Ozempic And Beyond: The Growing Applications Of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists In Medicine
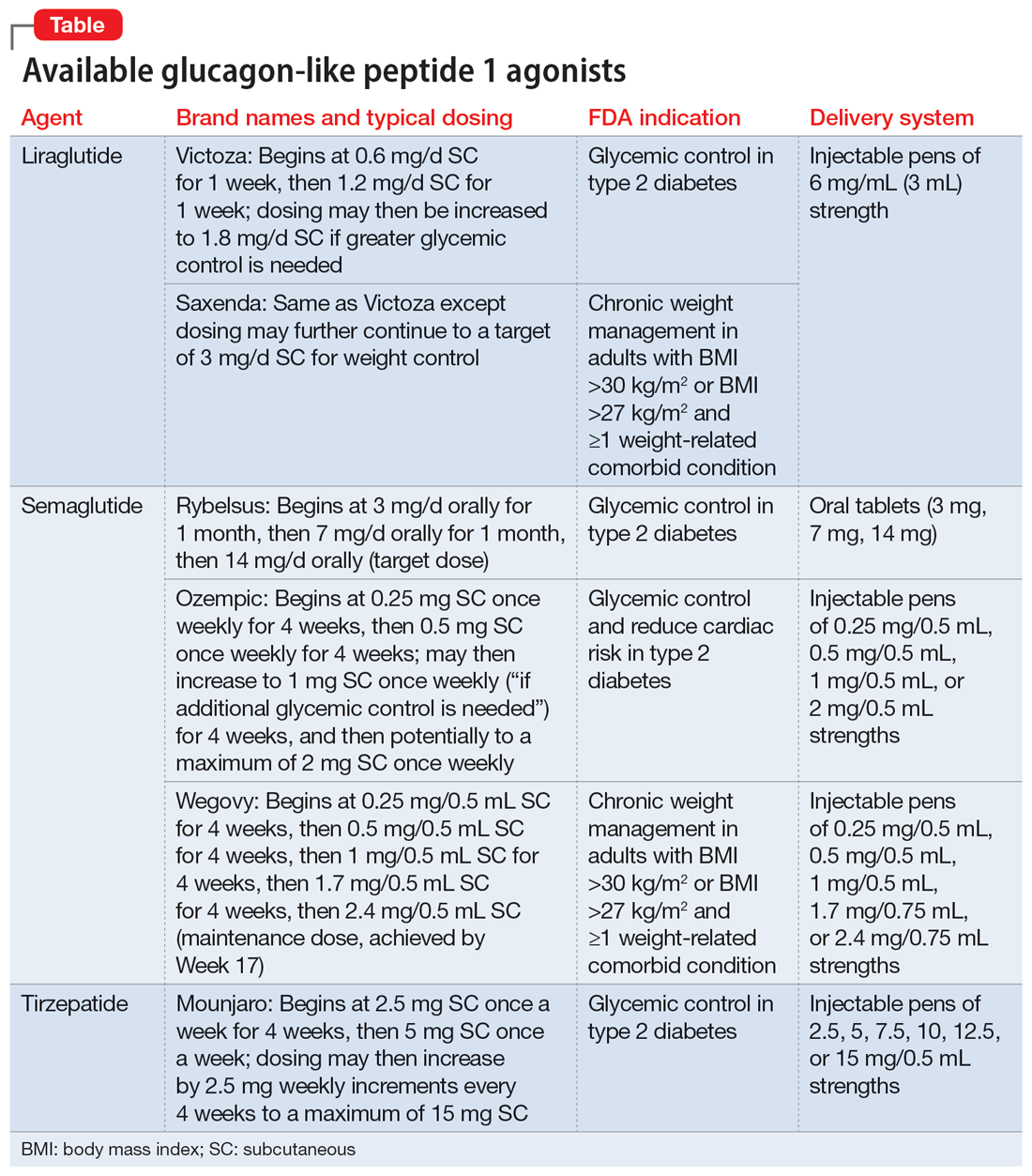
Table of Contents
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Mechanisms of Action and Benefits
GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a naturally occurring hormone that plays a crucial role in glucose regulation and appetite control. Their mechanism of action involves multiple pathways leading to significant clinical benefits.
Weight Management and Obesity
GLP-1 agonists effectively combat obesity by influencing several key factors:
- Appetite Suppression: They reduce appetite by acting on the brain's satiety centers, leading to decreased food intake.
- Increased Satiety: They promote a feeling of fullness, helping individuals consume fewer calories.
- Improved Metabolism: Some evidence suggests they may also slightly increase metabolic rate.
The efficacy of different GLP-1 agonists varies. Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) and Liraglutide (Saxenda) have demonstrated considerable weight loss in clinical trials. However, it's crucial to acknowledge potential side effects, including nausea, diarrhea, and constipation, which are often dose-dependent and tend to lessen over time. Moreover, GLP-1 agonists play a crucial role in managing obesity-related comorbidities such as hypertension and dyslipidemia, further improving overall cardiovascular health.
Type 2 Diabetes Management
GLP-1 receptor agonists are highly effective in managing type 2 diabetes by:
- Improving Glycemic Control: They enhance insulin secretion in response to glucose, thus lowering blood sugar levels.
- Increasing Insulin Sensitivity: They improve how the body utilizes insulin, leading to better glucose uptake by cells.
- Protecting Pancreatic Beta-Cells: They may help preserve the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Drugs like Ozempic and Victoza have demonstrated significant reductions in HbA1c levels (a marker of long-term blood sugar control), contributing to better overall diabetes management and reduced risks of complications.
Cardiovascular Benefits
Growing evidence suggests GLP-1 receptor agonists offer significant cardiovascular protection:
- Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Events: Large clinical trials have shown a reduced risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death.
- Improved Heart Rate Variability: They improve the heart's ability to adapt to changing demands.
- Blood Pressure Control: Studies have shown improvements in blood pressure regulation.
These cardiovascular benefits are likely linked to their impact on weight management, improved glycemic control, and other metabolic improvements. The significant clinical trial data supporting these benefits strengthens the case for GLP-1 agonists in preventing and managing cardiovascular disease.
Expanding Applications of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
The therapeutic potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists extends beyond weight management and diabetes. Research is underway exploring their applications in diverse areas:
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Preliminary research suggests GLP-1 receptor agonists may offer benefits in treating NAFLD and NASH by:
- Reducing Liver Fat Content: They may help decrease the amount of fat accumulation in the liver.
- Improving Liver Inflammation: They might reduce the inflammation associated with NASH.
While more extensive studies are needed, the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in managing NAFLD represents a promising avenue for future therapies.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Studies show promise in using GLP-1 agonists to manage PCOS symptoms such as:
- Weight Loss: Assisting in weight management, a key factor in improving PCOS symptoms.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Addressing insulin resistance, a common feature of PCOS.
- Menstrual Regularity: Potentially restoring regular menstrual cycles.
The impact on ovarian function and hormone levels is still under investigation, but early findings are encouraging.
Other Potential Applications
Research is ongoing to explore the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists in other conditions, including:
- Alzheimer's disease: Some studies suggest a potential neuroprotective effect.
- Certain types of cancer: Preliminary research indicates a potential role in slowing cancer progression.
- Chronic kidney disease: Studies are evaluating their impact on kidney function.
These areas are in early stages of investigation, and further research is crucial to determine their effectiveness.
Conclusion
GLP-1 receptor agonists have emerged as versatile and effective treatments for a range of metabolic and cardiovascular conditions. Their ability to induce weight loss, improve blood sugar control, and provide cardiovascular protection makes them valuable therapeutic tools. From managing type 2 diabetes and obesity to showing promise in treating NAFLD and PCOS, the applications of GLP-1 receptor agonists continue to expand. The ongoing research exploring their potential in other areas further highlights their importance in modern medicine. Learn more about how GLP-1 receptor agonists might benefit you. Speak to your doctor today about exploring GLP-1 receptor agonist therapies.

Featured Posts
-
 Is A Kalvin Phillips Return To Leeds On The Cards This Summer
May 28, 2025
Is A Kalvin Phillips Return To Leeds On The Cards This Summer
May 28, 2025 -
 One Piece Pirates Who Served Multiple Captains
May 28, 2025
One Piece Pirates Who Served Multiple Captains
May 28, 2025 -
 Cuaca Bali Besok Dominan Berawan Potensi Hujan Ringan
May 28, 2025
Cuaca Bali Besok Dominan Berawan Potensi Hujan Ringan
May 28, 2025 -
 Euro Millions Live Results 34m Tuesday April 15th Draw
May 28, 2025
Euro Millions Live Results 34m Tuesday April 15th Draw
May 28, 2025 -
 Sanctions Looming Trumps Response To Deteriorating Relations With Russias Putin
May 28, 2025
Sanctions Looming Trumps Response To Deteriorating Relations With Russias Putin
May 28, 2025
