New Algorithmic Standards And Migration Strategies Accelerate Post-Quantum Cryptography Market Growth To Billions By 2030
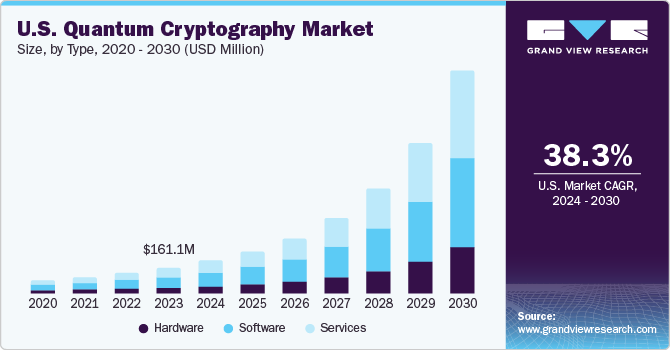
Table of Contents
The Rise of New Algorithmic Standards for Post-Quantum Cryptography
The development of robust and standardized quantum-resistant algorithms is crucial for widespread PQC adoption. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has spearheaded a global effort to standardize PQC algorithms, a process involving rigorous testing and evaluation to ensure the security and performance of these algorithms. Other organizations are also contributing to standardization efforts, promoting interoperability and accelerating the transition to quantum-safe systems.
Different PQC algorithms leverage various mathematical problems that are believed to be hard even for quantum computers to solve. These include:
- Lattice-based cryptography: This approach relies on the difficulty of finding short vectors in high-dimensional lattices.
- Code-based cryptography: This method utilizes error-correcting codes and the difficulty of decoding random linear codes.
- Multivariate cryptography: This relies on the hardness of solving systems of multivariate polynomial equations.
Each algorithm offers a unique balance between security and performance. Here's a look at some key NIST-approved PQC algorithms:
- CRYSTALS-Kyber (lattice-based): Offers excellent performance and is considered a strong candidate for widespread adoption. Security Level 1, 3, and 5.
- CRYSTALS-Dilithium (lattice-based): Focuses on digital signatures and provides high levels of security. Security Level 1, 3, and 5.
- Falcon (lattice-based): Another digital signature algorithm known for its compact signatures. Security Level 1, 3, and 5.
- SPHINCS+ (hash-based): Provides a high level of security but with a larger signature size and slower performance compared to lattice-based alternatives. Security Level 1, 3, and 5.
The selection of an appropriate algorithm depends on the specific application's security requirements and performance constraints. Cryptographic agility, the ability to easily switch to different algorithms as needed, is becoming increasingly important to adapt to future advancements and security threats.
Challenges and Strategies for Migrating to Post-Quantum Cryptography
Migrating existing systems to PQC presents significant technical challenges. It requires careful planning, a phased implementation approach, and a deep understanding of the intricacies involved. Simply replacing existing algorithms isn’t sufficient; it's vital to ensure seamless integration and interoperability with existing infrastructure.
Key challenges in PQC migration include:
- Interoperability: Ensuring compatibility between different PQC algorithms and systems.
- Cost: The financial investment required for upgrading hardware and software.
- Compatibility: Integrating PQC with legacy systems and applications.
- Performance overhead: PQC algorithms might have a performance impact compared to classical algorithms.
Successful PQC migration strategies often involve:
- Hybrid approaches: Combining classical and PQC algorithms to provide a robust, transitional solution.
- Parallel implementation: Running both classical and PQC algorithms simultaneously during a transition period.
- Phased implementation: Gradually migrating systems and applications to PQC over time, minimizing disruption.
A robust risk assessment is crucial, identifying vulnerabilities and developing appropriate mitigation strategies. Thorough testing and validation are also vital to ensure the successful and secure deployment of PQC.
Market Growth Projections and Key Players in the Post-Quantum Cryptography Market
The PQC market is experiencing explosive growth, fueled by the increasing awareness of quantum computing threats and the availability of standardized algorithms. Market analysts project the market to reach billions of dollars by 2030. This growth is driven by increasing government and private sector investment in quantum-resistant cryptography.
Major players in the PQC ecosystem include:
- Companies providing PQC libraries and software development kits (SDKs).
- Hardware vendors integrating PQC into their products.
- Consultancy firms offering PQC migration services.
Various market segments are contributing to this expansion, including:
- Government and defense: High demand for securing sensitive data and infrastructure.
- Financial services: Protection of financial transactions and sensitive customer data.
- Healthcare: Protecting patient data and medical records.
Government funding and initiatives are driving further research and development in the field, bolstering the growth trajectory of this vital market.
Government Regulations and Initiatives Driving Post-Quantum Cryptography Adoption
Government agencies worldwide are playing a crucial role in promoting PQC adoption. They are issuing cybersecurity directives and regulations to mandate or encourage the use of quantum-resistant cryptography for critical infrastructure and sensitive data. This regulatory push significantly influences the speed of PQC adoption and market growth.
Key government agencies and initiatives include:
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) in the US.
- ENISA (European Union Agency for Cybersecurity) in Europe.
- National cybersecurity agencies in various countries.
These agencies are actively involved in:
- Funding research and development in PQC.
- Developing standards and guidelines for PQC implementation.
- Raising awareness about the importance of PQC.
The proactive approach by governments is accelerating the transition to a more secure digital landscape, ensuring that critical systems are prepared for the quantum era.
Conclusion: Securing the Future with Post-Quantum Cryptography
The emergence of new algorithmic standards and comprehensive migration strategies is significantly accelerating the growth of the Post-Quantum Cryptography market, poised to reach billions by 2030. The importance of PQC in securing data against the threats posed by future quantum computing cannot be overstated. Quantum-resistant cryptography is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a crucial element of modern cybersecurity.
Don't be left behind: Invest in quantum-resistant cryptography now. Prepare your organization for the quantum era; explore Post-Quantum Cryptography solutions today!

Featured Posts
-
 Half Of Manilas Schools Closed Amidst Dangerous Heat Wave
May 13, 2025
Half Of Manilas Schools Closed Amidst Dangerous Heat Wave
May 13, 2025 -
 Pendekatan Sby Yang Bijak Mengatasi Konflik Myanmar Tanpa Menggurui
May 13, 2025
Pendekatan Sby Yang Bijak Mengatasi Konflik Myanmar Tanpa Menggurui
May 13, 2025 -
 50 Evesen Is Bombazo Eva Longoria Bikinifotoi
May 13, 2025
50 Evesen Is Bombazo Eva Longoria Bikinifotoi
May 13, 2025 -
 16 3 Billion Record April For U S Customs Duty Revenue
May 13, 2025
16 3 Billion Record April For U S Customs Duty Revenue
May 13, 2025 -
 Le Futur De Gibraltar Progres Significatifs Vers Un Accord Post Brexit
May 13, 2025
Le Futur De Gibraltar Progres Significatifs Vers Un Accord Post Brexit
May 13, 2025
