New COVID-19 Variant: Is It Fueling The Recent Surge In Cases?
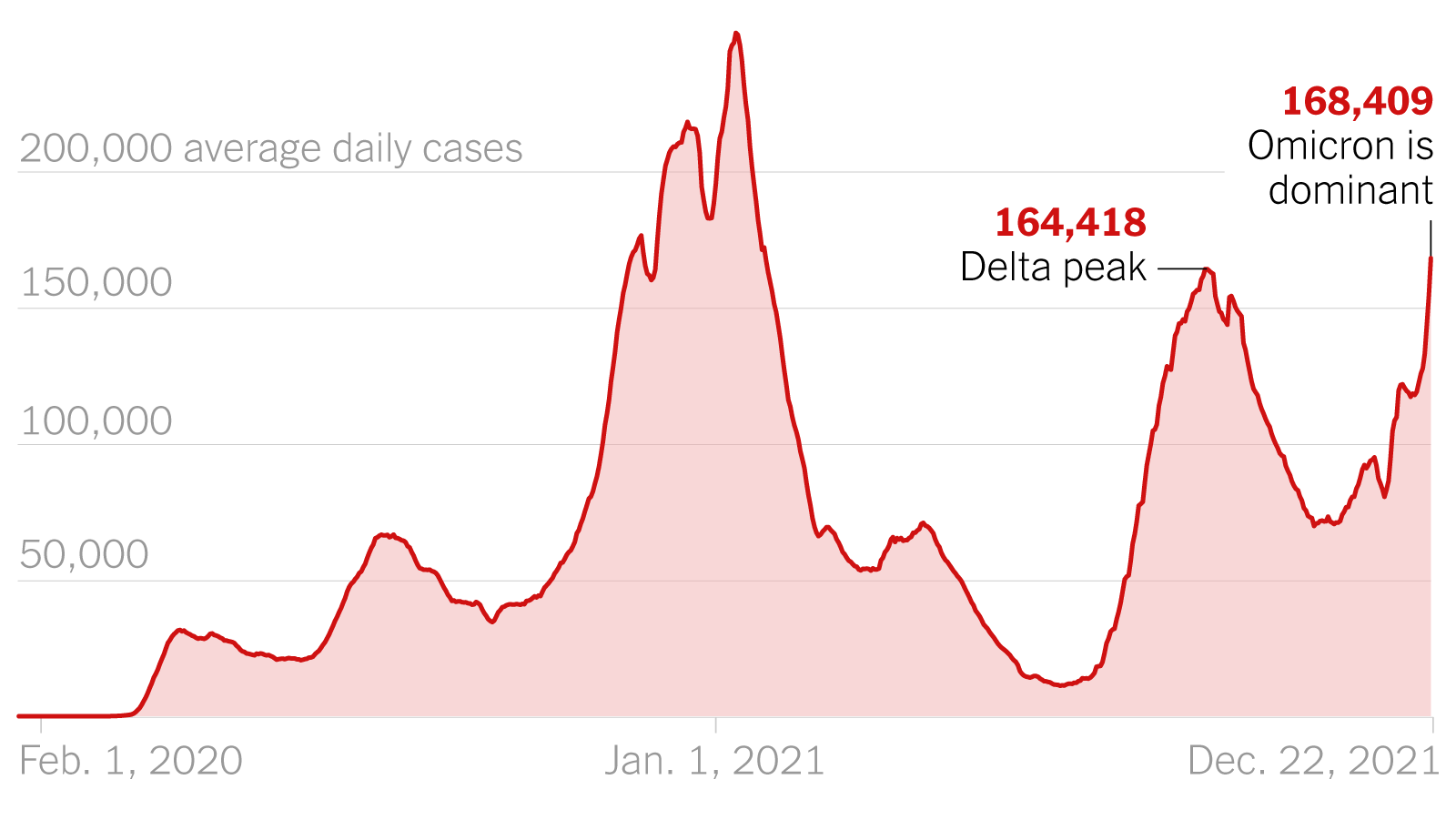
Table of Contents
The Emergence of the New COVID-19 Variant
The rapid spread of new COVID-19 variants continues to challenge global health efforts. Understanding the characteristics of these variants is crucial for effective pandemic management.
Identifying the Variant
Let's assume, for the sake of this example, the new variant is designated as "XBB.1.16" (replace with the actual name of a relevant new variant if available). It was first identified in [Country of origin] in [Month, Year] and has since spread rapidly to [mention regions/countries].
- Genetic Makeup: XBB.1.16 possesses several key mutations, including [list specific mutations and their potential impact, e.g., spike protein mutations affecting transmissibility or immune evasion]. These mutations differentiate it from previous variants like Omicron BA.5 and other subvariants.
- Scientific Publications: Ongoing research is being conducted to fully characterize XBB.1.16. Preliminary findings have been published in [cite relevant pre-print servers like medRxiv or bioRxiv, or peer-reviewed journals]. These studies are crucial for understanding its behavior and impact.
Transmission Rate and Severity
Early evidence suggests XBB.1.16 may exhibit increased transmissibility compared to previous variants.
- R0 Value: While precise R0 values are still being calculated, preliminary estimations suggest a potential increase in the basic reproduction number compared to earlier strains. This implies a higher potential for person-to-person spread.
- Hospitalization and Mortality Rates: Data on hospitalization and mortality associated with XBB.1.16 are still emerging. Initial reports [cite sources if available] indicate [mention trends - e.g., potentially higher or similar hospitalization rates compared to previous variants]. Further analysis is necessary to determine the variant's true impact on disease severity.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Understanding the clinical presentation of XBB.1.16 is vital for early diagnosis and management.
Differentiating Symptoms
While many symptoms overlap with previous variants, some subtle differences may exist.
- Common Symptoms: Commonly reported symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, sore throat, runny nose, and loss of taste or smell.
- Unusual Symptoms: Some individuals have reported [mention any unusual symptoms reported, if any, with citations]. Further research is needed to confirm these observations.
- Diagnostic Tests: Current PCR and rapid antigen tests are generally effective in detecting the presence of SARS-CoV-2, regardless of the specific variant. However, genomic sequencing is required for precise variant identification.
The Link Between the New Variant and the Case Surge
Establishing a definitive causal link between XBB.1.16 and the recent case surge requires rigorous epidemiological investigation.
Correlational Evidence
A strong correlation exists between the emergence and spread of XBB.1.16 and the observed increase in COVID-19 cases in several regions. [Include charts or graphs showing this correlation, if available].
- Limitations of Correlational Data: It is crucial to acknowledge that correlation does not equal causation. Other factors could be contributing to the surge.
- Ongoing Studies: Numerous epidemiological studies are underway to investigate the variant's contribution to the current wave. Results from these studies will provide a clearer understanding of its role.
Other Contributing Factors
Several factors beyond the new variant might be driving the case increase.
- Waning Immunity: Decreased immunity from previous infections or vaccinations could contribute to increased susceptibility.
- Reduced Public Health Measures: Relaxation of preventative measures like masking and social distancing might have increased viral spread.
- Seasonal Changes: Seasonal variations in weather patterns might influence viral transmission.
- Interaction of Factors: It's likely that a combination of these factors, interacting with the new variant's characteristics, is responsible for the current surge.
Public Health Response and Prevention Strategies
Effective public health strategies are crucial to mitigate the impact of the new variant.
Updated Guidelines
Public health authorities are adapting their recommendations based on the characteristics of XBB.1.16.
- Prevention Recommendations: Vaccination remains a cornerstone of protection. Boosters are recommended for individuals eligible to maintain optimal immune response. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, and considering mask-wearing in crowded indoor settings are still important.
- Testing and Treatment: Access to timely testing and treatment options, including antiviral medications, remains critical.
Vaccine Effectiveness
While the effectiveness of existing vaccines might be somewhat reduced against XBB.1.16, vaccination still offers significant protection against severe disease, hospitalization, and death.
- Vaccine Efficacy Data: Studies on vaccine efficacy against XBB.1.16 are ongoing. Preliminary data [cite sources if available] suggests [mention findings].
- Vaccine Updates: Research and development are ongoing to adapt vaccines if necessary to improve their effectiveness against emerging variants. Booster shots tailored to newer variants may be developed and rolled out as needed.
Conclusion
The emergence of the new COVID-19 variant, potentially XBB.1.16 (replace with actual name), is a significant concern, and its potential role in the recent surge requires continuous monitoring and research. While correlation between the variant and increased cases is apparent, further investigation is necessary to definitively establish causation. Other factors, including waning immunity and reduced public health measures, also contribute to the current situation. Staying informed about the latest developments, following public health guidelines, and getting vaccinated are crucial steps in protecting ourselves and our communities. Continued vigilance in tracking this new COVID-19 variant and its impact is paramount. Refer to the [link to CDC or WHO website] for the most up-to-date information and resources.

Featured Posts
-
 Covid 19 Jn 1 Variant Symptoms Spread And What You Need To Know
May 31, 2025
Covid 19 Jn 1 Variant Symptoms Spread And What You Need To Know
May 31, 2025 -
 Munguias Doping Allegations A Response To Adverse Test Results
May 31, 2025
Munguias Doping Allegations A Response To Adverse Test Results
May 31, 2025 -
 Suge Knight Wants Diddy To Testify A Plea For Humanization
May 31, 2025
Suge Knight Wants Diddy To Testify A Plea For Humanization
May 31, 2025 -
 New Banksy Painting The Mystery Behind The Tag And Its Upcoming Sale
May 31, 2025
New Banksy Painting The Mystery Behind The Tag And Its Upcoming Sale
May 31, 2025 -
 Estevan Street Sweeping Schedule 2024 Full Dates Released
May 31, 2025
Estevan Street Sweeping Schedule 2024 Full Dates Released
May 31, 2025
