Reciprocal Tariffs: Assessing Second-Order Risks To Key Indian Sectors
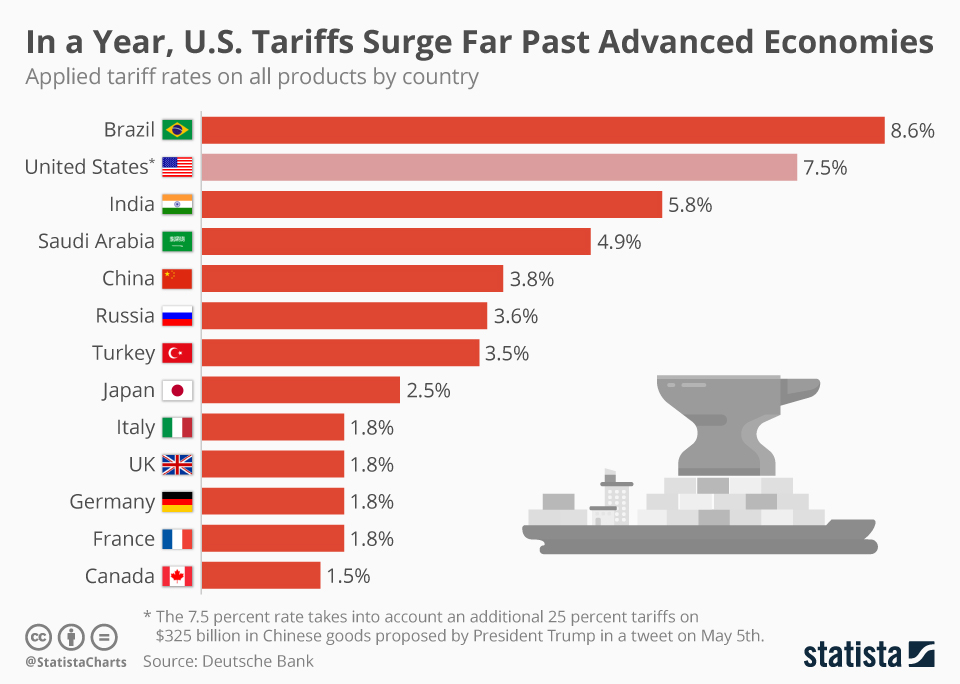
Table of Contents
Impact of Reciprocal Tariffs on Indian Exports
Retaliatory tariffs imposed by trading partners directly impact Indian export volumes and profitability across various sectors. This section explores the challenges and potential solutions.
Reduced Export Competitiveness
Reciprocal tariffs significantly reduce the competitiveness of Indian exports in global markets. The immediate consequences include:
- Loss of market share: Higher prices due to tariffs make Indian goods less attractive compared to competitors from countries not subject to the same tariffs.
- Price increases: To maintain profitability, exporters may absorb some of the tariff impact, leading to price increases and reduced competitiveness.
- Decreased demand: Higher prices lead to reduced demand for Indian goods in international markets, resulting in lower export volumes.
- Challenges in accessing foreign markets: Tariffs act as trade barriers, making it more difficult for Indian businesses to access and penetrate foreign markets.
These challenges affect sectors like textiles, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural products disproportionately. The impact varies depending on the specific product, the destination market, and the magnitude of the tariff.
Diversification Strategies and Market Adaptation
To mitigate the negative impact of reciprocal tariffs, Indian businesses must adopt diversification strategies and adapt their market approach. This involves:
- Exploring new markets: Identifying and penetrating new markets less affected by retaliatory tariffs is crucial to reduce dependence on vulnerable markets.
- Product diversification: Expanding product lines and offering a wider range of goods reduces reliance on single products vulnerable to tariff increases.
- Enhancing value addition: Increasing the value added to products can improve their competitiveness and offset the impact of tariffs.
- Negotiating trade agreements: Actively participating in and negotiating favorable trade agreements with other countries can secure preferential access to markets and reduce tariff barriers.
These strategies require investment in research, development, and market intelligence, but they are vital for long-term export growth and resilience in the face of global trade uncertainties.
Second-Order Effects on Domestic Industries
The impact of reciprocal tariffs extends beyond direct export impacts, affecting domestic industries through increased input costs and reduced consumption.
Increased Input Costs
Reciprocal tariffs increase the cost of imported raw materials and intermediate goods, significantly impacting the profitability and competitiveness of various Indian industries. This leads to:
- Increased prices for raw materials: Tariffs on imported raw materials directly translate into higher production costs.
- Reduced profit margins: Higher input costs squeeze profit margins, forcing businesses to either absorb the costs or raise prices.
- Potential for job losses: Reduced profitability can lead to cost-cutting measures, including job losses and reduced investment.
- Inflationary pressures: Increased input costs contribute to inflationary pressures across the economy, impacting consumers and businesses alike.
Impact on Domestic Consumption
Higher prices due to increased input costs and reduced competition impact domestic consumption and economic growth. This can result in:
- Reduced consumer spending: Increased prices for goods and services reduce consumer purchasing power, leading to lower demand.
- Decreased demand: Lower consumer demand translates into lower production levels and potential economic slowdown.
- Potential for economic slowdown: Reduced consumer spending and business investment can lead to a broader economic slowdown.
- Impact on various consumer goods sectors: Industries producing consumer goods are particularly vulnerable to decreased demand resulting from higher prices.
Understanding these interconnected effects is vital for developing effective policy responses.
Sector-Specific Analysis: Identifying Vulnerable Sectors
Specific Indian sectors face unique challenges due to reciprocal tariffs.
Agriculture
Indian agricultural exports like rice, sugar, and cotton are highly vulnerable to reciprocal tariffs. The consequences include:
- Impact on farmer incomes: Reduced export volumes and lower prices directly impact the incomes of farmers.
- Export restrictions: Some countries may impose import restrictions in addition to tariffs, further limiting export opportunities.
- Government support measures: Government intervention through subsidies and support programs may be necessary to mitigate the impact on farmers.
Information Technology (IT)
India's IT sector, heavily reliant on exports and global collaborations, is also exposed to risks:
- Impact on outsourcing: Protectionist measures in other countries can limit outsourcing opportunities for Indian IT firms.
- Potential for protectionist measures: Countries may implement policies favoring domestic IT companies, impacting Indian firms' competitiveness.
- Competition from other countries: Increased competition from other countries offering similar services can further reduce market share.
Pharmaceuticals
India's generic pharmaceutical industry, a global supplier of affordable medicines, faces significant challenges:
- Impact on access to medicines globally: Tariffs can limit access to affordable medicines in developing countries.
- Pricing strategies: Companies may need to adjust pricing strategies to remain competitive in the face of tariffs.
- Intellectual property rights: Trade disputes can involve issues related to intellectual property rights, impacting the pharmaceutical industry.
Conclusion
Reciprocal tariffs present substantial second-order risks to various key sectors within the Indian economy. Understanding the interconnectedness between export competitiveness, domestic industries, and consumer markets is crucial for developing robust mitigation strategies. Diversification of export markets and strengthening domestic industries are essential. Proactive policy interventions, including targeted support for vulnerable sectors and strategic trade negotiations, are also necessary to navigate the complexities of the global trade landscape. Further research is needed to comprehensively assess and address the implications of reciprocal tariffs and formulate sound policy responses. Ignoring these risks could significantly hamper India's economic progress. A strategic approach to managing reciprocal tariffs is crucial for the long-term health of the Indian economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Kibris A Direkt Ucuslar Tatar In Son Goerueslerinin Analizi
May 15, 2025
Kibris A Direkt Ucuslar Tatar In Son Goerueslerinin Analizi
May 15, 2025 -
 Npo En College Van Omroepen Weg Naar Vertrouwen
May 15, 2025
Npo En College Van Omroepen Weg Naar Vertrouwen
May 15, 2025 -
 Npo Medewerkers Beschrijven Angstcultuur Onder Leiding Leeflang
May 15, 2025
Npo Medewerkers Beschrijven Angstcultuur Onder Leiding Leeflang
May 15, 2025 -
 Angstcultuur Bij De Npo Medewerkers Spreken Zich Uit Over Leeflangs Leiding
May 15, 2025
Angstcultuur Bij De Npo Medewerkers Spreken Zich Uit Over Leeflangs Leiding
May 15, 2025 -
 The Promise Of Gender Euphoria Scales In Improving Transgender Wellbeing
May 15, 2025
The Promise Of Gender Euphoria Scales In Improving Transgender Wellbeing
May 15, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Actie Tegen Npo De Rol Van Frederieke Leeflang Onder De Loep
May 15, 2025
Actie Tegen Npo De Rol Van Frederieke Leeflang Onder De Loep
May 15, 2025 -
 Analyse De Actie Tegen Npo Baas Frederieke Leeflang
May 15, 2025
Analyse De Actie Tegen Npo Baas Frederieke Leeflang
May 15, 2025 -
 De Gevolgen Van De Actie Tegen Npo Directeur Frederieke Leeflang
May 15, 2025
De Gevolgen Van De Actie Tegen Npo Directeur Frederieke Leeflang
May 15, 2025 -
 Wordt Frederieke Leeflang Npo Baas Getroffen Door Een Nieuwe Actie
May 15, 2025
Wordt Frederieke Leeflang Npo Baas Getroffen Door Een Nieuwe Actie
May 15, 2025 -
 Reacties Op De Actie Gericht Tegen Frederieke Leeflang Npo Baas
May 15, 2025
Reacties Op De Actie Gericht Tegen Frederieke Leeflang Npo Baas
May 15, 2025
