Over-the-Counter Birth Control: Increased Access And Its Implications Post-Roe

Table of Contents
Increased Accessibility and Convenience
The current system of obtaining birth control presents numerous barriers for many women. Over-the-counter birth control aims to dismantle these obstacles, promoting greater accessibility and convenience.
Breaking Down Barriers to Access
Many women face significant challenges in accessing prescription birth control. These barriers include:
- Long travel distances to clinics: Women in rural areas or those lacking reliable transportation often face lengthy journeys to reach healthcare providers.
- High cost of prescription birth control: The price of prescription birth control can be prohibitive, particularly for those without adequate insurance coverage. Even with insurance, co-pays and deductibles can create financial strain.
- Insurance coverage issues: Navigating insurance complexities, including pre-authorization requirements and limited formularies, adds another layer of difficulty for many women seeking birth control.
- Appointment scheduling difficulties: Scheduling appointments with healthcare providers can be challenging due to limited availability, long wait times, and inflexible scheduling options.
Over-the-counter birth control could significantly mitigate these issues. The increased convenience of purchasing birth control at a pharmacy or drugstore eliminates the need for appointments, reduces travel time and costs, and simplifies the overall process. This improved accessibility is a crucial step towards ensuring reproductive healthcare for all women.
Empowerment and Self-Determination
Access to over-the-counter birth control is intrinsically linked to women's empowerment and self-determination.
- Reduced reliance on healthcare providers: OTC birth control empowers women to manage their reproductive health without the need for constant medical intervention.
- Ability to discreetly manage reproductive health: Purchasing birth control OTC offers increased privacy and avoids the potential stigma associated with seeking reproductive healthcare services.
- Increased privacy: Women can purchase and use birth control without disclosing their reproductive health decisions to others.
This increased autonomy allows women to make informed decisions about their bodies and futures, free from external constraints. Accessibility directly translates to increased control over reproductive health choices, fostering a sense of agency and empowerment.
Potential Public Health Benefits
Wider access to over-the-counter birth control promises substantial public health benefits.
Reduced Unintended Pregnancies
Increased access to readily available and affordable birth control is strongly correlated with a reduction in unintended pregnancies.
- Improved family planning: Convenient access allows for better family planning and enables women to proactively manage their reproductive lives.
- Reduced reliance on less effective methods: Women may be more likely to consistently use effective contraception when it is easily accessible, reducing reliance on less effective methods like withdrawal.
- Potential decrease in abortions: While not a direct replacement for all abortion needs, increased access to effective contraception is widely believed to reduce the number of unintended pregnancies, thus potentially reducing the demand for abortions. Studies have repeatedly shown this correlation. (Cite relevant studies here).
Improved Sexual and Reproductive Health Outcomes
The impact of over-the-counter birth control extends beyond pregnancy prevention.
- Early detection and management of reproductive health issues: Increased interaction with healthcare providers during the process of obtaining birth control might lead to earlier detection and management of various reproductive health concerns.
- Increased comfort and knowledge about contraception: Greater accessibility can lead to increased comfort levels and a broader understanding of different contraceptive methods.
- Potential reduction in sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Consistent use of contraception can also contribute to a decrease in the transmission of STIs.
Convenient access to contraception encourages consistent use, leading to better sexual and reproductive health outcomes for women.
Potential Challenges and Concerns
While the potential benefits of over-the-counter birth control are significant, several challenges and concerns must be addressed.
Misinformation and Self-Medication
The ease of access to OTC birth control raises concerns about potential misuse and the spread of misinformation.
- Lack of proper medical guidance: Some individuals might not understand how to properly use certain methods or might not be aware of potential side effects.
- Potential for incorrect usage: Improper use can lead to reduced effectiveness or adverse health consequences.
- Increased risk of side effects if not used as directed: Clear and comprehensive instructions, coupled with robust public education campaigns, are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Educational initiatives targeted at informing women about appropriate usage, potential side effects, and interactions with other medications are essential for safe and effective use of over-the-counter birth control.
Equity and Access for Marginalized Communities
Ensuring equitable access for all women, regardless of their socioeconomic status or geographic location, is paramount.
- Addressing potential disparities in access: Over-the-counter availability alone doesn't guarantee equitable access. Efforts must be made to ensure affordability and accessibility in underserved communities.
- Ensuring affordable options: The cost of OTC birth control must be affordable for all women, preventing price-based disparities in access.
- Promoting awareness in underserved communities: Targeted outreach programs are needed to raise awareness about the availability and benefits of over-the-counter birth control in communities with limited access to information.
Strategies to address these disparities include subsidized access programs, community-based education initiatives, and addressing underlying socioeconomic inequalities.
Political and Ethical Considerations
The issue of over-the-counter birth control is intertwined with significant political and ethical debates.
- Religious objections: Certain religious groups oppose contraception and might lobby against broader access to OTC birth control.
- Concerns about government regulation: Appropriate government oversight is necessary to ensure product safety and efficacy while avoiding excessive regulation that could hinder access.
- Potential impact on insurance coverage: The shift to OTC birth control could alter insurance coverage models and potentially impact the affordability of other reproductive healthcare services.
A nuanced approach is necessary to navigate these complex issues, ensuring a balanced perspective that respects diverse viewpoints while prioritizing women's health and reproductive rights.
Conclusion
The availability of over-the-counter birth control presents a significant opportunity to improve access to reproductive healthcare, particularly in the post-Roe landscape. While challenges exist regarding misinformation, equity, and political considerations, the potential public health benefits – including reduced unintended pregnancies, improved health outcomes, and increased autonomy for women – are substantial. Further research, public education initiatives, and thoughtful policymaking are crucial to maximizing the positive impacts of over-the-counter birth control while mitigating potential risks. Ultimately, ensuring widespread and equitable access to over-the-counter birth control is a critical step towards empowering women and improving reproductive health for all. Learn more about accessing over-the-counter birth control options in your area and advocate for policies that support broader access to this vital form of reproductive healthcare.

Featured Posts
-
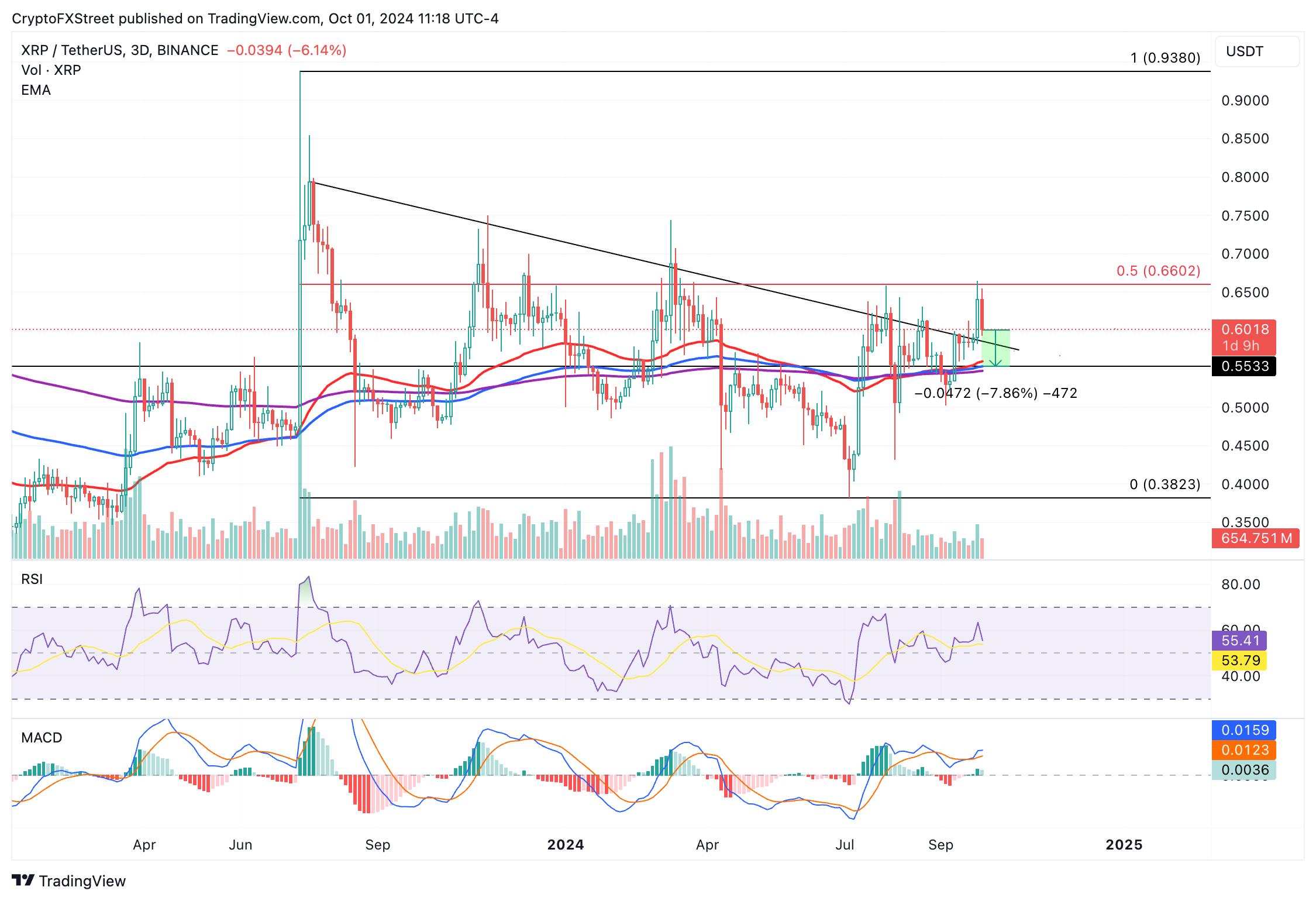 Ripples Dubai License Impact On Xrp Price And 10 Prediction
May 01, 2025
Ripples Dubai License Impact On Xrp Price And 10 Prediction
May 01, 2025 -
 Project Muse A Shared Experience Of Academic Research
May 01, 2025
Project Muse A Shared Experience Of Academic Research
May 01, 2025 -
 Navigating The Chinese Market The Struggles Faced By Bmw Porsche And Competitors
May 01, 2025
Navigating The Chinese Market The Struggles Faced By Bmw Porsche And Competitors
May 01, 2025 -
 France Clinches Six Nations Championship With Scotland Defeat
May 01, 2025
France Clinches Six Nations Championship With Scotland Defeat
May 01, 2025 -
 China Life Investment Strength Fuels Profit Increase
May 01, 2025
China Life Investment Strength Fuels Profit Increase
May 01, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Pressing Economic Concerns For Canadas Next Government
May 01, 2025
The Pressing Economic Concerns For Canadas Next Government
May 01, 2025 -
 How Open Ais Chat Gpt Is Disrupting Googles Shopping Dominance
May 01, 2025
How Open Ais Chat Gpt Is Disrupting Googles Shopping Dominance
May 01, 2025 -
 Canadas Economic Future Challenges For The Incoming Prime Minister
May 01, 2025
Canadas Economic Future Challenges For The Incoming Prime Minister
May 01, 2025 -
 The Automobile Industrys Resistance To Ev Mandates Grows
May 01, 2025
The Automobile Industrys Resistance To Ev Mandates Grows
May 01, 2025 -
 Shopping With Chat Gpt Open Ais Direct Challenge To Google Search
May 01, 2025
Shopping With Chat Gpt Open Ais Direct Challenge To Google Search
May 01, 2025
