Negative European Power Prices: A Solar Success Story?
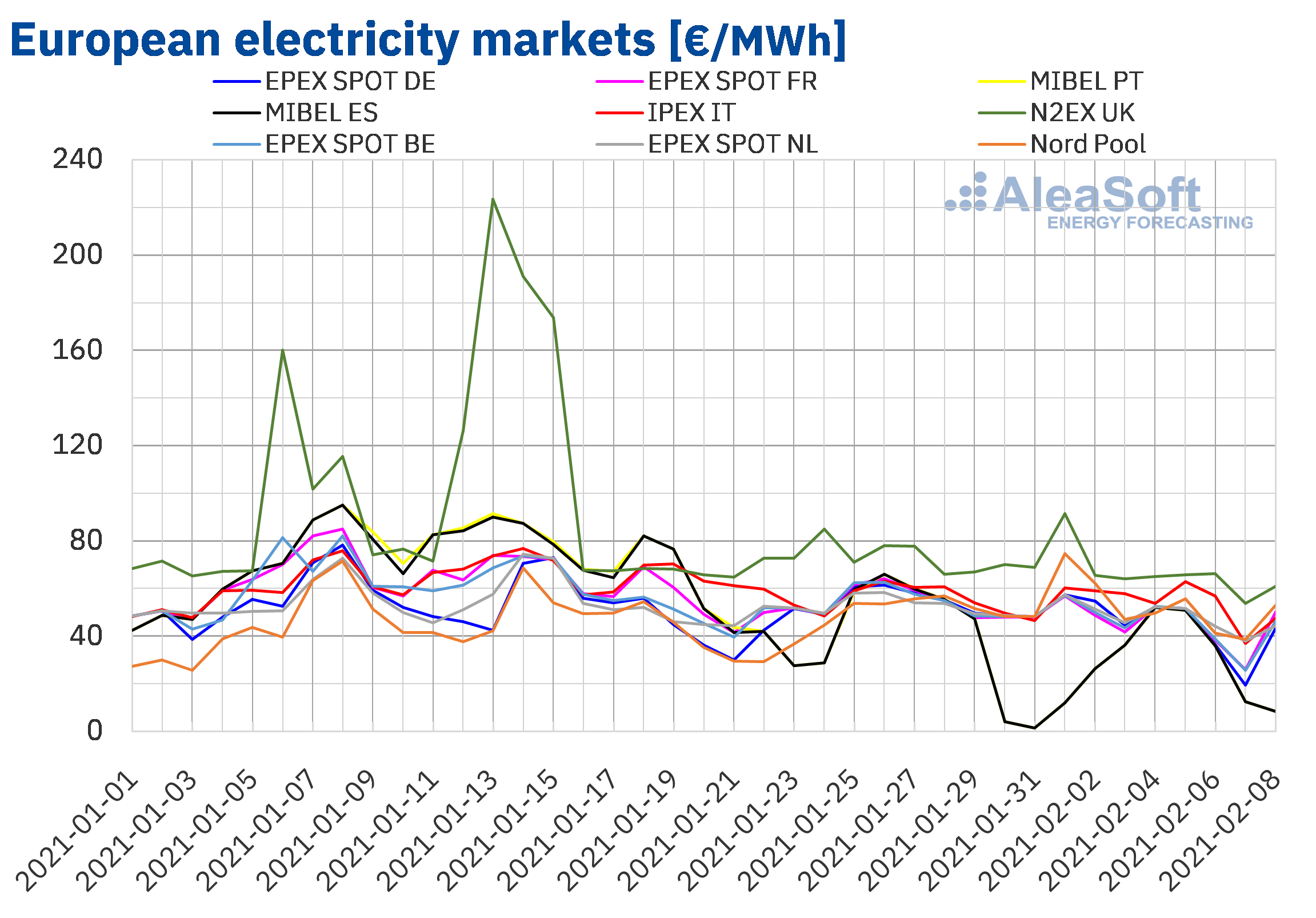
Table of Contents
The Role of Solar Power in the Energy Market Shift
The Explosive Growth of Solar Energy in Europe:
Europe has witnessed a dramatic increase in solar energy installations in recent years. The growth of solar PV capacity has been nothing short of explosive, driven by falling costs and increasingly ambitious renewable energy targets across the continent. For instance, Germany, Spain, and Italy have seen massive increases in solar PV capacity, leading the charge in solar adoption within the European Union. Technological advancements, particularly in photovoltaic technology, have significantly driven down the cost of solar energy, making it a highly competitive energy source.
- Statistics: [Insert relevant statistics on solar PV capacity growth in Europe, ideally with a chart showing the trend].
- Key Players: Germany, Spain, Italy, Netherlands, and France are among the leading countries in solar energy deployment.
- Cost Reduction: The cost of solar PV panels has fallen by over 80% in the last decade, making solar a more attractive investment than ever before.
Solar Power's Impact on Peak Demand:
The proliferation of solar power significantly reduces peak demand during daylight hours. As millions of solar panels generate electricity during the sunniest parts of the day, the strain on traditional power plants is lessened. This reduction in peak demand has significant implications for the operational costs of conventional power plants, which are often optimized for peak demand periods. The shift towards solar energy also necessitates smarter electricity grid management to ensure the efficient integration of intermittent renewable energy sources.
- Reduced Load on Fossil Fuel Plants: Solar power directly reduces the reliance on carbon-intensive power plants during peak hours.
- Grid Stability: The influx of solar power presents both opportunities and challenges to the stability of the electricity grid.
- Energy Demand Curve: The overall shape of the daily energy demand curve is being fundamentally altered by the widespread adoption of solar power.
Other Factors Contributing to Negative Power Prices
Increased Wind Energy Capacity:
Alongside solar power, the significant increase in wind energy capacity across Europe also contributes to an oversupply of electricity, particularly during periods of high wind. These intermittent renewable energy sources, while crucial for decarbonization, create challenges in managing the supply-demand balance. Periods of high wind and sun can lead to a surplus of energy, driving prices down into negative territory.
- Intermittency Challenges: Wind and solar power are intermittent sources, meaning their output fluctuates based on weather conditions.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Efficient integration of intermittent renewable energy sources into the existing electricity grid is a key challenge.
Economic Slowdowns and Reduced Industrial Demand:
Economic downturns and reduced industrial activity directly impact electricity consumption. During periods of recession, factories operate at reduced capacity, and overall energy demand decreases. This reduced demand, combined with the increasing capacity of renewable energy sources, can lead to electricity surpluses and negative prices.
- Impact on Electricity Consumption: Industrial activity is a major driver of electricity demand. Economic slowdowns reduce this demand.
- Correlation with Negative Prices: Periods of economic slowdown have been observed to coincide with instances of negative electricity prices.
Grid Management Challenges and Inefficiencies:
Limitations in grid infrastructure can exacerbate the issue of negative prices. The electricity grid, in many regions, is not optimally designed to handle the influx of intermittent renewable energy. Inefficiencies in managing supply and demand in this rapidly changing energy landscape can lead to situations where the supply significantly exceeds demand, resulting in negative prices.
- Grid Modernization: Investments in modernizing and expanding the electricity grid are necessary to better manage the integration of renewable energy sources.
- Smart Grid Technologies: Advanced technologies such as smart grids can help optimize the flow of electricity and improve grid stability.
The Long-Term Implications of Negative Power Prices
Accelerated Renewable Energy Adoption:
Negative power prices, paradoxically, can further incentivize renewable energy investment. While seemingly disadvantageous for producers, the long-term effect could be a faster transition to a decarbonized energy system. Fossil fuel power plants, struggling to compete with the increasingly cheap renewable energy, may face accelerated phaseout.
- Investment in Renewables: The lower cost of energy could lead to more investments in renewable energy projects.
- Fossil Fuel Phaseout: Negative prices could accelerate the decline of fossil fuel power plants.
Implications for Energy Market Design and Regulation:
The prevalence of negative power prices necessitates a reform of energy market regulations. The current mechanisms may not be adequately designed to handle the challenges posed by a high penetration of intermittent renewable energy. Improved grid management, energy storage solutions, and innovative electricity pricing mechanisms are crucial for addressing these issues.
- Energy Market Reform: Policy changes may be needed to create more stable and efficient electricity markets.
- Energy Storage Technologies: Investing in battery storage and other energy storage technologies is vital for balancing supply and demand.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Negative European Power Prices
The emergence of negative European power prices is a complex phenomenon driven by a confluence of factors, including the explosive growth of solar power, increased wind energy capacity, economic slowdowns, and grid management challenges. While initially seemingly counterintuitive, this trend highlights the rapid transformation of the European energy landscape and the successful integration of renewable energy sources like solar power. The long-term implications are profound, suggesting an accelerated shift toward a cleaner energy future, but also highlighting the need for significant reforms in energy market design and regulation to fully harness the potential of renewable energy while ensuring grid stability. Stay informed on the evolving landscape of negative European power prices and the continued success story of solar power. Explore further resources on sustainable energy solutions and how you can contribute to a greener future.

Featured Posts
-
 Levensverwachting Volwassenen Met Adhd Wat Zegt Het Onderzoek
Apr 29, 2025
Levensverwachting Volwassenen Met Adhd Wat Zegt Het Onderzoek
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Vancouver Festival Hit By Car Crash Injuries Reported
Apr 29, 2025
Vancouver Festival Hit By Car Crash Injuries Reported
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Report On Black Hawk Helicopter And American Airlines Crash Fatal Mistakes Revealed
Apr 29, 2025
Report On Black Hawk Helicopter And American Airlines Crash Fatal Mistakes Revealed
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Anchor Brewing Company To Shutter A Legacy Concludes After 127 Years
Apr 29, 2025
Anchor Brewing Company To Shutter A Legacy Concludes After 127 Years
Apr 29, 2025 -
 North Carolina University Campus Shooting Casualties Reported
Apr 29, 2025
North Carolina University Campus Shooting Casualties Reported
Apr 29, 2025
