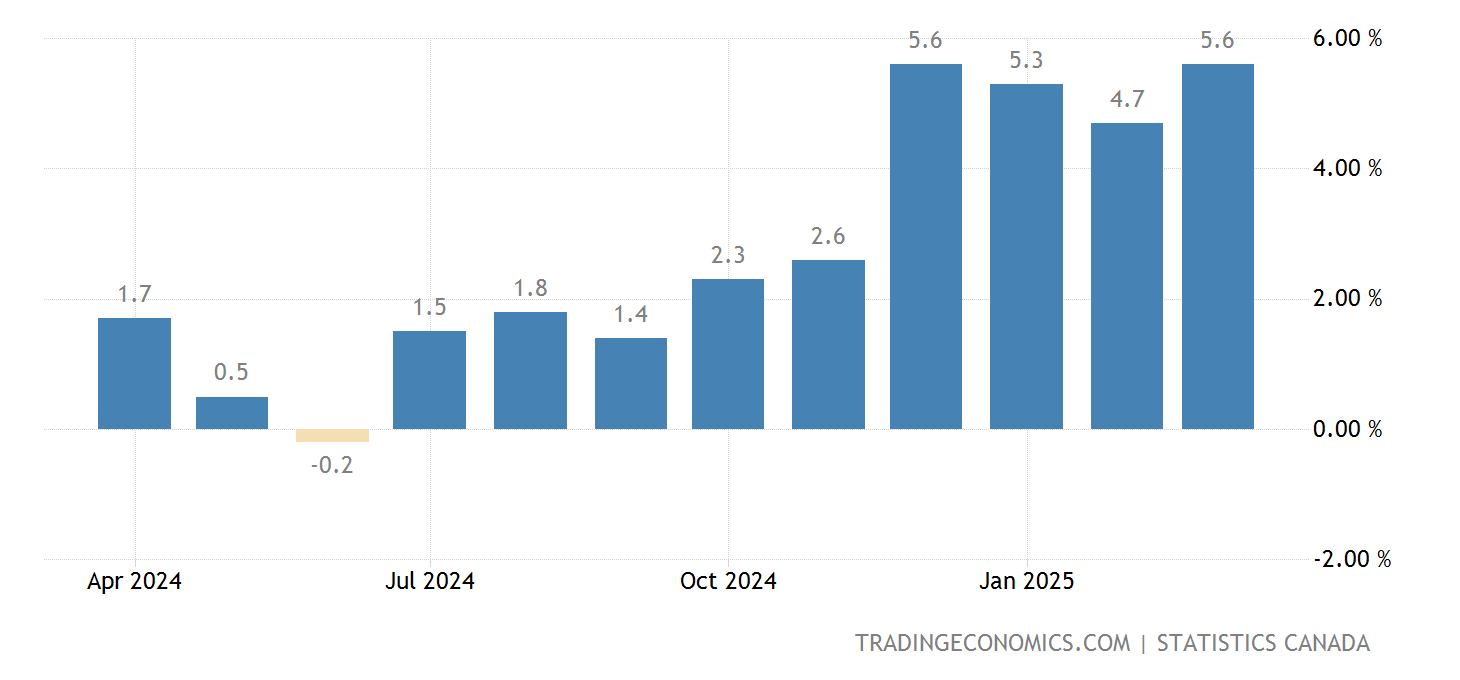
Table of Contents
Retail Sales as a Key Economic Indicator
Retail sales data serves as a leading indicator of the overall health of the Canadian economy. It provides a direct measure of consumer spending, a significant driver of economic growth. Analyzing retail sales allows economists and policymakers to gauge consumer confidence and predict future economic trends. The data is often categorized into durable goods (long-lasting items like appliances) and non-durable goods (short-lived items like groceries), offering a more nuanced picture of consumer behavior.
- Strong retail sales suggest robust consumer confidence and a healthy expansion of the economy. This positive sentiment usually translates into increased investment and job creation.
- Weak retail sales, conversely, signal a potential economic slowdown or even a recession. Decreased spending can lead to business cutbacks and job losses, creating a ripple effect throughout the economy.
- Seasonal adjustments are crucial for accurately interpreting retail sales data. Factors like holidays and weather patterns can significantly influence sales figures, so adjustments are necessary to reveal underlying trends. Understanding these adjustments is vital for accurate analysis of the Canadian economy and the Bank of Canada's subsequent actions.
Inflationary Pressures and Retail Sales Growth
Rapid growth in retail sales can fuel inflationary pressures. When consumer demand significantly outpaces the available supply, prices inevitably rise – a phenomenon known as demand-pull inflation. This is particularly true when supply chain disruptions occur, further limiting the availability of goods and pushing prices even higher. This upward pressure on prices directly impacts the purchasing power of consumers and overall economic stability.
- High consumer demand exceeding supply leads to price increases across various sectors. This erodes consumer purchasing power, potentially dampening future retail sales growth.
- Increased wages, while positive for workers, can contribute to inflationary pressure as businesses pass increased labor costs onto consumers.
- The Bank of Canada meticulously monitors retail sales data to anticipate and mitigate potential inflationary risks, using it as a crucial component in formulating its monetary policy.
The Bank of Canada's Response to Retail Sales Growth
The Bank of Canada utilizes retail sales data, alongside other key economic indicators, to inform its monetary policy decisions. Its primary tool is adjusting interest rates. When retail sales growth is strong and inflation is rising, the Bank may increase interest rates to cool down the economy. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing consumer spending and thus moderating demand-pull inflation.
- Increased interest rates aim to curb inflation by discouraging borrowing and investment, thereby slowing economic activity. This can also affect the housing market, another important economic indicator.
- Rate hikes can directly impact consumer spending, leading to a decrease in retail sales. The effect is often a lag, and the Bank carefully considers the potential consequences of any adjustments.
- The Bank of Canada constantly balances the need for economic growth with the imperative to control inflation. It's a delicate act of balancing the various economic indicators to promote sustainable and stable growth.
Other Factors Influencing Monetary Policy Decisions
While retail sales are a significant factor, they are not the sole determinant of the Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions. Other important indicators include:
- Employment data: Provides insights into wage growth, which influences consumer spending power and inflation. A strong labor market, with high employment and rising wages, can contribute to inflationary pressures.
- Housing market activity: Housing market trends reflect overall economic sentiment and consumer confidence. A booming housing market, for example, can inflate asset prices and increase overall demand in the economy.
- Global economic conditions: International events and global economic trends significantly impact the Canadian economy and therefore influence the Bank of Canada's decisions.
Conclusion: Understanding the Impact of Retail Sales Growth on the Bank of Canada's Monetary Policy
The relationship between retail sales growth, inflation, and the Bank of Canada's monetary policy is complex yet crucial to understanding the Canadian economy. Strong retail sales, while indicative of economic health, can lead to inflationary pressures, prompting the Bank to adjust interest rates to maintain stability. However, retail sales are just one piece of a larger economic puzzle. By understanding the interplay of various factors, including employment rates, housing market activity, and global economic conditions, we can better appreciate the Bank of Canada's policy decisions. To make informed financial decisions and understand the Canadian economy more comprehensively, monitor retail sales growth and understand Bank of Canada policy. Stay informed about monetary policy and the impact of retail sales on the Canadian economy to make better financial choices for yourself and your business.

Featured Posts
-
 Iifa 2025 Nora Fatehis Dazzling Alexandre Vauthier Gown
May 27, 2025
Iifa 2025 Nora Fatehis Dazzling Alexandre Vauthier Gown
May 27, 2025 -
 Un Pundit Turco Habla Sobre La Importancia De Osimhen Para El Galatasaray
May 27, 2025
Un Pundit Turco Habla Sobre La Importancia De Osimhen Para El Galatasaray
May 27, 2025 -
 Kai Cenat A Compilation Of Hilarious Facial Expressions
May 27, 2025
Kai Cenat A Compilation Of Hilarious Facial Expressions
May 27, 2025 -
 Congres Du Ps L Opposition A Olivier Faure Tente De S Unir
May 27, 2025
Congres Du Ps L Opposition A Olivier Faure Tente De S Unir
May 27, 2025 -
 Trumps Support For Nippon Steel Concerns And Considerations
May 27, 2025
Trumps Support For Nippon Steel Concerns And Considerations
May 27, 2025
