Private Credit Market Cracks: A Weekly Analysis Of Recent Turmoil

Table of Contents
The private credit market refers to the lending activities outside the traditional banking system. It includes financing from private equity firms, hedge funds, and specialized credit funds. This market plays a crucial role in financing businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMBs) and those deemed too risky for traditional bank loans. Its importance in the overall financial system is undeniable, as it provides crucial capital for economic growth and innovation. Understanding the current turmoil in this sector is therefore paramount.
Causes of the Private Credit Market Instability
Several factors have contributed to the recent instability in the private credit market.
Rising Interest Rates and Inflationary Pressures
Higher interest rates, driven by efforts to combat inflation, have significantly increased borrowing costs for private credit funds and their borrowers. This has led to:
- Increased funding costs: Private credit funds rely on various sources of capital, often borrowing at floating rates tied to benchmarks like LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate) or SOFR (Secured Overnight Financing Rate). As these benchmarks rise, the cost of funding for these loans increases substantially.
- Reduced investor appetite: Higher interest rates make alternative investments, such as government bonds, more attractive, leading to decreased investor demand for private credit products.
- Difficulty refinancing existing debt: Funds and borrowers with existing debt face higher costs when refinancing, creating refinancing risk.
Overreliance on Leveraged Lending
The private credit market has witnessed a significant increase in leveraged lending – loans with a high debt-to-equity ratio. This strategy, while potentially lucrative, presents inherent risks:
- Increased default risk: Highly leveraged borrowers are more vulnerable to economic downturns, making defaults more likely.
- Vulnerability to economic downturns: Even small changes in economic conditions can trigger financial distress for highly leveraged borrowers.
- Concerns about underwriting standards: Concerns have been raised about the rigor of underwriting standards in some segments of the private credit market, increasing the overall risk profile. Leveraged lending, by its nature, amplifies these risks.
Lack of Liquidity and Transparency
The private credit market is often characterized by a lack of transparency and liquidity. This opacity presents significant challenges:
- Difficulty assessing risk: The limited availability of data makes it difficult for investors and lenders to accurately assess the risk associated with private credit investments.
- Limited data availability: Unlike publicly traded securities, information on private credit transactions is not readily available, hindering effective risk management.
- Potential for information asymmetry: Differences in information access between lenders and borrowers can lead to adverse selection and moral hazard, increasing the chances of defaults. Improved transparency and standardized reporting are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Consequences of the Private Credit Market Cracks
The cracks appearing in the private credit market have several significant consequences.
Impact on Credit Availability
The turmoil is already restricting access to credit for many SMBs, who rely heavily on the private credit market for funding. This translates to:
- Reduced lending activity: Private credit funds are becoming more selective in their lending, resulting in reduced overall lending activity.
- Higher borrowing costs for SMBs: Even those securing loans face significantly higher borrowing costs compared to the recent past.
- Potential for economic slowdown: Reduced access to credit can stifle economic growth and job creation, particularly for smaller businesses that are the backbone of many economies.
Spillovers to Other Financial Markets
The private credit market's instability poses a risk of contagion to other parts of the financial system. Potential spillover effects include:
- Increased volatility in equity and bond markets: Concerns about the health of the private credit market can lead to wider market volatility.
- Potential for a wider credit crunch: If the problems in the private credit market escalate, it could trigger a broader credit crunch, impacting all sectors of the economy.
- Impact on banks and other financial institutions: Banks and other financial institutions with exposure to the private credit market could face losses and increased regulatory scrutiny.
Investor Losses and Market Sentiment
The current turmoil is already leading to investor losses and a decline in market sentiment. This includes:
- Reduced investor returns: Investors in private credit funds are experiencing lower-than-expected returns, or even losses.
- Increased risk aversion: The market instability is increasing risk aversion amongst investors, making them less willing to invest in riskier assets.
- Potential for capital flight: Investors may pull their capital out of private credit altogether, exacerbating the market's problems.
Potential Solutions and Outlook for the Private Credit Market
Addressing the challenges in the private credit market requires a multi-pronged approach.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Reforms
Increased regulatory oversight and potential reforms are crucial for enhancing the stability of the private credit market. This includes:
- Stronger capital requirements: Higher capital requirements would increase the resilience of private credit funds to losses.
- Improved risk management frameworks: More robust risk management practices are necessary to mitigate the risks associated with leveraged lending and opaque transactions.
- Increased transparency standards: Mandating greater transparency in reporting and data disclosure would improve investor understanding and facilitate better risk assessment.
Improved Due Diligence and Underwriting
More rigorous risk assessment and loan underwriting are essential for preventing future defaults. This includes:
- More thorough credit checks: Lenders need to conduct more thorough background checks and credit assessments on borrowers.
- Stricter lending criteria: Lenders should adopt more conservative lending criteria to reduce the risk of defaults.
- Better risk modeling: Sophisticated risk models can help lenders better assess the probability of default and price the risk appropriately.
Market Consolidation and Restructuring
Market consolidation and restructuring of distressed assets could also play a role in stabilizing the private credit market. This may involve:
- Mergers and acquisitions: Consolidation through mergers and acquisitions could lead to stronger, more resilient institutions.
- Debt workouts: Negotiated restructurings of distressed debt can help prevent defaults and mitigate losses.
- Liquidation of non-performing loans: Liquidating non-performing loans can help clean up the market and improve overall health.
Conclusion: Understanding the Private Credit Market Cracks and Looking Ahead
The recent turmoil in the private credit market stems from a confluence of factors, including rising interest rates, excessive leverage, and a lack of transparency. The consequences are far-reaching, potentially impacting credit availability for businesses, creating volatility in broader financial markets, and leading to investor losses. Addressing this requires a concerted effort involving increased regulatory oversight, improved due diligence, and potential market consolidation.
Stay informed about developments in the private credit market. Regularly review our weekly analysis to navigate this evolving landscape and make informed decisions regarding your private credit investments. [Link to subscribe to future updates]

Featured Posts
-
 Bill Ackmans View The Trade Wars Timeline And Its Winners And Losers
Apr 27, 2025
Bill Ackmans View The Trade Wars Timeline And Its Winners And Losers
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Is A Fifth Champions League Place For The Premier League Now Inevitable
Apr 27, 2025
Is A Fifth Champions League Place For The Premier League Now Inevitable
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Professional Analysis Ariana Grandes Style Evolution
Apr 27, 2025
Professional Analysis Ariana Grandes Style Evolution
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Anti Vaccine Activists Role In Hhs Review Of Autism Vaccine Claims Sparks Outrage
Apr 27, 2025
Anti Vaccine Activists Role In Hhs Review Of Autism Vaccine Claims Sparks Outrage
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Controversial Mafs Groom Sam Carraros Brief Appearance On Stans Love Triangle
Apr 27, 2025
Controversial Mafs Groom Sam Carraros Brief Appearance On Stans Love Triangle
Apr 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Investigation Reveals Lingering Toxic Chemicals In Buildings After Ohio Train Derailment
Apr 28, 2025
Investigation Reveals Lingering Toxic Chemicals In Buildings After Ohio Train Derailment
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Long Term Effects Of Ohio Train Derailment Toxic Chemical Residue In Buildings
Apr 28, 2025
Long Term Effects Of Ohio Train Derailment Toxic Chemical Residue In Buildings
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Ohio Train Derailment Persistent Toxic Chemical Contamination In Buildings
Apr 28, 2025
Ohio Train Derailment Persistent Toxic Chemical Contamination In Buildings
Apr 28, 2025 -
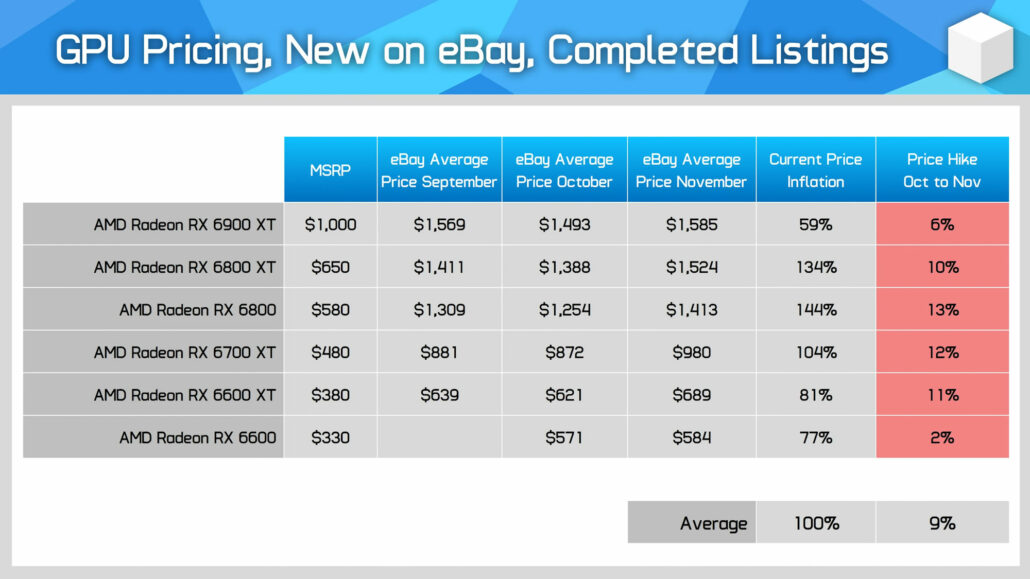 Rising Gpu Prices What To Expect In The Coming Months
Apr 28, 2025
Rising Gpu Prices What To Expect In The Coming Months
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Navigating The High Cost Of Gpus In 2024
Apr 28, 2025
Navigating The High Cost Of Gpus In 2024
Apr 28, 2025
