Plastic Glove Project: Strengthening The RCN-Vet Nursing Partnership

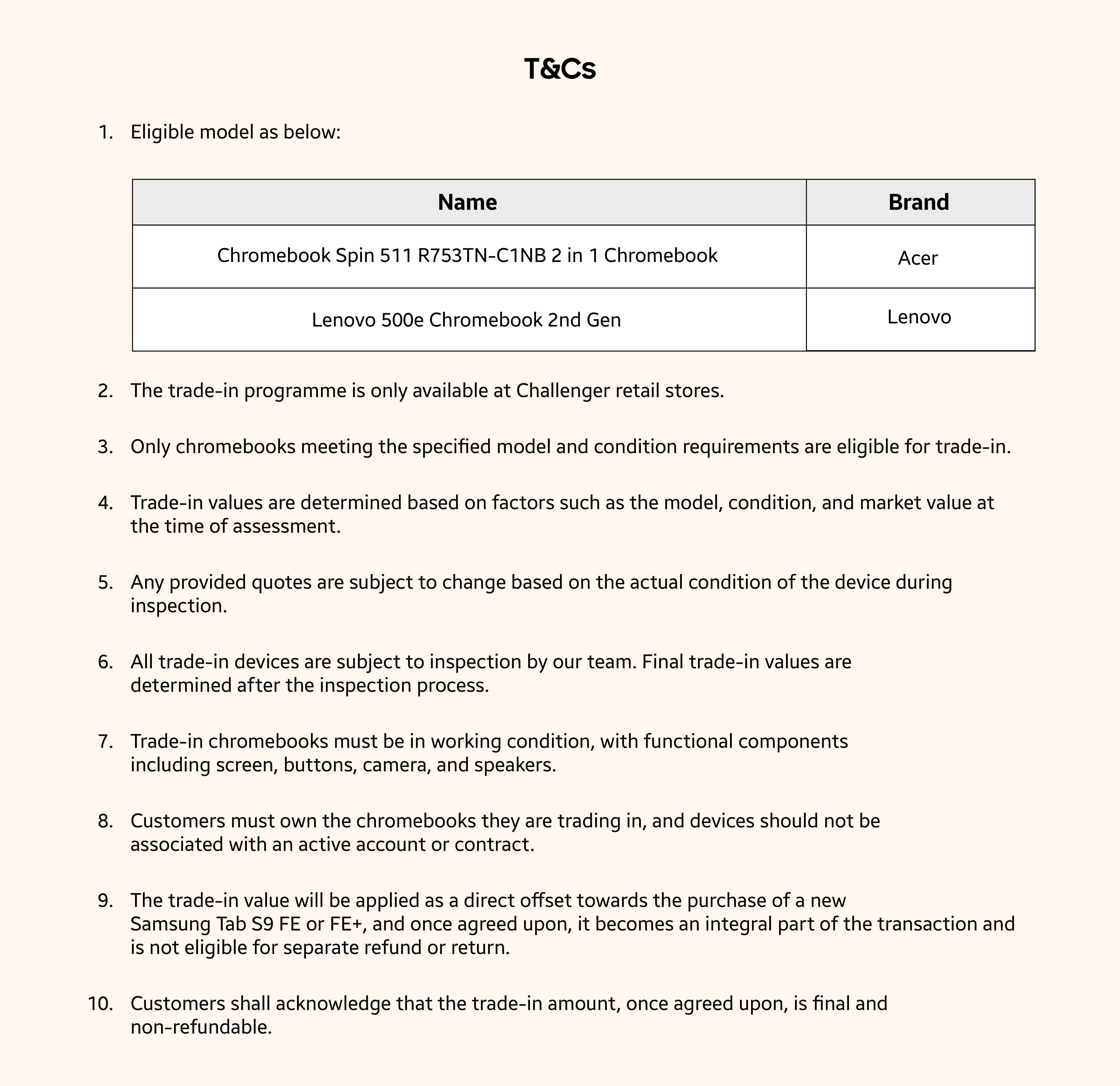
Table of Contents
Enhancing Infection Control Protocols Through Collaboration
The Plastic Glove Project facilitated a significant advancement in infection control protocols by fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange between RCN nurses and veterinary nurses. This interdisciplinary approach proved invaluable in improving safety and hygiene standards across both human and animal healthcare settings.
Shared Knowledge and Best Practices
The project created a platform for sharing best practices related to infection control. This included:
- Sharing of best practices for hand hygiene: Participants shared and refined techniques for effective handwashing and hand sanitization, crucial in preventing the spread of pathogens.
- Appropriate PPE usage (including plastic glove selection and disposal): The project emphasized the correct selection and use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including plastic gloves, focusing on appropriate glove types for different situations and safe disposal methods to minimize contamination risk.
- Waste management: Participants discussed and implemented improved waste management strategies, including the segregation and disposal of contaminated materials, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
- Discussions on emerging infectious diseases and their impact on both human and animal health: The collaborative environment allowed for the discussion of emerging infectious diseases and their potential impact on both human and animal populations, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of preventative measures.
- Joint training workshops and online resources: The project facilitated the development and delivery of joint training workshops and online resources, ensuring consistent and up-to-date infection control practices across both professions.
Standardized Procedures for Safer Handling of Hazardous Materials
Harmonizing protocols for handling hazardous materials and waste was another key achievement. This resulted in improved safety for all healthcare workers. Specific improvements included:
- Development of standardized operating procedures: The project led to the creation of standardized operating procedures (SOPs) for handling hazardous materials and waste, ensuring consistency and reducing the risk of errors.
- Implementation of color-coded waste disposal systems: A color-coded waste disposal system was implemented to simplify waste segregation and improve safety.
- Improved tracking and reporting of incidents: A more robust system for tracking and reporting incidents related to hazardous materials handling was put in place, allowing for better identification of areas for improvement.
Promoting Sustainable Practices in Healthcare
Beyond infection control, the Plastic Glove Project prioritized sustainable practices within the healthcare sector.
Reducing Plastic Waste and Environmental Impact
A core focus was on minimizing the environmental impact of plastic glove usage:
- Exploration of biodegradable alternatives: The project explored and evaluated the viability of biodegradable and sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic gloves.
- Implementation of glove recycling programs: Recycling programs were implemented to reduce the amount of plastic waste sent to landfills.
- Education campaigns on reducing plastic consumption: Education campaigns were launched to raise awareness about the environmental impact of plastic glove use and promote more responsible consumption.
- Improved waste segregation and management: Improved waste segregation and management practices further reduced the environmental impact of plastic waste.
Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Optimization
The project demonstrated that sustainable practices can also be cost-effective:
- Analysis of cost savings from waste reduction initiatives: Analysis showed significant cost savings resulting from reduced waste disposal fees and lower consumption of single-use plastics.
- Improved inventory management and procurement strategies: The project led to improvements in inventory management and procurement strategies, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing waste.
- Identification of cost-effective alternatives to single-use plastics: The project identified cost-effective alternatives to single-use plastics, further contributing to cost savings and sustainability goals.
Strengthening the RCN-Vet Nursing Partnership
The Plastic Glove Project played a crucial role in strengthening the professional relationship between the RCN and veterinary nursing professionals.
Improved Communication and Networking
The project fostered improved communication and networking:
- Joint conferences and workshops: Joint conferences and workshops provided opportunities for knowledge sharing and networking.
- Establishment of communication channels for knowledge sharing: Dedicated communication channels were established to facilitate ongoing knowledge exchange and collaboration.
- Collaborative research projects: The project spurred collaborative research projects focusing on shared areas of interest.
Shared Advocacy and Policy Influence
The combined expertise strengthened advocacy efforts:
- Joint submissions to policy makers: Joint submissions to policy makers were made to advocate for improved healthcare policies and standards.
- Participation in relevant committees and working groups: Representatives from both professions participated in relevant committees and working groups, influencing policy development.
- Development of joint advocacy campaigns: Joint advocacy campaigns were developed to raise awareness and influence policy change.
Conclusion
The Plastic Glove Project stands as a testament to the successful collaboration between the RCN and veterinary nursing professionals. By focusing on infection control, sustainability, and partnership building, this initiative has significantly improved healthcare practices and strengthened the working relationship between these two vital sectors. The project’s success emphasizes the benefits of interdisciplinary collaboration in addressing complex challenges. Further development and expansion of similar initiatives will continue to strengthen the RCN-Vet Nursing partnership and improve healthcare standards across the board. To learn more about the Plastic Glove Project and how you can contribute to this important partnership, visit [link to relevant website/resource]. Let’s continue to build upon the success of this Plastic Glove Project and foster further collaborations to improve healthcare for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Important Weather Information Wind Advisory Plus Snow On Tuesday
May 31, 2025
Important Weather Information Wind Advisory Plus Snow On Tuesday
May 31, 2025 -
 Authenticating A Potential Banksy In Westcliff Bournemouth
May 31, 2025
Authenticating A Potential Banksy In Westcliff Bournemouth
May 31, 2025 -
 Guardians Opening Day Weather History Is It Typically This Cold
May 31, 2025
Guardians Opening Day Weather History Is It Typically This Cold
May 31, 2025 -
 101 Samsung Tablet A Challenger To The Apple I Pad
May 31, 2025
101 Samsung Tablet A Challenger To The Apple I Pad
May 31, 2025 -
 High Fentanyl Levels Found In Princes Autopsy March 26th 2016
May 31, 2025
High Fentanyl Levels Found In Princes Autopsy March 26th 2016
May 31, 2025
